* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intestinal Obstruction
Rectal prolapse wikipedia , lookup
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
Intestine transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Appendicitis wikipedia , lookup
Inflammatory bowel disease wikipedia , lookup
Surgical management of fecal incontinence wikipedia , lookup
Large intestine wikipedia , lookup
Gastrointestinal tract wikipedia , lookup
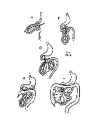
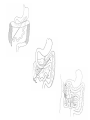
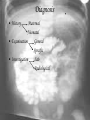
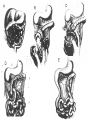
Intestinal Obstruction Malrotation & Hirschsprung disease Supervised by:- Dr/AAyed Al-Qahtany Presented by:- Maram Al-Zain Malrotation • Embryology :- -Disproportional growth& elongation of the midgut beginning in the 5th gestational week results in :* Herniation of the 1ry midgut loop ( base of umbilical cord,10th week) . *Reduction of the extracoelomic gut (10th-12th weeks,180 degree ) . * Fixatation of the intestine into the posterior wall of the body after the 12th gestational week . Cont….. -Malrotation classified into:1- Non-rotation . 2- Mixed OR Incomplete rotation . 3- Mesocolic hernias . Cont……. • Non-rotation :Commonest abnormality. Chch. By inadequate counterclockwise rotation of the midgut loop around SMA,(absent or arrested before exceeding 90 degrees). Colon resides in Lt. abdomen, Cecum is near in the midline, SI is to the right of midline. MidgutVOLVULUS & Duodenal OBSTRUCTION are significant . Cont…… • Mixed OR Incomplete rotation :2nd common rotational abnormalities . Chch. By arrest of normal rotational process or at near 180 degree Prearterial segment has failed to complete its rotation post. & Lt. of the SMA . Cecum resides in the upper abdomen (usually Lt. to the SMApertoneal band ) . Midgut volvulus & dudenal obstruction are relatively common from extrinsic compression. Cont….. • Mesocolic hernias:Result from failure of fixation of either the RT. Or Lt. mesocolon to the post. Body wall . Rare BUT surgically important anomaly . The resulting potential cavities may allow entrapment of small intestine on either side of the abdomen. As with any hernia Obstruction, Incarceration & Strangulation are potential risk . Clinical presentation • Incidense :- As high as 1% of the total population . • Sex :- M:F 2:1 (neonate),But no sexual predilection in pt. older than 1yr . • 40% in the 1st week of life . • 75% of the pt. diagnosed by the age of 1yr. • The remaining 25% present after age of 1yr & late adulthood • Presentation :- 1- Asymptomatic . 2- Duodenal obstruction . 3- Midgut volvulus . • Older children & adults may present :1- Acute volvulus . 2- Episodic obstructive symptoms . 3- Chronic abdominal pain . Diagnosis • History Maternal Neonatal • Examination General Specific • Investigation Lab Radiological History & Examination • Most of the infant present with Acute duodenal obstructionforceful vomiting, may/may NOT bilious . • Chronic duodenal obstructionintermittent abdominal pain, failure to thrive, bilious vomiting . • Abdominal distention . • Bloody stool . • Tachycardia . • Tachypnea . • Shock . Radiological Investigation • Plain abdominal x-ray . • Contrast study . • Barium swallow . • Barium enema . Management -General :1) 2) 3) 4) NPO . IV. Fluid . Antibiotics . Pre-operative preparation . -Specific :1) 2) NO role of non-operative management of malrotation . Operative repair of malrotation is nearly achieved by LADD procedure . Cont….. • Surgical repair is performed, the bowel is untwisted & checked carefully for damage . • Exploratory laparotomy (1st) . • If the intestine is healthy, an operation called LADD’s procedure to prevent another volvulus . • Appendectomy usually done . • ?? Bowel viability Abdomen will be left open & 2nd look procedure will be planned within 24-48 hrs . • If there is a section of necrotic bowel colostomy may be needed temporarily . Hirschsprung disease • Def. :- It is a congenital agangliosis of the intestine which result of disordered emberyogenesis involving the myenteric nervous system . • Etiology :- Lack of migratory nerve cells to develop . • Esophagus 6th week . • Transverse colon 8th week . • Rectum 12th week . • Incidence :- 1 per 5000 live births . • Sex :- M:F 4:1 • Most cases are sporadic, but long segment or total colonic agangliosis & female gender are strongly associated with familial disease Clinical presentation • 50% of pt. present in the neonatal age . • Most infant Don’t have normal passage of meconium in the 1st 24 - 48 hrs . • They maybe discovered during the evaluation of chronic constipation . • Abdominal distention . • Bilious vomiting . • Malnutrition . • Failure to thrive . Physical examination • Physical examination NOT diagnostic . • PR. Examination shows spasm of the rectum, empty rectum . • Gush of stool or Forceful decompression of gray liquid ,?? Bloody stool at the time of the rectal examination ??Enterocolitis. Diagnosis • History & physical examination . • Investigation :Lab test Radiology 1- Plain abdominal x-ray . 2- Contrast enema . RECTAL BIOBSY . Anorectal manometry . Management 1 - General : • NPO . • NGT • IV. Fluid . • Antibiotic . 2- Specific : • All operations depend on resection or bypass of distal aganglionic rectum in conjunction with a low rectal anastomosis to normally innervated pulled-through proximal intestine. • 1st stage Rlieve obstruction Laparotomy Identify transition zone between dilated upstream normal bowel and non-peristaltic,aganglionic distal bowel . Colostomy above transition zone . • 2nd stage Swenson :- Proctocolectomy . Duhamel :- Post. Pull-through with side to side anastomosis to a ganglionic rectum . Soave :- Pull ganglionated bowel through sleeve of rectum. Rectal myomectomy & All the best Maram Al-Zain