* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oriental archer on an Attic red-figure bowl by
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
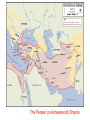
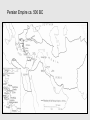
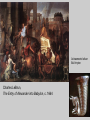
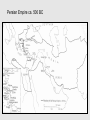
CLAS 0810A ALEXANDER THE GREAT AND THE ALEXANDER TRADITION CLASS 5 SEPTEMBER 12, 2014 THE PERSIAN EMPIRE AND EAST-WEST RELATIONS Canvas.brown.edu/courses/927769 The Greek “othering” of the Persians • “The invention of the barbarian” • Not seen before the 5th century B.C. • Set in train by the conflict between Greeks and Persians in late 6th century, leading to the Persian War of ca. 490-479 B.C. Oriental archer on an Attic red-figure bowl by Epiktetos Frieze from Temple of Apollo at Bassae, Greece Greeks fighting “others” — centaurs, Amazon women Centaurs Amazons Bassae Temple, ca. 450-425 BC Alexander’s “Panhellenic Crusade” • An invasion by Greek states as a whole of those parts of Persian territory where Greeks lived (coastal Turkey) • Twofold objective: (a) to free the Greeks from Persian rule, and (b) punish Persians for invading Greece in 480 BC • This idea had been active for 150 years • Strong sense of poetic justice, of a symmetry of events, of history rewinding itself The Persian (or Achaemenid) Empire Persian Empire ca. 500 BC Tomb of Cyrus at Pasagardae, 529 BC The Shah of Iran celebrates the 2,500th anniversary of Cyrus’ death in 529 BC, at his tomb [1971] Babylon Ishtar Gate, Babylon Proskynesis [Greek name for the ritual greeting in Oriental courts] The Behistun relief of Darius I (521-519 BC) The Persian Empire Tribute for Darius I at Persepolis Darius I The site of Persepolis Duties of Satraps • Administration, maintenance of order, suppression of rebellions • Collect royal tribute and pass it on to the King • Act as supreme judge, locally • Maintain and pay troops stationed in the province; command them in the field • Negotiate with neighboring independent states Checks on Satraps’ Powers • Appoint members of the King’s family to important satrapies (or induce loyalty via marriage alliances involving the King’s many daughters • Direct royal appointment of commanders of troops in key garrison locations, to ensure loyalty • An annual military inspection by the King, or his delegate, helped maintain royal control of troops • Satrap not allowed to leave his province except with royal consent • Royal “secretary” attached to satraps, and the “king’s eye” [a kind of officially sanctioned spy] could be sent at any time Achaemenid silver Bull rhyton Charles LeBrun, The Entry of Alexander into Babylon, c. 1664 Persian Empire ca. 500 BC Commemorating the Battle of Marathon (490 BC) The burial mound for the Athenian dead at Marathon The horsemen on the Parthenon frieze may be a specific reference to those who fell at Marathon Cities of the Delian League (which by the 430s BC were paying tribute to Athens) Athens Delos At the Battle of the River Eurymedon in 465 BC, the Athenian admiral Cimon defeated the Persians twice in one day, at sea and on land A red-figure Attic oinochoe (wine-jug) made shortly afterwards: An Athenian in heroic nudity approaches… …a Persian bent forward in the position for homosexual activity The inscription on the vase reads: My name is Eurymedon. I’m getting screwed!