* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Ms. Thresher
Separation of powers wikipedia , lookup
2008–09 Canadian parliamentary dispute wikipedia , lookup
Head of state wikipedia , lookup
Presidential system wikipedia , lookup
Dual mandate wikipedia , lookup
Parliament of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Separation of powers in Singapore wikipedia , lookup
Bicameralism wikipedia , lookup
Federal government of the United States wikipedia , lookup
Separation of powers under the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Government of Pakistan wikipedia , lookup
Government of Japan wikipedia , lookup
Legislative violence wikipedia , lookup
39th Canadian Parliament wikipedia , lookup
Westminster system wikipedia , lookup
Politics of Denmark wikipedia , lookup
Government of Australia wikipedia , lookup
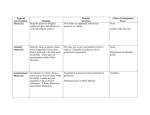
The Canadian Government System So far, we have learned: • The government is divided into Municipal, Provincial and Federal The Canadian Government • Consists of 3 Branches: – The Executive Branch – The ability to carry out laws – The Legislative Branch – The power to make laws – The Judicial Branch – The power to interpret the laws and judge those who break them FEDERAL The Queen • Queen Elizabeth II • Ascended to the throne Feb 6, 1952 • Coronation on June 2, 1953 – How many years will the Queen be in ruling this year? Role of the Queen • Canada’s official head of state • Recognized but no real power • Performs important ceremonial duties when visiting Canada • Overseas all 3 branches federally, and provincially Governor General • David Johnston • Assumed office on Oct 1, 2010 • 28th Governor General since confederation Role of the Governor General • The Queen’s representative in Canada, appointed by the Queen • Usually serves for 5 years • Welcomes Foreign dignitaries and visits other countries representing Canada • One of the main duties is to ensure that Canada always has a Prime Minister • Signs important documents Executive Branch • Has the power to administer and carry out laws • Day to day operations of the government • Consists of: The Prime Minister, Cabinet and Public Service (Civil Servants) Prime Minister • Stephen Harper • Canada’s 22nd Prime Minister • Sworn in on Feb 6, 2006 Role of Prime Minister • Leader of the Nation • Leader of the party with the most number of seats (which party is Stephen Harper a part of?) • Chooses a cabinet that makes up his/her team • Usually elected for a 4 year term – Has the power to call an election but must get permission from the GG first The Cabinet • Made up of Members of Parliament (MP’s) that help the PM to run the government • Usually made up of members of the same party • Cabinet Ministers usually have the responsibility of running certain departments • They are helped in the day to day by the Civil Servants, that make up the Public Service Ministers – Have you heard their names in the news? • Minister of Finance – Jim Flaherty, – MP Oshawa – Whitby • Minister for the Status of Women – Rona Ambrose, – MP Edmonton – Spruce Grove Legislative Branch • Also known as Parliament • Has the power to make and change laws • Consists of: The Senate and the House of Commons House of Commons (Lower House) House of Commons House of Commons • Where the MP’s who are voted in by the people debate and vote on bills to become laws • Bills are proposed laws and they must be debated and approved by the House of Commons before becoming a law • PM is the leader of the House of Commons House of Commons – 3 Major Activities • The speech from the Throne – Although the speech is given by the GG, it is written by the governing party’s cabinet and outlines the policies and laws they plan to bring to Parliament during the upcoming season • Question Period – lasts for 45 minutes each day and is televised in English and French to all Canadians. This allows MPs to ask questions about proposed bills, policies and government actions, and brings issues to the attention of Canadians House of Commons – 3 Major Activities • Debates and Legislation – When an MP has an idea for a new law, they present it to the Legislature as a bill. Most bills are presented by Cabinet Ministers and are called “Government Orders” – When a non-Cabinet MP presents a bill, it is called a “private members bill” Seats in the House of commons Members of Parliament • MP’s represent each community in Canada in the Federal Government • Represent and support the ideas / policies (party platform) of their party on Federal issues • Term: Every 4 years, same as PM The Opposition • The party with the 2nd largest number of elected MP’s becomes the Official Opposition • The NDP are the Official Opposition of our current government • The opposition must criticize government policies they do not agree with and provide alternatives if they are displeased Leader of the Official Opposition • Thomas Muclair, replacing Jack Layton • Elected by his party Opposition • All other parties who had MP’s elected into the House of Commons are part of the Opposition • Other opposition leaders include Bob Rae (Liberals), Daniel Paille (Bloc Quebecois) and Elizabeth May (The only Green Party MP elected!) The Senate (Upper House) • The Senate studies, amends, and either rejects or approves bills passed in the house of commons • No bill can become a law until it is passed by the Senate • Can propose own bills but not where they are spending public money or impose taxes, which must be introduced in the HoC • One of the duties of the Senate is to represent the interests of Canada’s regions, provinces, territories and minority groups Senators • Approve all bills to make them into laws • Act as government advisors on specific issues and problems • Are appointed by the GG, on advice from the PM • Term: Appointed until age 75, usually from the PM’s party (hmmmm…) Standings in the Senate Conservative 59 Liberal 41 IDP PC 2 1 British Columbia 6 Alberta 6 Ontario 23 Quebec 24 Manitoba 6 Saskatchewan 6 Nova Scotia 9 Newfoundland and Labrador 6 New Brunswick 10 Northwest Territories 1 Prince Edward Island 4 Yukon 1 Nunavut 1 Judicial Branch • Decides who has broke the law and sets the penalties • Works to ensure that the government does not go above the law • Consists of: Supreme Court of Canada, Court of Appeal, Criminal Courts and Civil Courts Court System • Canada has two court systems, the civil court deals with the protection of private rights where as the criminal court deal with crimes against society • If you are not happy with your verdict, you can appeal it to the Supreme Court of Canada. – It’s verdicts are final because members of this court have been selected by Parliament out of respect for years of sound service to the legal system PROVINCIAL Comparisons to FEDERAL • Also consists of 3 branches – Executive, legislative and Judicial Executive • Same functions as federal • Consists of: Premier, Cabinet and Public Service Lieutenant-Governor • David Onley Premier • Kathleen Wynne • Liberal Party of Canada Role of the Premier • Leadership role, similar to the Prime Minister • Addressed the citizens of the province and works with other Premiers and the Federal government to defend the province’s interests • Chooses cabinet members to direct specific provincial affairs MPP’s • Members of Provincial Parliament • Elected by citizens, party with the most MPP’s ends up as Premier of the province Cabinet • Similar to Federal government Civil Servants • Public servants within the Provincial government consist of police officers, health care personnel and education workers. Legislative Branch • Similar to Federal, except no Senate • Instead of HoC, it is called a Legislative Assembly, or Legislature • Once bills are passed by a majority in legislature, it goes directly to the lieutenant-governor for royal assent Judicial Branch • Same as Federal • Consists of: Provincial Supreme Court, Criminal Courts and Civil Courts MUNICIPAL Executive • Consists of: The Mayor, City Councillors and Council Committees Mayor • Hazel McCallion • Longest running Mayor in Guinness Book of World Records City Councillors • Elected by citizens • Term: 4 years • City Councillors do not usually state their political parties, but it is generally known once they state their platforms Council Committees • City councillors are assigned to various committees to discuss policies and structures within different departments Legislative • For Municipalities, it is the Town or City Council that works to pass bylaws Judicial • Municipal bylaws