* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Dynamics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
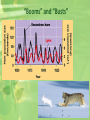
Population Ecology TERMS • Biotic: all living organisms. • Ex. Trees, flowers, moss, birds, monkeys, people, mold, fish, plankton, pumpkins, grass, giant squid • Abiotic: all non-living factors • Ex. Wind, temperature, rocks, water, altitude, sunlight TERMS • Habitat: home or environment of a living organism • Ex. The habitat of the chimpanzee is the rainforest • The habitat of the saguaro cactus is? TERMS • Niche: the role and position a species has in its environment • how it meets its needs for food and shelter • A species' niche includes all of its interactions with the biotic and abiotic factors of its environment Red Squirrel’s Niche The red squirrel lives in coniferous forests. It makes its nests in a variety of places including hollows in the ground, in tree hollows, logs or crotches in trees. The red squirrel is very vocal and chatters, growls and screeches. It eats insects, seeds, bark, nuts, fruits, mushrooms and pine seeds or cones. It also stores nuts and seeds in piles under logs, at the base of trees and underground. It doesn't always find or eat all of the seeds and nuts it has stored. Because of this, the red squirrel fills an important niche in spreading seeds in the forest. Its predators are hawks, owls, and foxes. Population Dynamics • Population: • All the individuals of a species that live together in an area • Community: • All the populations of different species that live together in an area Population Dynamics • Ecosystem: • The community plus all the abiotic factors in an area • Biosphere: • The entire planet, with all biotic and abiotic factors involved What is this picture? Population What is this picture? Biosphere What is this picture? Community What is this picture? Ecosystem What is this picture? Population What is this picture? Community Key Features of Populations Density: measurement of population per unit area or unit volume Pop. Density = # of individuals ÷ unit of space How Do You Affect Density? 1. Immigration: movement of individuals into a population 2. Emigration: movement of individuals out of a population 3. Density-dependent factors: Biotic factors in the environment that have an increasing effect as population size increases (disease, competition, parasites) 4. Density-independent factors: Abiotic factors in the environment that affect populations regardless of their density (temperature, weather) Factors That Affect Future Population Growth Immigration Natality + + Population Emigration - Mortality How Are Populations Measured? • Population density = number of individuals in a given area or volume • Count all the individuals in a population Carrying Capacity • Carrying Capacity: • The maximum population size that can be supported by the available resources • There can only be as many organisms as the environmental resources can support Graphing Carrying Capacity Factors Limiting Growth Rate • Declining birth rate or increasing death rate are caused by several factors including: • Limited food supply • The buildup of toxic wastes • Increased disease • Predation “Booms” and “Busts” Reproductive Strategies • R Strategists Short life span Small body size Reproduce quickly Have many young Little parental care Ex: cockroaches, weeds, bacteria Reproductive Strategies • K Strategists Long life span Large body size Reproduce slowly Have few young Provides parental care Ex: humans, elephants