* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Template
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
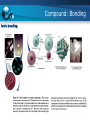
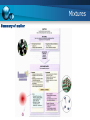
14/15 Fall semester Engineering Chemistry Instructor: Rama Oktavian Email: [email protected] Office Hr.: M.13-15, Tu. 13-15, W. 13-15, Th. 13-15, F. 09-11 Outlines 1. Mass conservation theory of matter 2. Atom: Theory 3. Compounds: Bonding 4. Mixtures Review Unit conversion Physical and chemical properties Review Significant figure in measurement Mass conservation Fundamental law the total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction - Antoine Lavoisier (1 743-1 794) The number of substances may change, but the total amount of matter remains constant. matter cannot be created or destroyed. Mass conservation Fundamental law - the law of definite (or constant) composition no matter what its source, a particular compound is composed of the same elements in the same parts (fractions) by mass Denoted as mass fraction or mass percent, mass % Mass conservation Fundamental law - the law of definite (or constant) composition Mass conservation Example Mass conservation Multiple proportion if elements A and B react to form two compounds, the different masses of B that combine with a fixed mass of A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers. Mass conservation Conceptual question Atom theory Atomic Number , Mass Number , and Atomic Symbol Isotopes of an element are atoms that have different numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers. Example: 12C, 13C, 14C Compound: Bonding Elements combine in two general ways: 1. Transferring electrons from the atoms of one element to those of another to form ionic compounds 2. Sharing electrons between atoms of different elements to form covalent compounds Compound: Bonding Ionic bonding Compound: Bonding Covalent bonding Covalent compounds form when elements share electrons, which usually occurs between nonmetals Atoms of different elements share electrons to form the molecules of a covalent compound Compound: Bonding Covalent bonding mechanism Mixtures Classification of mixtures matter usually occurs as mixtures, such as air, seawater, soil, and organisms A heterogeneous mixture has one or more visible boundaries between the components Example: rocks A homogeneous mixture has no visible boundaries because the components are mixed as individual atoms, ions, and molecules. Example: sugar dissolves in water Mixtures Summary of matter