* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Singly-Linked List
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
1/ 124
1
COP 3503 FALL 2012
SHAYAN JAVED
LECTURE 18
Programming Fundamentals using Java
2/ 124
Data Structures
3/ 124
So far...
Looked at Arrays and ArrayLists as our data
structures
4/ 124
So far...
Looked at Arrays and ArrayLists as our data
structures
Very useful, but not always the best options
5/ 124
So far...
Looked at Arrays and ArrayLists as our data
structures
Very useful, but not always the best options
Going to look at some other data structures
6/ 124
Data Structures
Stack
Queue
Linked List
Trees
Graph
Hashtable
etc.
7/ 124
Data Structures
Stack
Queue
Linked List
Trees
Graph
Hashtable
etc.
8/ 124
Stack
Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) Data Structure
9/ 124
Stack
Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) Data Structure
Basically...a stack of data.
10/ 124
Stack
Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) Data Structure
Basically...a stack of data.
Used when you want the oldest added data first.
11/ 124
Stack
Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) Data Structure
Basically...a stack of data.
Used when you want the oldest added data first.
Abstract data type (can store any kind of data).
12/ 124
Stack
Three Operations:
13/ 124
Stack
Three Operations:
push(Object): Pushes an object on top of a stack
14/ 124
Stack
Three Operations:
push(Object): Pushes an object on top of a stack
pop(): Returns the object at the top of the stack
and removes it
15/ 124
Stack
Three Operations:
push(Object): Pushes an object on top of a stack
pop(): Returns the object at the top of the stack
and removes it
peek(): Returns the object at the top without
removing it
16/ 124
Stack
Some uses:
17/ 124
Stack
Some uses:
“Stack Frame” for method calls.
18/ 124
Stack
Some uses:
“Stack Frame” for method calls.
Used for evaluating arithmetic expressions:
(prefix,
postfix, infix)
19/ 124
Stack
Java provides a Stack class (java.util.Stack)
20/ 124
Stack
Java provides a Stack class (java.util.Stack)
Has all the operations
21/ 124
Stack
Java provides a Stack class (java.util.Stack)
Has all the operations
But how does it actually store the data? (What’s
the “back-end”?)
22/ 124
Stack
Java provides a Stack class (java.util.Stack)
Has all the operations
But how does it actually store the data? (What’s
the “back-end”?)
Uses the java.util.Vector class (similar to ArrayList)
23/ 124
Queue
A First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure.
24/ 124
Queue
A First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure.
Used when you want the oldest added data first.
25/ 124
Queue
A First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure.
Used when you want the oldest added data first.
Often used for scheduling (handle first in line)
26/ 124
Queue
Three Operations:
enqueue(Object): Adds an object to the queue
dequeue(): Returns the object at the front of the
queue and removes it
peek(): Returns the object at the front without
removing it
27/ 124
Queue
Java provides a Queue interface (java.util.Queue)
28/ 124
Queue
Java provides a Queue interface (java.util.Queue)
Has all the operations
enqueue
= add
dequeue = poll
29/ 124
Queue
Java provides a Queue interface (java.util.Queue)
Has all the operations
enqueue
= add
dequeue = poll
Interface implemented in classes like LinkedList
30/ 124
Queue
Java provides a Queue interface (java.util.Queue)
Has all the operations
enqueue
= add
dequeue = poll
Interface implemented in classes like LinkedList
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
31/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
Work well in a lot of cases.
32/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
Work well in a lot of cases.
Can use as “back-end” data structures
33/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
Work well in a lot of cases.
Can use as “back-end” data structures
But where do they fall short?
34/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
Work well in a lot of cases.
Can use as “back-end” data structures
But where do they fall short?
Data
retrieval – excellent O(1)
35/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
Work well in a lot of cases.
Can use as “back-end” data structures
But where do they fall short?
Data
retrieval – excellent O(1)
Adding data
36/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
Work well in a lot of cases.
Can use as “back-end” data structures
But where do they fall short?
Data
retrieval – excellent O(1)
Adding data – inefficient O(n) in some cases
37/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
Work well in a lot of cases.
Can use as “back-end” data structures
But where do they fall short?
Data
retrieval – excellent O(1)
Adding data – inefficient O(n) in some cases
38/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
Work well in a lot of cases.
Can use as “back-end” data structures
But where do they fall short?
Data
retrieval – excellent O(1)
Adding data – inefficient O(n) in some cases
Fixed size – have to shift/copy to new array
39/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
What if your application requires a lot of adds but
not retrievals?
40/ 124
Arrays and ArrayLists
What if your application requires a lot of adds but
not retrievals?
Use Linked Lists
41/ 124
Linked List
A list – a collection of linked nodes.
42/ 124
Linked List
A list – a collection of linked nodes.
Dynamic data structure – size is not fixed, and
memory is not contiguous (unlike an array)
43/ 124
Linked List
A list – a collection of linked nodes.
Dynamic data structure – size is not fixed, and
memory is not contiguous (unlike an array)
Insertion to the list is very fast – O(1) in most cases
44/ 124
Linked List
A list – a collection of linked nodes.
Dynamic data structure – size is not fixed, and
memory is not contiguous (unlike an array)
Insertion to the list is very fast – O(1) in most cases
Indexing is slow. Random access also not possible
45/ 124
Linked List
Many variations:
Singly-Linked List (can only traverse forward)
Doubly-Linked List (can traverse in reverse too)
Circular Linked Lists
Multi-Linked Lists
etc.
46/ 124
Node
Basic structure – collection of linked nodes make a
linked list.
47/ 124
Node
Basic structure – collection of linked nodes make a
linked list.
Stores some data and a link to the next Node.
48/ 124
Node
Basic structure – collection of linked nodes make a
linked list.
Stores some data and a link to the next Node.
int
null
49/ 124
Node
Basic structure – collection of linked nodes make a
linked list.
Stores some data and a link to the next Node.
int
int
null
50/ 124
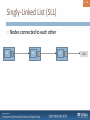
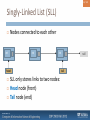
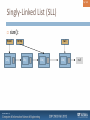
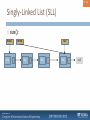
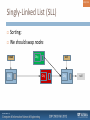
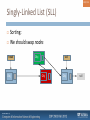
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Nodes connected to each other
51/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
int
Nodes connected to each other
int
int
null
52/ 124
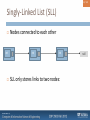
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
int
Nodes connected to each other
int
int
SLL only stores links to two nodes:
null
53/ 124
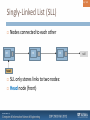
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Nodes connected to each other
int
int
int
head
SLL only stores links to two nodes:
Head node (front)
null
54/ 124
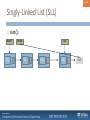
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Nodes connected to each other
int
int
int
head
SLL only stores links to two nodes:
Head node (front)
Tail node (end)
tail
null
55/ 124
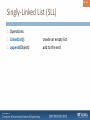
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Operations:
LinkedList():
create an empty list
56/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Operations:
LinkedList():
append(Object):
create an empty list
add to the end
57/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Operations:
LinkedList():
append(Object):
insert(Object, index):
create an empty list
add to the end
add at a certain index
58/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Operations:
LinkedList():
append(Object):
insert(Object, index):
remove(index):
remove(Object):
create an empty list
add to the end
add at a certain index
remove Object at index
remove Object
59/ 124
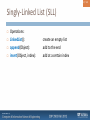
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Operations:
LinkedList():
append(Object):
insert(Object, index):
remove(index):
remove(Object):
get(Object):
get(index):
create an empty list
add to the end
add at a certain index
remove Object at index
remove Object
return index of Object
return Object at index
60/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Operations:
LinkedList():
append(Object):
insert(Object, index):
remove(index):
remove(Object):
get(Object):
get(index):
size():
create an empty list
add to the end
add at a certain index
remove Object at index
remove Object
return index of Object
return Object at index
return size of the list
61/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Operations:
LinkedList():
append(Object):
insert(Object, index):
remove(index):
remove(Object):
get(Object):
get(index):
size():
clear():
create an empty list
add to the end
add at a certain index
remove Object at index
remove Object
return index of Object
return Object at index
return size of the list
empty the list
62/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Create an Empty SLL:
63/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Create an Empty SLL:
head
tail
null
64/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Create an Empty SLL:
head
tail
null
public SLL() {
head = null;
tail = null;
}
65/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
append(Object):
66/ 124
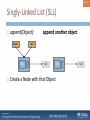
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
append(Object):
Obj
null
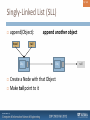
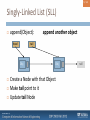
Create a Node with that Object
67/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
append(Object):
head
tail
Obj
null
Create a Node with that Object
68/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
append(Object):
head
append another object
tail
Obj
null
69/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
append(Object):
head
tail
Obj
append another object
null
Obj
Create a Node with that Object
null
70/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
append(Object):
head
tail
Obj
append another object
Obj
Create a Node with that Object
Make tail point to it
null
71/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
append(Object):
head
tail
Obj
append another object
Obj
Create a Node with that Object
Make tail point to it
Update tail Node
null
72/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
size():
73/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
size():
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
74/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
size():
head
Obj
temp
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
75/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
size():
head
Obj
temp
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
76/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
size():
head
Obj
temp
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
77/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
size():
head
Obj
temp
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
78/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
size():
head
Obj
temp
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
79/ 124
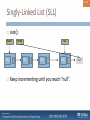
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
size():
head
Obj
temp
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
Keep incrementing until you reach “null”.
null
80/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
get(Object): Returns index of first Node with that
object
81/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
get(Object): Returns index of first Node with that
object
You should know how to traverse
82/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
get(Object): Returns index of first Node with that
object
You should know how to traverse
Compare object with equals() method
83/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
get(Object): Returns index of first Node with that
object
You should know how to traverse
Compare object with equals() method
Return index if found
-1 if not found
84/ 124
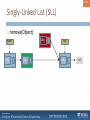
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
remove(Object):
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
85/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
remove(Object):
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
86/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
remove(Object):
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
87/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
remove(Object):
Obj
head
Obj
Obj
tail
Obj
null
88/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
remove(Object):
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
null
89/ 124
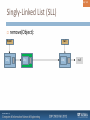
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
remove(Object):
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
remove(index) - remove at a certain index
remove(Node) - remove a certain Node
Work
the same way
null
90/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
So now we know how to:
append, prepend, insert
91/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
So now we know how to:
append, prepend, insert
find the size
92/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
So now we know how to:
append, prepend, insert
find the size
find the index of a specific element
93/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
So now we know how to:
append, prepend, insert
find the size
find the index of a specific element
remove an object/Node
94/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
So now we know how to:
append, prepend, insert
find the size
find the index of a specific element
remove an object/Node
What about sorting?
95/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
Bubble Sort
Selection Sort
Insertion Sort
96/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
Bubble Sort
Selection Sort
Insertion Sort
How many of these can you implement for Linked
Lists?
97/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
98/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
99/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
100/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
head
Obj
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
null
101/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
head
Obj
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
null
102/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
head
Obj
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
null
103/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
104/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
How many nodes were changed?
Obj
null
105/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
We should swap nodes
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
How many nodes were changed? 3
Obj
null
106/ 124
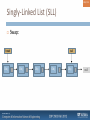
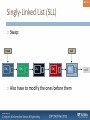
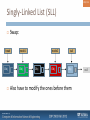
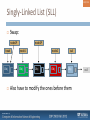
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Swap:
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
107/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Swap:
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
Obj
null
108/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Swap:
head
Obj
tail
Obj
Obj
Obj
Obj
Also have to modify the ones before them
null
109/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Swap:
head
Obj
node1
Obj
node2
Obj
Obj
tail
Obj
Also have to modify the ones before them
null
110/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Swap:
node1P
head
Obj
node2P
node1
Obj
node2
Obj
Obj
tail
Obj
Also have to modify the ones before them
null
111/ 124
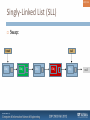
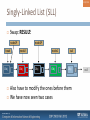
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Swap: RESULT:
node1P
head
Obj
node2P
node2
Obj
node1
Obj
Obj
tail
Obj
Also have to modify the ones before them
We have now seen two cases
null
112/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
113/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
114/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
115/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
116/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
117/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
118/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
// the node before node2
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
119/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
// the node before node2
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
120/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
void swap(Node node1, Node node2, Node node1P, Node node2P) {
if (node1.next == node2) {
// side-by-side (1st case)
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = node1;
}
// 2nd case
else {
Node temp = node1.next;
node1.next = node2.next;
node2.next = temp;
node2P.next = node1;
// the node before node2
}
if (node1P != null)
node1P.next = node2;
// what about the head and tail nodes?
// update them accordingly
}
// why?
121/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
So swap is not straightforward
122/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
So swap is not straightforward
Once you figure out swap, you can implement
Bubble and Selection Sort
123/ 124
Singly-Linked List (SLL)
Sorting:
So swap is not straightforward
Once you figure out swap, you can implement
Bubble and Selection Sort
Try to implement the Sorting Methods for Linked
Lists
124/ 124
Summary
Arrays/ArrayLists: useful data structures but not
always optimal. Retrieval very quick, insertion can
be slow
Stacks/Queues: Abstract data types useful for
LIFO/FIFO storage. Implemented using arrays/SLLs
Linked Lists: Alternative to arrays – insertion is fast
but retrieval is slow.