* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes and Active Sites
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
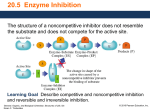
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup