* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Organization
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Carbohydrate wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
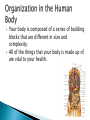
Notes Your body is composed of a series of building blocks that are different in size and complexity. All of the things that your body is made up of are vital to your health. Everything is made of matter. Matter is made up of particles called atoms. An atom is the smallest part of matter. Elements and compounds Matter that has the same composition and properties throughout is a substance. Substances are either elements or compounds. An element is made up of only one kind of atom Scientists have discovered 90 natural elements on Earth! Elements and Compounds Substances that are made of more than one element are called compounds. A compound is two or more elements that are chemically combined. Think: What elements make up the compounds carbon dioxide (CO2) and ammonia (NH3)? Chemicals in living things are classified as either organic or inorganic. Inorganic substances usually come from nonliving sources, such as the air, soil, or water. Example: Minerals (see table) Inorganic chemicals play an important role in your body. Salt is an important chemical in your blood. Chemically, blood is mostly water (H2O) but it also contains sodium ions (Na+) and chlorine ions (Cl-) in the form of dissolved sodium (NaCl), or table salt. Water makes up more than 70% of the body’s tissues and plays a role in almost every bodily function (digestive system, musscle function, delivering oxygen to cells, removing bodily wastes) Lack of water can cause problems with the digestive system, circulatory system and kidney function. ◦ Lack of water daily leads to dry skin, headaches, and fatigue. Living things are made of organic compounds, which are compounds containing carbon (with the exception of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide) There are four groups of organic compounds: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Lipids Carbohydrates Nucleic Acids Proteins Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for living things. Carbohydrates are made up of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). Lipids (fats and oils) contain more energy per molecule than carbohydrates. Lipids are stored in your body as energy reserves. When your carbohydrates are low, your body turns to fat reserves for energy. Nucleic acids are large complex organic compounds that store information in the form of a code. DNA is an example. DNA carries information that directs all cells activities and instructions for making proteins. RNA is another example. RNA is responsible for making proteins from amino acids. Proteins are important to living things because many of the structural parts of your body are made of proteins. ◦ Example: hair, nails, skin, muscles, blood vessels Enzymes are an example of another type of protein. Enzymes help your body carry out important processes, such as growth, repair, digestion, respiration, and transmission of nerve impulses. The human body is complex, but organized. Your body is composed of many different types of cells. These cells perform their own functions yet work together so the whole organism can function. Level 1: Cells Level 2: Tissues Level 3: Organ Level 4: Organ Systems Level 5: Organism Cells represent the first level of organization. Cells are organized into tissues. Tissues are groups of similar cells that do the same sort of work. Tissues are organized into larger structures called organs. Organs are structures made up of different tissues that work together. Organ Systems are a group of organs that work together to do a certain job. Organism is made of organ systems working together 1. 2. 3. 4. List, in order, the levels of organization in the human organism. Explain why your body needs minerals. Think Critically: Explain why cells are vital for life. Solve One-Step Equations: Every milliliter of blood has five million red blood cells. On average, a person has 3.3 L of blood. Calculate how many red blood cells are found in a typical human body.