* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download First Principle Calculations of Positron
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Density matrix wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
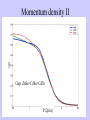
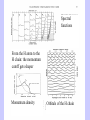
First Principle Calculations of Positron Annihilation in CdSe Quantum Dots B. Barbiellini, A. Bansil (Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115), P. Mijnarends (Delft University of Technology,Delft, The Netherlands), R. Saniz (UCB, Cochabamba, Bolivia), P. Sterne (Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory), M. Weber, K. Lynn (Washington State University, Pullman WA 99164), A. Denison (INEEL, Idaho Falls, ID 83415 and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory) Theory I The Density Functional Theory (DFT) is generalized to positron-electron systems by including electron and positron density( The ground-state value of any operator is a functional of the electron and positron densities and be calculated via the Hellmann-Feynman theorem: : Coupling constant Theory II The Local Density Approximation (LDA) was the first implementation. It provides an explicit formula for the Exchange-Correlation Energy The Generalized Gradient Approximation (GGA) reduces the LDA electron-positron correlation. The GGA is very successful for positron lifetimes, energetics, and momentum distributions of the annihilating pairs. Positron lifetime in bulk CdSe An experimental lifetime of 275 ps was found in agreement with the theoretical value of 279 ps based on the DFT GGA. A highly accurate description of the electron-positron correlation effects is needed to find such a good agreement. Such agreement indicates also that our bulk sample is of good quality (without any significant concentration of atomic point defects). Positron state in a CdSe Qdot • The state of the positron can be explained in terms of the positron Affinity (calculated by DFT GGA) between the Qdot and the matrix. • Potential well is about 2 eV therefore positrons are trapped in the CdSe Qdots. • Using an LMTO basis set we find that almost 80% of the positron wave function is confined to the interstitial region between the atoms thus limiting the fraction that could extend beyond the quantum dot volume. MOMENTUM DENSITY I DOS The variation of the gap is proportional to the variation of the momentum density smearing width (Peter & Friedel model). Momentum density II Gap: ZnSe>CdSe>CdTe P (2pi/a) Mometum smearing: width of -dn(p)/dp Smearing = width P (2pi/a) Spectral functions From the H atom to the H chain: the momentum cutoff gets shaper Momentum density Orbitals of the H chain Conclusion The scheme based on measuring and calculating positron lifetime and momentum distributions is a reliable tool to analyze materials properties. The study (Lifetime and Doppler profile) of bulk CdSe gives credence to use the DFT GGA scheme. The localized positron states at Qdots have also been found well described by the DFT GGA (Affinity). The Doppler profile shows a smearing at the boundary of the Jones zone proportional to the widening of the band gap that may occur due to a reduction in the size of the quantum dots.