* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download compound - Coal City Unit #1
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
List of phenyltropanes wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
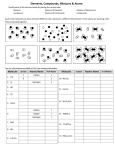
How is Matter Classified? • Matter is classified using chemical and physical props. Pure Substances • a sample of matter that has definite chemical and physical properties • Elements • Compounds ATOM • the basic unit of matter • all matter is composed of atoms ELEMENTS • simplest substances from which more complex substs. are made • ea. elem. contains single type of atom • 111 diff. elements discovered to date • represented by symbols – usually one or two letters 1st letter is always capitalized, second letter is always sm. case • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. Small number of elements make up most common substs. • H is most common element • Living things are made primarily of C, H, O, and N MOLECULE • neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds • two or more atoms combined in a definite ratio • atoms may be of the same or different elements Elements may exist as single atoms or as molecules • Helium gas consists of single atoms (monatomic gas) • Nitrogen gas consists of molecules • Ea. molec. consists of two nitrogen atoms (diatomic gas) 7 diatomic gases are elements: • Bromine • Iodine • Nitrogen • • • • Chlorine Hydrogen Oxygen Fluorine ALLOTROPES • one of a number of different molecular or crystalline forms of an element • diff. forms of the same element • Oxygen consists of 2 allotropes – O2 and O3 (ozone) • Carbon has many allotropes • most common are graphite and diamond • Allotropes have different properties COMPOUND • the product that results when two or more different elements are chemically combined Two types of compounds: • Ionic compounds – consist of positively and negatively charged ions • ION – an atom or group of atoms w/ an electrical charge • Covalent compounds – made of neutral molecules ACID • a class of compounds whose water solns. taste sour, turn blue litmus paper red, and react with bases to form salts (ionic compounds) pH • a numerical scale used to express acidity • 0 to 14 • 7 is neutral • comps. w/ pH less than 7 are acids • comps. w/ pH greater than 7 are bases BASE • a class of compounds that taste bitter, feel slippery in water soln., turn red litmus to blue, and react with acids to form salts ORGANIC COMPOUNDS • covalent compounds containing carbon (except carbonates and oxides) INORGANIC COMPOUNDS • compounds outside the organic family of compounds Compounds are represented by formulas • molecular formula - C12H22O11 (sugar) • ionic formula – NaCl (table salt) • shows numbers of atoms of ea. elem. present in compound Structural Formulas • show the exact number of atoms present in a molecule and how these atoms are bonded to one another • lines represent the bonds betw. atoms MIXTURE • a collection of 2 or more pure substs. physically mixed together • proportions can vary • properties can vary ALLOY • solid mixture (usually mixture of metals) Two diff. classifications of mixtures: HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE • a mixture containing substs. that are uniformly distributed • solution • • • • salt water koolaid tea brass (alloy) • all regions are identical in composition & properties HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE • a mixture containing substs. that are not uniformly distributed • some regions have different properties than other regions • • • • • dirt granite choc. chip ice cream veg. soup ice water How mixtures differ from compounds: • Props. of mixtures reflect props. of components. Props. of compounds do not • reflect. props. of elems. that compose it. • Comps. have definite composition. Composition of mixtures can vary. Most mixtures can be separated by physical means. Some mixtures may need to be separated by chemical means. • react one component so it can be removed easier All compounds must be separated by chemical means