* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OLFACTORY AND OPTIC NERVE - part 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
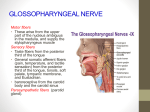
Cranial Nerve VI: Abducens Fibers leave the pons and enter the orbit via the superior orbital fissure Primarily a motor nerve innervating the lateral rectus muscle (abducts the eye; thus the name abducens) Abducens Oculamotor paralysis Abducent nerve injury Trigeminal nerve The largest cranial nerve Mixed cranial nerve Has 4 nuclei: 1. 2. 3. 4. Main sensory nucleus Spinal nucleus Mesencephalic nucleus Motor nucleus Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal Trigeminal nerve Components of fibers SVE fibers: originate from motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve, and supply masticatory muscles, tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini, mylohyoid and digasteric(anterior bellly) GSA fibers: transmit facial sensation to sensory nuclei of trigeminal nerve, the GSA fibers have their cell bodies in trigeminal ganglion, which lies on the apex of petrous part of temporal bone Branches Ophthalmic nerve (Ⅴ1, sensory) leave the skull through the superior orbital fissure, to enter orbital cavity Branches – Frontal nerve • Supratrochlear nerve • Supraorbital nerve – Lacrimal nerve – Nasociliary nerve Distribution: carries sensory information from: the scalp and forehead the upper eyelid, the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye the nose (including the tip of the nose, except alae nasi), the nasal mucosa, the frontal sinuses parts of the meninges (the dura and blood vessels). Maxillary nerve (Ⅴ2, sensory) Leave skull through foramen rotundum Branches – – – – Infraorbital nerve Zygomatic nerve Superior alveolar nerve Pterygopalatine nerve Distribution: carries sensory information from : the lower eyelid cheek the nares and upper lip, the upper teeth and gums, the nasal mucosa the palate and roof of the pharynx, the maxillary, ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses parts of the meninges. Mandibular nerve (Ⅴ3, mixed) Leave the skull through the foramen ovale to enter the infratemporal fossa Branches – – – – – Auriculotemporal nerve 耳 Buccal nerve Lingual nerve Inferior alveolar nerve Nerve of masticatory muscles Distribution: Sensation from cerebral dura mater Teeth and gum of lower jaw Mucosa of floor of mouth Anterior 2/3 of tongue Skin of auricular and temporal regions and below the mouth Motor to masticatory muscles, mylohyoid, and anterior belly of digastric Facial nerve (Ⅶ) Mixed cranial nerve Has 3 nuclei: 1. Main motor nucleus 2. Parasympathetic nuclei( superior salivatory and lacrimal nucleus) 3. Sensory nucleus Facial nerve (Ⅶ) Components of fibers SVE fibers originate from nucleus of facial nerve, and supply facial muscles, auricular muscles, stapedius, posterior belly of digasteric and the stylohyoid muscles GVE fibers derived from superior salivatory nucleus and relayed in pterygopalatine ganglion and submandibular ganglion. The postganglionic fibers supply lacrimal, submandibular and sublingual glands SVA fiber from taste buds of anterior two-thirds of tongue which cell bodies are in the geniculate ganglion of the facial nerve and end by synapsing with cells of nucleus of solitary tract GSA fibers from skin of external ear Course: leaves skull through internal acoustic meatus, facial canal and stylomastoid foramen, it then enters parotid gland where it divides into five branches which supply facial muscles Branches within the facial canal Chorda tympani : joins lingual branch of mandibular nerve – To taste buds on anterior two-thirds of tongue – Relayed in submandibular ganglion, the postganglionic fibers supply submandibular and sublingual glands Branches outside of facial canal Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Marginal mandibular Cervical Cranial Nerve VII: Facial Figure VII from Table 13.2 Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Fibers arise from the hearing and equilibrium apparatus of the inner ear, pass through the internal acoustic meatus, and enter the brainstem at the pons-medulla border Two divisions – cochlear (hearing) and vestibular (balance) Functions are solely sensory – equilibrium and hearing Vestibular nerve Conduct impulses from saccule and utricle and semicircular canal Vestibular ganglion in internal acoustic meatus Enter vestibular nuclear complex Efferent fibers pass to cerebellum, spinal cord, and MLF Cochlear nerve Conduct impulses from organ of Corti in cochlea spiral ganglia in the cochlea Enter cochlear nuclei End in trapezoid body lateral leminiscus inferior colliculus MGB auditory cortex through acoustic radiation Vestibulocochlear nerve Vestibular ganglion(SSA) ↘ ↗ Vestibular nuclei Internal acoustic meatus Cochlear ganglion (SSA) ↗ ↘ Cochlear nuclei Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Figure VIII from Table 13.2 Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal Fibers emerge from the medulla, leave the skull via the jugular foramen, and run to the throat Nerve IX is a mixed nerve with motor and sensory functions Motor – innervates part of the tongue and pharynx, and provides motor fibers to the parotid salivary gland Sensory – fibers conduct taste and general sensory impulses from the tongue and pharynx Has 3 main nuclei: 1. Main motor nucleus( stylopharyngeus muscle) 2. Sensory nucleus 3. Parasympathetic nucleus( inferior salivatory nucleus) CN IX: Glossopharyngeal Nerve Inf. salivatory nucleus Parotid gland, parasympathetic Spinal trigeminal tract N. solitarious Sensory nucleus for CN VII, IX, X Posterior 1/3 of the tongue N. ambiguus Motor nucleus for CN V, VII, IX, X CN IX, X & XI Sensation behind ear Stylopharyngeus (lifts pharynx) Glossopharyngeal nerve (Ⅸ) Components of fibers SVE fibers: originate from nucleus ambiguus, and supply stylopharygeus GVE fibers: arise from inferior salivatory nucleus and ralyed in otic ganglion, the postganglionic fibers supply parotid gland SVA fibers: arise from the cells of inferior ganglion, the central processes of these cells terminate in nucleus of solitary tract, the peripheral processes supply the taste buds on posterior third of tongue GVA fibers: visceral sensation from mucosa of posterior third of tongue, pharynx, auditory tube and tympanic cavity, carotid sinus, and end by synapsing with cells of nucleus of solitary tract GSA fibers: sensation from skin of posterior surface of auricle Course: leaves the skull via jugular foramen Branches Lingual branches : to taste buds and mucosa of posterior third of tongue Pharyngeal branches : take part in forming the pharyngeal plexus Tympanic nerve : GVE fibers via tympanic and lesser petrosal nerves to otic ganglion, with postganglionic fibers via auriculotemporal (Ⅴ3) to parotid gland Carotid sinus branch : innervations to both carotid sinus and glomus Others: tonsillar and stylophayngeal branches Otic ganglion : situated just below foramen ovale Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal Figure IX from Table 13.2 Cranial Nerve X: Vagus The only cranial nerve that extends beyond the head and neck Fibers emerge from the medulla via the jugular foramen The vagus is a mixed nerve Most motor fibers are parasympathetic fibers to the heart, lungs, and visceral organs Its sensory function is in taste Has 3 main nuclei: 1. Main motor nucleus( constrictors of the pharynx and intrinsic muscles of the larynx) 2. Sensory nucleus 3. Parasympathetic nucleus( dorsal nucleus of vagus) Vagus nerve (Ⅹ) components of fibers GVE fibers: originate from dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve, synapse in parasympathetic ganglion, short postganglionic fibers innervate cardiac muscles, smooth muscles and glands of viscera SVE fibers: originate from ambiguus, to muscles of pharynx and larynx GVA fibers: carry impulse from viscera in neck, thoracic and abdominal cavity to nucleus of solitary tract GSA fiber: sensation from auricle, external acoustic meatus and cerebral dura mater SVA: taste sensation CN X: Vagus Nerve “Wanderer” Dorsal motor nucleus of X Parasympathetic, preganglionic Spinal trigeminal tract N. solitarious Sensory nucleus for CN VII, IX, X Taste, epiglottis Cardiorespiratory N. ambiguus Motor nucleus for CN V, VII, IX, X CN IX, X & XI Ear Pharynx Larynx Cranial Nerve X: Vagus Course Exits the skull from jugular foramen Descends in the neck in carotid sheath between internal (or common) carotid artery and internal jugular vein Right vagus nerve Enter thoracic inlet on right side of trachea Travels downward posterior to right brachiocephalic vein and superior vena cava Passes posterior to right lung root Forms posterior esophageal plexus Forms posterior vagal trunk at esophageal hiatus where it leaves thorax and passes into abdominal cavity, then divides into posterior gastric and celiac branches Left vagus nerve Enter thoracic inlet between left common carotid and left subclavian arteries, posterior to left brachiocephalic vein Crosses aortic arch where left recurrent laryngeal nerve branches off Passes posterior to left lung root Forms anterior esophageal plexus Forms anterior vagal trunk at esophageal hiatus where it leaves thorax and passes into abdominal cavity , then divides into anterior gastric and hepatic branches Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory Formed from a cranial root emerging from the medulla and a spinal root arising from the superior region of the spinal cord The spinal root passes upward into the cranium via the foramen magnum The accessory nerve leaves the cranium via the jugular foramen Primarily a motor nerve – Supplies fibers to the larynx, pharynx, and soft palate – Innervates the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid, which move the head and neck Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory Figure XI from Table 13.2 Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal Fibers arise from the medulla and exit the skull via the hypoglossal canal Innervates both extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue, which contribute to swallowing and speech(except palatoglossus) GSE fibers Cranial Nerves of the Medulla Vestibular nuclei CN XII Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal Figure XII from Table 13.2 Nerve injury Trigeminal neuralgia Facial nerve lesion(pells palsy) Vestibulocochlear nerve injury Glossopharyngeal nerve injury Vagus nerve injury Accessory nerve injury Hypoglossal nerve injury