* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 Lesson 1 - Effingham County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
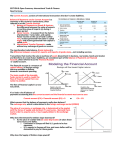
Unit 3 Lesson 1 Exchange Rates 1) Grab your clicker. 2) Pick up a “Mall of the World” menu… …and pick out three things you want to eat. Which of the following best explains why the Pesos per Dollar changed from year 1 to year 2? Year 1 2 3 • A) Mexican consumers started buying more Levi’s. • B) More American investors invested in Mexican companies. Pesos per Dollar 1,356 1,148 1,493 • C) Prices were rising faster in Mexico than in USA. • D) Mexican drug wars kept U.S. tourists from going to Mexico. How do American producers like to be paid?? How do French producers like to be paid?? Do foreign producers sell us their stuff?? How do Americans get foreign stuff? Foreign Exchange • Banks and other financial institutions exchange currencies. • When you buy a good from another country, at some point your dollars are changed into that country’s currency. Exchange Rates • Does one of these QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • equal one of these??? QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Reading Exchange Rate Tables • How many Yen equal 1 dollar? • How many US dollars does it take to buy one Mexican Peso? • How many US dollars does it take to buy one Ruble? How much in dollars does it take to buy one Shekel? • A) $0.23 • B) $4.44 How many British pounds does it take to buy a dollar? • A) 1.58 • B) 0.63 Which currency is worth the most compared to the U.S. dollar? • • • • A) Won B) Pound C) Shekel D) Ruble Currency Converter Ratios and Equations for Foreign Exchange • • • • • • • • If 1 peso = 3/4 dollar… 1 peso = 0.75 dollar 10 pesos = ______ 100 pesos = ______ 2 pesos = _______ 3 pesos = _______ 1 dollar = _______ 2 dollars = _______ Clicker Quiz Foreign Exchange Conversion If 1.5 dollars buys 1 yen, then • A) One dollar is more valuable than one yen. • B) One yen is more valuable than one dollar. • C) There is not enough information to determine which one is more valuable. If 1.5 dollars buys 1 yen, then 2 yen buys • • • • A) 2 dollars B) 2.5 dollars C) 3 dollars D) 3.5 dollars If 1.5 dollars buys 1 yen, then 10 yen buys • • • • A) 7.5 dollars B) 15 dollars C) 75 dollars D) 150 dollars If 1.5 dollars buys 1 yen, then 1 dollar buys • • • • A) 0.67 yen B) 0.75 yen C) 6.67 yen D) 7.5 yen If 2.5 yen buy 1 dollar, then 10 dollars buys • • • • A) 5 yen B) 25 yen C) 50 yen D) 250 yen If 2.5 yen buy 1 dollar, then 1 yen buys • • • • A) 0.4 dollars B) 0.5 dollars C) 0.6 dollars D) 2.5 dollars 10 British pounds can be exchanged for how many U.S. dollars? • • • • A) $158.00 B) $15.80 C) $63.29 D) $632.90 Keisha traveled to the U.S. with 100 Canadian dollars. How much did she receive when she exchanged her money for U.S. dollars? • A) $6.63 • C) $15.10 B) $66.25 D) $150.95 1000 Great Britain Pounds (GBP) will buy how many Australian Dollars? • A) 43.21 • C) 231.63 B) 432.10 D) 2316.30 Jenna traveled to Canada with $1,000 (U.S.). About how much did she receive in Canadian dollars? • • • • A) 66 Canadian Dollars B) 663 Canadian Dollars C) 150 Canadian Dollars D) 1,510 Canadian Dollars Hamilton traveled to the USA with 10 Canadian Dollars. About how much did he receive in U.S. Dollars? • A) $15.10 • B) $150.95 • C) $66.25 • D) $6.63 How many Pounds (GBP’s) can I get for 10 Swiss Francs? • • • • A) 5.5 B) 55 C) 18 D) 181 Lunch time at the “Mall of the World” Your Annual Vacation To France Appreciation/Depreciation • Exchange rates change. • When 1 dollar buys more euros, the dollar has appreciated. • Appreciation of dollar / depreciation of euro: • Year 1: $1 = 2 euros Year 2: $1 = 3 euros • Year 1: 1 euro = $0.5 Year 2: 1 euro = $0.33 • $1 buys more euros. • It takes more euros to buy a dollar. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Between 1996 and 1998… QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • A) The yen appreciated, or rose against, the dollar. • B) The yen depreciated, or fell against, the dollar. Between 1998 and 2000… QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • A) The yen appreciated, or rose against, the dollar. • B) The yen depreciated, or fell against, the dollar. Between 1996 and 1998… QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • A) The Canadian dollar appreciated, or rose against, the dollar. • B) The Canadian dollar depreciated, or fell against, the dollar. Between 2000 and 2002… QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • A) The Canadian dollar appreciated, or rose against, the dollar. • B) The Canadian dollar depreciated, or fell against, the dollar. Between years one and two, the peso _____ against the dollar. • A) appreciated, rose, gained on • B) depreciated, fell against Exchange Rate Consultants Make Believe World QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. One bank, on an island in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean, handles all currency exchanges between the U.S. and Europe. You Manage The Bank • For as long as the bank has been open, the exchange rate has been $1 : 1 euro. • Americans have bought the same amount of stuff from Europe as Europeans have bought from America. • So, you have never had to worry about running out of either currency. One day, • you notice that many more ships from America are sitting in the harbor, • and very few European ships. • At the end of the day, you have many more dollars in the vault than euros. • The rest of the week goes the same way. Time For A Decision • The rest of the week goes the same way. • You are running very low on euros. • What do you do????????? Floating Exchange Rates When Supply and Demand Determine the Value of Currency Why Exchange Rates Change • If U.S. goods or investments become more popular, demand for dollars _______. • This makes the dollar __preciate. • Higher inflation in U.S. would make dollar __preciate. 2 Countries: Mac-land and Bean-ico Macks and Beaners The Exchange Rate Over Time • This chart shows the number of Yen it took to buy 1 Euro each year. • When the number gets bigger, the yen has lost value, & vice versa. Between years one and two, the dollar _____ against the peso. • A) appreciated, rose, gained on • B) depreciated, fell against Between years 1 and 2, the demand for dollars could have… • A) increased. • B) decreased. Between years one and two, the supply of dollars could have… • A) increased. • B) decreased. Which of the following best explains why the Pesos per Dollar changed from year 1 to year 2? • A) Inflation was higher in the U.S. than in Mexico. • B) Mexican drug wars caused a decrease in U.S. tourists going to Mexico. Which of the following BEST explains why the Yen per Euro changed from year 1 to year 2? • A) Japanese consumers demand more European goods & services. • B) Japanese business firms increased their exports to Europe. Which of the following BEST explains why the Yen per Euro changed from year 1 to year 2? • A) Japanese investment in European companies increased. • B) The inflation rate in Europe increased at a faster rate than it did in Japan. 4 Groups U.S. Producers U.S. Consumers European Consumers European Producers Within your group, decide whether you benefit or lose from the change in the exchange rate. Who loses and who benefits? If the dollar rises against the euro 1. U.S. producers………….• 2. U.S. consumers………..• 3. European producers….• 4. European consumers..• 5. U.S. exports………………• 6. U.S. imports……………..• lose benefit benefit lose rise fall If the Japanese Yen rises against the Euro, Japanese producers • A) sell more products • B) sell fewer products • C) are unaffected If the U.S. Dollar falls against the South Korean Won, South Korean consumers • A) buy more U.S. goods • B) buy fewer U.S. goods • C) are unaffected