* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Week10.2 Stocks - B-K
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 1980s wikipedia , lookup
Mark-to-market accounting wikipedia , lookup
Algorithmic trading wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Stock market wikipedia , lookup
Securities fraud wikipedia , lookup
Stock trader wikipedia , lookup
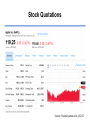
Personal Finance Stocks (Equities) Bill Klinger Personal Finance • Review – – – – – Asset classes Types of risk Measuring risk Calculating returns Taxes on returns Equities • Common Stock – Share of ownership in a company. – Common stock owners can vote on major company decisions – They expect to receive cash dividends and to benefit from capital gains. (Often no dividends are issued.) • Preferred Stock – Stock whose holders receive preference in the payment of dividends – Seldom confers voting rights – Dividends are fixed 1-3 Equities • Convertible Securities – Bonds or stock that contains a conversion feature – Gives the holder the right to exchange their securities for a fixed number of shares of common stock 1-4 Buying Stock • Stock exchanges – NYSE, AMEX – Over-the-counter, e.g. NASDAQ • Brokers • Bid-ask spread • Commissions Stock Quotations Source: finance/yahoo.com 1/12/17 Stock Quotes • • • • Bid – what a person is willing to pay Ask – what a person wants for the stock Market Cap – Value of the company = price x (# shares) P/E – Price/earnings ratio = price / EPS – The higher the P/E, the more the market thinks the company’s profits will grow • EPS – earnings per share, – the profit on one share of stock = net income / # shares • Dividend – dividend paid per share of stock – ( N/A means no dividends are paid ) • Yield – dividend / price. ( N/A means no dividends are paid ) Buying and Selling Securities • Brokerage Firm—financial intermediary that buys and sells securities for individual and institutional investors. • E*trade: An Online Brokerage Firm 1-8 Costs of Trading • When investors buy or sell securities through a brokerage firm, they pay a fee • These costs vary widely among brokerage firms • A full-service firm charges higher fees, but provides a large number of services and offers investment advice • A discount firm charges lower fees, but offers less advice and fewer services 1-9 Buying and Selling Securities • Placing an Order – A market order instructs a brokerage firm to obtain the highest price possible – if the investor is selling – or the lowest price possible – if the investor is buying – A limit order instructs the brokerage firm not to pay more than a specified price for stock if the investor is buying, or accept less than a specified price if the investor is selling • Buying on margin – – – – Borrow a portion of funds to purchase Fed limits margin to 50% Subject to margin call if value drops Using leverage • Short selling 1-10 – Sell stock you don’t own now – Purchase at a later date Equity Returns • Dividends – – – – Optional Usually quarterly Sometimes one-time event Not guaranteed for common stock • Change in price – Based on investors’ view of a firm’s future – Will cause a capital gain or loss 1-11 Not All Risk is the Same Firm Risk = Business Cycles Systemic risk Financial Markets + Global Conditions Idiosyncratic Risk Risk Unique to the Firm Source of Correlation Idiosyncratic risk can be diversified away! Stock Indexes • Reflect the general activity of the stock market • Most common indices – Dow Jones Industrial Average (the Dow or DJIA), – Standard & Poor’s 500 (S&P 500), – NASDAQ composite • Foreign indices – DAX (Germany) – FTSE, FT-100 or “Footsie” (London), – Nikkei (Tokyo) 1-13 How’s the Market Doing? • Bull market • Bear market 1-14 In Class • In groups of two – Chapter 15 Financial Planning Exercises