* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Theory of Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
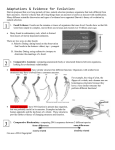
The Theory of Evolution Evolution The change of populations over time. Charles Darwin • The father of evolution. • Published book, On the Origins of the Species, in 1859 Darwin’s studies • Began on the Galapagos Islands • He noticed many species of animals that were unique to each island, but similar to species elsewhere. Darwin’s four basic thoughts: One Very Crazy Saying 1. Overproduction of offspring: • Species produce more offspring than can survive. • Example- fish lay millions of eggs at a time. 2. Variation: • In any population, individuals have variations (differences). • Size, speed, color, etc. 3. Competition: • Individuals compete for a limited amount of resources • Such as food, shelter, protection, from predators, mates, etc. 4. Survival: • Certain individuals survive, based on variations. • The individuals that survive pass on their genes, producing generations full of individuals with those helpful genes. These four steps make up Darwin’s theory of Evolution Natural Selection • The mechanism for change in populations • Change is considered a mutation. • Mutations can be good and/or bad. • Mutations occur in the organism’s? DNA Artificial Selection: • Purposely breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits. • A.K.A. Selective Breeding Evidence for Evolution Adaptations-Changes in species that occur over time. 1. Structural Adaptations • Change in an organisms body parts that help an individual survive in their environment. • Examples: coloring, teeth, claws, etc. • These adaptations happen over millions of years Examples of Structural Adaptations: A. Mimicry- a structural adaptations that allows one species to resemble another species. • A harmless species will resemble a harmful species A. Mimicry • A predator that avoids the harmful species will also now avoid the harmless species out of a fear that it is the harmful one. B. Camouflage • A structural adaptation that allows a species to blend into their surroundings. • Species is then not easily found by its predators. 2. Physiological Adaptations • Changes in an organisms metabolic processes. • These adaptations happen very quickly. • Examples- Weeds becoming resistant to pesticides. • Bacteria becoming resistant to antibiotics. Other Evidence for Evolution 1. Fossils • Scientists use fossils to form timelines from one species to another that evolved from it. 2. Anatomy Physical structure of an organism A. Homologous structures • Structural features with a common evolutionary origin. • Example- Whale fin, Crocodile limb, bird wing, human arm • Evidence that organisms evolved from a common ancestor. B. Analogous Structures • Body parts of organisms that do not have a common ancestry, but do have similar functions. • Example- Bird wing and Butterfly wing. • Evidence that species adapted independently to similar ways of life. C. Vestigial Structures • A body structures that has no present day use, but was useful to an ancestor. • The body structure became vestigial due to lack of use. • Example- Ostrich forelimbs, Human appendix. 3. Embryology • Comparing Embryos of different species for similarities. Embryology • Compare an adult mammal, fish, reptile, and bird. • Do they look alike? • NO Embryology • Compare the embryos of these species • Do they look alike? • YES • All have gill slits, and tails when they are embryos, but as they develop, you start to see differences. • This provides evidence that they all evolved from a common ancestor. 4. Biochemistry • Comparing the DNA and RNA of different species is the best way to determine the relationships of organisms Biochemistry • Humans and bananas have • 50% same DNA Word Bank • • • • • • • • • Variation Evolution Overproduction Survival Competition Mimicry DNA Camouflage Fossils Homologous structures Analogous structures Biochemistry