* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War Part I
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Sailor's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Chancellorsville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of White Oak Road wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Petersburg wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Spotsylvania Court House wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
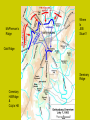
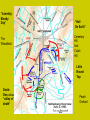
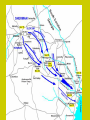
Civil War Part I Eastern & Western Campaign Mid 1863-1865 Gettysburg Battle – July 1-3, 1863 Union & Confederacy Major Players UNION • Commander: General George Meade • Brig. Gen. John Buford’s cavalry (1st day) • Major Gen. John Reynolds (Union 1st Corps), 1st Day) • General Abner Doubleday (1st day ordered retreat from McPherson and Oak Ridge to Seminary Ridge and ultimately Cemetery Hill) • Major General Winfield S. Hancock (took over after Reynolds as Meade’s second, organized defenses on Cemetery Hill, wounded from P.C.) • Colonel Joshua Chamberlain (Little Round Top) • Major General Daniel Sickles (Devils’ Den CONFEDERATE • Commander: General Robert E. Lee • Three Large Corps – – – • • Gen Henry Heth (1st day) Jeb Stuart – – • • • General James Longstreet General Richard Ewell (did not pursue at night of 1st day) General A.P. Hill (Cashtown) Where was he 1st and 2nd day? What are his orders for the 3rd day? Successful or not? John Bell Hood (Devils Den,– 6000 from both sides”) George Pickett Brig. General Lewis Armistead (lone general of Pickett’s charge who was able to cross the stonewall (The ANGLE) with about 300 men McPherson’s Ridge Where Is JEB Stuart? Oak Ridge Seminary Ridge Cemetary Hill/Ridge & Culp’s Hill “A terribly Bloody Day” The Wheatfield “Hell On Earth” Cemetary Hill And Culp’s Hill Little Round Top Devils Den, a.k.a. “valley of death” Peach Orchard “I will strike him there” --Robert E. Lee Dreadful Aftermath • Casualties, more than: U (23,000), C (28,000) • Townspeople had to deal with dead, wounded soldiers long after armies retreated • Churches, barns, private homes turned into to hospitals • Gettysburg Address – Nov. 19, 1863 – National Cemetery – Reinvigorate the war effort The Battle at Vicksburg • Key to controlling the Mississippi River • Siege of Confederate citadel (May-July 1863) • Grant’s forces (@70,000) vs. Pemberton’s forces (@ 30,000) • Horrors of war experienced by civilians – Disease, starvation, seeking shelter from bombs • Pemberton and his soldiers surrendered on July 4th, an unconditional surrender • Led to surrender of Port Hudson (July 8th), last Confederate port • Confederacy had been split in 2 (AK, LA, TX) Grant takes Command – Spring 1864 • • War of Attrition – Grant’s plan to attack Lee and never let up despite any losses Union may encounter; Continue fighting until the South had run out of men, supplies, and the will to fight. Grant’s 3 Prong offensive a. Union under the command of General Sheridan, 30,000 men advance up James River towards Richmond b. General Sherman march south towards Atlanta to destroy Southern center c. Grant and Meade would target Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia 1864 – East and West 10 min. movie clip Grant’s Eastern Campaigns (The Final Campaigns) • May 5th: Wilderness (inconclusive) – Fighting among tangled underbrush and dense woods – brushfires and fog, friendly fire – James Longstreet accidentally shot • May 9th-12th: Spotsylvania Court House – Bloody frenzy – Death of JEB Stuart – Inconclusive but reiterates Grant’s strategy – war of attrition Further Fighting in VA • • June 3rd: Cold Harbor – Direct frontal assault by Grant – Lee had built a 6 mile long entrenchment, with rivers protecting both flanks – Union forces knew this was bad – pinned scraps of paper to their uniforms – Worse decisions he ever made – Within 30 minutes, 7000 Union troops were cut down – rebel entrenched – 4 weeks of grueling battles here – Union loses more than 50,000 men The Siege of Petersburg begins – A mere matter of time and numbers – Lee – Avoid a direct conflict with Lee at Richmond and instead wear them down – Important supply, rail, and communications center (connected directly to Richmond) – Siege would last over 10 months until end of war --- trench warfare – Grant brought in reinforcements, but Lee could not “Tecumseh” Was it Necessary? Sherman’s Western Campaign INSERT in MARGIN NEXT TO J & K ON NOTES • Sherman’s Atlanta Campaign, @ 108,000 men – Advanced from Chatt. To Atlanta in May 1864 – Confed General: Joe Johnston (60,000 troops) replaced by Gen. John Bell Hood – Sherman troops surround city slowly but methodically – By Sept, city of Atlanta in Union hands • • • • Significant victory, a manufacturing city South deprived of important communication center Lost last rail link across Appalachian Mts. Boosted morale of soldiers/Northerners giving Lincoln what he needed to win reelection The Burning of Atlanta The March to the Sea • Grant had encouraged Sherman to stay in Georgia to defeat all troops there, but he had bigger plans • March forces from Atlanta to Savannah, Georgia seaport ---- begins Nov. 15th – 62,000 troops cut a 60 mile wide (300 mile path) front across the state intending to “make Georgia howl” – Sherman cut off all supply lines and live off landscape – Strip the South of everything the could support war effort • By Dec. 21st – Sherman outside Savannah “I beg to present you as a Christmas gift the city” • Next stop South Carolina and then North– extending same type of damage as was done in GA • Gen. Johnston finally surrenders to Sherman pm April 26, 1865 The Destruction of Richmond and Surrender (April 1865) • Early 1865, Lee abandons Petersburg and heads to Richmond • Davis and Confederacy gov’t told to abandon Richmond • Panic in the street – Richmond ablaze • Union troops enter and place under military control • Lee’s army quickly moved west to no avail – The Generals had already been in contact – “There is nothing left for me to do then go see General Grant, and I would rather die a thousand deaths” – Lee’s surrender at Appomattox Court House in VA on April 9, 1865– surrender terms were generous What did the Civil War cost us? Loss of innocence Devastated landscape 2% of the population