* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Backed by Gold Fiat Money - Saint Joseph High School
Currency War of 2009–11 wikipedia , lookup
Black Friday (1869) wikipedia , lookup
Currency war wikipedia , lookup
Fixed exchange-rate system wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy of the United States wikipedia , lookup
Fractional-reserve banking wikipedia , lookup
Bretton Woods system wikipedia , lookup
Reserve currency wikipedia , lookup
Gold standard wikipedia , lookup
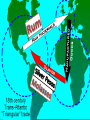
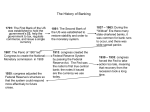
The Evolution of Money Barter Economy “”Mutual Coincidence of Wants Functions of Money • Medium of Exchange – Accepted by ‘all’ in payment of goods and services • Measure of Value – Provides a way to compare the worth of one product to another • Store of Value – Can be saved until needed Commodity Money • Can be used to settle debts or consumed Musket Balls Compressed Tea Leaves Gun Powder FIAT MONEY • Money by Government Decree Porpoise Teeth Wampum PAPER MONEY • Originated by 17th Century England Goldsmith – Became a safe place to store gold – Depositor receipts served as the first paper money – Goldsmiths issued more receipts than gold held in reserve causing a liquidity problem. The First U.S. Paper Currency • Individuals and Banks began printing their own paper money – Backed by Gold or Silver (Commodity Money) • Continental Dollars were issued to finance the Revolutionary War – Not backed by Gold or Silver (Fiat Money – Printed by the Continental Congress Backed by Gold Fiat Money Massachusetts State First US Currency Continental Currency Specie Most desirable form of money – Limited in supply ORIGINS OF THE DOLLAR • George Washington commissions Benjamin Franklin and Alexander Hamilton to establish money supply • To eliminate the Peso from circulation • Pesos were used in Triangular Trade – Most Common Currency used in the U.S. in 1789 Characteristics of Money • Portable • Durable • Divisible • Limited in Supply MONETARY STANDARD • Tool or mechanism used to keep the money supply portable, durable, divisible and limited in supply • Article 1,Section 8 – gave Congress the power to coin money • Article 1, Section 10 – Prohibited states from coining money (did not prohibit state banks from issuing paper money) State Banks • Received charter from State Government • Issued paper currency that was backed by either gold or silver • More notes issued than could be backed with gold or silver • Each bank’s currency varied in size, color and denominations • 1,600 banks with 10,000 kinds of paper money by the Civil War Era • Counterfeiting was widespread as a result Civil War and the Greenback • Bonds to raise money for war was insufficient • Congress prints paper money - $60 million – Not backed by silver or gold – Declared legal tender – fiat currency – Must be accepted as payment for debts – Greenback – green ink to distinguish from state notes GREENBACK #2 • Legal Tender Act (1862)– Union government prints $150 million United States Notes CONFEDERACY CURRENCY • To finance Civil War National Currency Established • Lost confidence in Greenbacks • Congress created the National Banking System (NBS) – National Banks chartered by Congress • Required to purchase government bonds –Issued National Bank notes or national currency backed by U.S. Government Bonds –Uniform Appearance • State Banks join or pay 10% tax on their notes • Rigorous bank inspections NATIONAL BANK NOTES • National Currency • Eventually squeezed out all privately issued (state) bank notes from circulation. 1863 Gold Certificates • Backed by Gold – In Large denominations • Original Purpose – End of Day Balancing Transactions between Banks • In 1882 smaller denominations printed for public use SILVER CERTIFICATES • Introduced in 1886 • Backed by Silver Dollars and Bullion (Too Bulky) – Placed on reserve with the U.S. Treasury • Increased demand and price for silver Treasury Coin Notes • • • • Redeemable in both gold and silver Issued in 1890 Last paper currency until 1913 Law Repealed in 1893 The GOLD STANDARD • 1900 Gold Standard Act • Made possible by huge discovery of gold – South Africa and Klondike region of Canada • $20.67 an ounce • All current notes could be redeemed for gold at the U.S. Treasury The Gold Standard Advantages • Security • Gave the impression that paper currency was limited to the amount of gold on deposit with the Treasury Disadvantages • Increase in stock of gold was insufficient to meet growing economy • More paper currency was printed than gold to back it up • Price of gold did not stay fixed at $20.67 an ounce The Great Depression (1930) • People cash in dollars for gold • Gold felt safer • 1934 – U.S. confiscated gold from private citizens and went off the Gold Standard Inconvertible Fiat Money Standard • 1934 – New Monetary Standard • Government controls quantity, composition and quality of money supply • National Currency and Treasury Coin Notes withdrawn from circulation in 1934 • Federal Reserve Notes issued Characteristics of Modern Money • Portable – lightweight and transferrable -Cybercurrency, smart cards, electronic money • Transfer velocity/instantaneous transfer/low cost/reduced fees • Durable – Metal currency lasts 20 years/$1 bill lasts 18 mos. • Divisible – pennies, checks, cybermoney, etc. • Limited Availability - perception • Stable Value - questionnable THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM • • • • First Central Bank Issued Federal Reserve Notes Privately owned by banks who bought shares Publicly controlled – President appoints Board of Governors and Chair FDIC • Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation • Created by Glass-Steagall Act/The Banking Act of 1933 • Insure customer’s deposit in case of bank failure • Provide sense of security • Reduced runs on the banks