* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Torque - Site Prof. Bertolo
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Mitsubishi AWC wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Torque wrench wikipedia , lookup
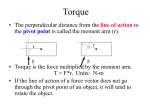
Chapter 8 Torques and Moments of Force: Maintaining Equilibrium or Changing Angular Motion To this juncture Analysis focused on linear motion (translation) – kinematics: position, change of position, rate of change of position, acceleration – kinetics: Newton’s 3 laws of linear motion » F = ma » Ft = mv What about rotation? All points on a body or object move in circles (or parts of circles) about the same fixed central line or axis – body spin around an axis (real or imaginary) Force ==> linear motion ????? ==> angular motion What about rotation? All points on a body or object move in circles (or parts of circles) about the same fixed central line or axis – body spin around an axis (real or imaginary) Force ==> linear motion Torque ==> angular motion – moment of force – moment Characteristics of a Force Characteristics of a Force Magnitude Characteristics of a Force Magnitude Direction Characteristics of a Force Magnitude Direction Point of Application Line of Action Line of action relative to axis of rotation Centric force – line of action passes through the axis of rotation – tends to cause translation Line of action relative to axis of rotation Centric force Eccentric force – line of action does not pass through the axis of rotation – tends to cause translation and rotation Line of action relative to axis of rotation Centric force Eccentric force Force couple – two eccentric forces – tends to cause rotation Torque http://www.tri-c.cc.oh.us/metro/faculty/gram/web/torque.htm Definition – the turning effect of a force – the tendency of a force to cause rotation What factors affect the tendency of the force to cause rotation??? Torque http://www.tri-c.cc.oh.us/metro/faculty/gram/web/torque.htm Definition – the turning effect of a force – the tendency of a force to cause rotation What factors affect the tendency of the force to cause rotation??? Why my pinky can whip your football team. Torque Definition – the turning effect of a force – the tendency of a force to cause rotation T=Fxr T = torque F = force (magnitude & direction) r = moment arm (MA) Moment Arm (lever arm) Perpendicular distance from line of action of a force to a specified axis of rotation (fulcrum, pivot point) Moment Arm (lever arm) Perpendicular distance from line of action of a force to a specified axis of rotation Moment Arm (lever arm) Perpendicular distance from line of action of a force to a specified axis of rotation Axis Moment Arm (lever arm) Perpendicular distance from line of action of a force to a specified axis of rotation Moment Arm (r) Characteristics of a Force Note how changing the line of action of a force may change the sense of the torque Moment Arm (r) Effect of changing the line of action of force To describe a torque Specified axis of rotation Torque magnitude (F x r) – units: Newtons x meters (Nm) – foot x pound (ft-lb) Direction (sense) of the torque – clockwise (-) – counterclockwise (+) Examples of Torque Examples of Torque Show the moment arm and identify the sense for each force on each figure Examples of Torque Calculate torque created in each figure Sculling: offsetting torques to create translation Are all three designs equal in net torque created at the stern?? ADLs must consider torque for safety and convenience Medicine caps must be removable by the disadvantaged, but inoperable by kids. Click on the picture to go to a website with more information. Muscle Names Muscle Torque Muscle applies force by ????? Muscle Torque Muscle applies force by pulling Muscle Torque Muscle applies force by pulling Muscle crosses a joint or joints – brachialis and biceps brachii – soleus and gastrocnemius – other examples???? Muscle Torque Muscle applies force by pulling Muscle crosses a joint or joints Muscle has a moment arm – eg palpate the biceps brachii and flex elbow » next three slides Elbow at 90o of flexion Elbow at 135o of flexion Elbow at 45o of flexion Question posed in a Physical Therapist Assistant Class Is it still a moment arm if the muscle inserts on the leg? Reported by Kris Green, BS ‘99 Muscle Torque Muscle applies force by pulling Muscle crosses a joint or joints Muscle has a moment arm Muscle creates torque at the joint – muscle is a torque generator »Bob Norman (1975) Game Day Draw the Resistance Torque Strength training and torque Biceps Curl Muscle as torque generator – moment arm changes through ROM – muscle’s ability to create force changes through ROM External forces as torque generators – segment weight – handheld weight (dumbbell) » moment arms change through ROM Strength training and torque Strength Training Machines So our answer is: Why could I control the two big guys with only my pinky? Because, …. Calculate Extensor Muscle Force Forces: P (hand held load) = 90 N W (HAT weight) = 80 N Moment Arms Lw = 25 cm Lp = 60 cm Lm = 5 cm Moment arm at the knee joint Go Click for knee website to and read the Web site to see how the moment arm at the knee is affected by knee joint angle. Ankle moment and standing Go Interesting Web Site on Balance to and read the Web site to see how the moment arm of the ground reaction force acts at the ankle joint. Forces and Torques in Equilibrium Static Equilibrium –sum of forces on the body = 0 » F = 0 –sum of torques on the body = 0 » T = 0 Demonstration of Net Torque Balancing Pennies Solving for Net Torque Mathematically Wt = -p (weight of a penny) r = distance (inches) from axis What is force on ruler from fulcrum??? Solving for Net Torque Mathematically Wt = -p (weight of a penny) r = distance (inches) from axis What is force on ruler from fulcrum??? T = 0 (static equilibrium)