* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arch Nerve Muscles Skeleton
Survey
Document related concepts
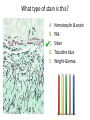
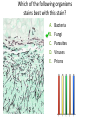
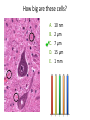
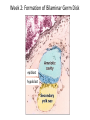
Transcript
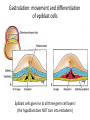
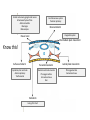
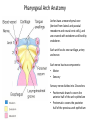
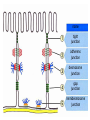
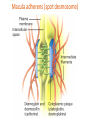
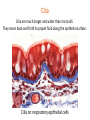
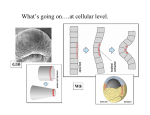
Clicker questions • Intro to histology • Embryology • Epithelium These are the slides we went through at the beginning of class on Tuesday, August 11. What type of stain is this? A. B. C. D. E. Hematoxylin & eosin PAS Silver Toluidine blue Wright-Giemsa Which of the following organisms stains best with this stain? A. B. C. D. E. Bacteria Fungi Parasites Viruses Prions How big are these cells? A. B. C. D. E. 10 nm 2 µm 7 µm 15 µm 1 mm Which of the following forms during week two of embryonic development? A. B. C. D. E. Blastocyst Amniotic cavity Neural tube Mesoderm Pharyngeal arch system Embryology Lecture Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 • Formation of bilaminar disk • Formation of trilaminar disk (gastrulation) Embryonic period phase 2 • Formation of neural tube • Differentiation of mesoderm • Folding of embryo • Formation of pharyngeal arches Week 2: Formation of Bilaminar Germ Disk epiblast hypoblast Which of the following gives rise to endoderm? A. B. C. D. E. Hypoblast Mesoderm Neural crest Epiblast Notochord Gastrulation: movement and differentiation of epiblast cells Epiblast cells give rise to all three germ cell layers! (the hypoblast does NOT turn into endoderm) Which of the following is derived from mesoderm? A. B. C. D. E. Skeletal muscles Anterior pituitary Epidermis GI tract lining Central nervous system Cranial and sensory ganglia and nerves Ectomesenchyme of face Adrenal medulla Meninges Melanocytes Central nervous system Posterior pituitary Neuroectoderm Urogenital system Neural crest Intermediate plate mesoderm Know this! Surface ectoderm Paraxial mesoderm Epidermis, hair and nails Anterior pituitary Tooth enamel Skeleton and trunk muscles Pharyngeal arches Connective tissue Skin Endoderm Lining of GI tract Lateral plate mesoderm Pharyngeal arches Connective tissue Which nerve supplies the muscles derived from the second pharyngeal arch? A. B. C. D. E. II (optic) V (trigeminal) VII (facial) IX (glossopharyngeal) X (vagus) Pharyngeal Arch Anatomy Arches have a mesenchymal core (derived from lateral and paraxial mesoderm and neural crest cells), and are covered with ectoderm and lined by endoderm. Each arch has its own cartilage, artery and nerve. Each nerve has two components: • Motor • Sensory Sensory nerve divides into 2 branches: • Posttrematic branch: covers the anterior half of the arch epithelium • Pretrematic: covers the posterior half of the previous arch epithelium Know this! Arch Nerve Muscles Skeleton 1 V (trigeminal) Mastication* Mylohyoid, anterior digastric Tensors tympani and veli palatini Meckel’s cartilage (malleus, incus) 2 VII (facial) Facial expression** Posterior digastric Stylohyoid Stapedius Reichert’s cartilage: stapes, styloid, lesser hyoid 3 IX (glossopharyngeal) Stylopharyngeus Greater hyoid 4-6 X (vagus) Cricothyroid Levator veli palatini Constrictors of pharynx Larynx muscles Laryngeal cartilages * Temporal, masseter, and medial & lateral pterygoids ** Buccinator, auricularis, frontalis, platysma, orbicularis ori and oculi. Important! Meckel’s cartilage indicates where the mandible will develop – but it does not turn into the mandible! Which cell junction attaches epithelial cells to the basal lamina? A. B. C. D. E. Gap junction Hemidesmosome Macula adherens Zonula adherens Zonula occludens name tight junction adherens junction desmosome junction gap junction hemidesmosome junction Which substance is in these linear, intercellular structures? A. B. C. D. E. Desmoplakin Cytokeratin Catenin Plakoglobin Desmoglein Macula adherens (spot desmosome) Which of the following structures moves back and forth to help particles move along the epithelial surface? A. B. C. D. E. Microvilli Stereocilia Cilia Brush border Glycocalyx Cilia Cilia are much longer and wider than microvilli. They move back and forth to propel fluid along the epithelial surface. Cilia on respiratory epithelial cells Microvilli Microvilli + cell coat (or glyocalyx) = brush border or striated border Purpose of microvilli: increase surface area for absorption or secretion