* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Personality
Personalism wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
George Kelly (psychologist) wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Id, ego and super-ego wikipedia , lookup
Team composition wikipedia , lookup
Raymond Cattell wikipedia , lookup
Zero-acquaintance personality judgments wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
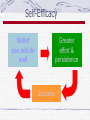
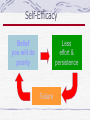
Personality Psychology 2012 – Fall 2003 Introduction: What is Personality? An individual’s unique and relatively consistent patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving Personality – an attempt to describe and explain how people are similar, how they are different, and why every individual is unique Tries to explain the whole person Introduction: What is Personality? Personality theories can be roughly grouped under four basic perspectives: The psychoanalytic perspective – emphasizes the importance of unconscious processes and the influence of early childhood experiences The humanistic perspective – represents an optimistic look at human nature, emphasizing the self and the fulfillment of a person’s unique potential The social cognitive perspective – emphasizing learning and conscious cognitive processes, including the importance of beliefs about the self, goal-setting, and self-regulation The trait perspective – emphasizes the description and measurement of specific personality differences among individuals The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Austrian neurologist Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, was one of the most influential figures of the twentieth century Psychoanalysis – the theory of personality that stresses the influence of: Unconscious mental processes Sexual and aggressive instincts, and The enduring effects of early childhood experience on personality Sigmund Freud Assumptions: Traits transcend situations Personality formed in childhood The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The life of Sigmund Freud Freud studied medicine, became a physician, and then proved himself an outstanding physiological researcher However, prospects for an academic career in scientific research were very poor, especially for a Jew in Vienna, which was intensely antiSemitic at that time The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Influences in the development of Freud’s ideas Joseph Breuer – a highly respected physician, who found that when patients were hypnotized and allowed to talk freely about a given symptom, forgotten memories of traumatic events would emerge After patients freely expressed the pent-up emotions associated with the events, symptoms would disappear A process Breuer call catharsis Freud dropped the use of hypnosis and developed his own technique of free association to help patients uncover forgotten memories Freud’s patients would spontaneously report their uncensored thoughts, mental images, and feelings as they came to mind The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Influences in the development of Freud’s ideas Breuer and Freud described several of their case studies in their landmark book Studies on Hysteria; published in 1895, it marked the beginning of psychoanalysis In 1900, Freud published what many consider his most important work, The Interpretation of Dreams Freud came to focus on humanity’s destructive tendencies; Freud wrote Civilization and Its Discontents, in which he applied his psychoanalytic perspective to civilization as a whole The central theme: human nature and civilization are in basic conflict – a conflict that cannot be resolved The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Freud’s Dynamic Theory of Personality Freud saw personality and behavior as resulting from a constant interplay between conflicting psychological forces that operate at three different levels of awareness 1. 2. 3. All the thoughts, feelings, and sensations that you are aware of at this particular moment represent the conscious level The preconscious contains information of which you’re not currently aware, but is easily capable of entering your consciousness, such as childhood memories or your social security number The bulk of Freud’s psychological iceberg is made up of the unconscious, which lies below the waterline of the preconscious and the conscious We are not directly aware of these submerged thought, feelings, wishes, and drives But the unconscious exerts an enormous influence on our conscious thoughts and behavior The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Freud’s Dynamic Theory of Personality Freud believed that unconscious material often seeps through to the conscious level in distorted disguised, or symbolic forms Dream analysis was particularly important to Freud Beneath the surface images (manifest content) of a dream lies the true, hidden, unconscious meaning of the dream symbols (latent content) The unconscious also can be revealed in unintentional actions, Such as accidents, mistakes, instances of forgetting and inadvertent slips of the tongue (often referred to as “Freudian Slips”) The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The structure of personality Psychological energy evolves to form the three basic structures of personality – the id, the ego, and the superego. These are distinct psychological processes. The id, the most primitive part of the personality, is entirely unconscious and present at birth – it is completely immune to logic, values, morality, danger, and the demands of the external world Two conflicting instinctual drives fuel the id: the life instinct and the death instinct 1. Eros – the life instinct; consists of biological urges that perpetuate the existence of the individual and the species (hunger, thirst, physical comfort, sexuality) 2. Thanatos – the death instinct; destructive energy that is reflected in aggressive, reckless, and life-threatening behaviors, including self-destructive actions The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The id is rules by the pleasure principle The relentless drive toward immediate satisfaction of the instinctual urges, especially sexual urges. The id strives to increase pleasure, reduce tension, and avoid pain The newborn infant is completely driven by the pleasure principle The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The structure of personality A new dimension of personality develops from part of the id’s psychological energy – the ego Partly conscious, the ego represents the organized, rational, and planning dimensions of personality The mediator between the id’s instinctual demands and the restrictions of the outer world, the ego operates on the reality principle The capacity to postpone gratification until the appropriate time or circumstances exist in the external world The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The ego is the pragmatic part of the personality that learns various compromises to reduce the tension of the id’s instinctual urges. If the ego cannot identify an acceptable compromise to satisfy an instinctual urge, it can repress the impulse Remove it from conscious awareness The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The structure of personality Gradually, social values move from being externally imposed demands to being internalized rules and values By age 5-6, young children develop an internal, parental voice that is partly conscious – the superego As the internal representation of parental and societal values, the superego evaluates the acceptability of behavior and thoughts, then praises or admonishes Freud’s Model The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The ego defense mechanisms: unconscious self-deceptions When the demands of the id or superego threaten to overwhelm the ego, anxiety results If a realistic solution or compromise is not possible, the ego may temporarily reduce anxiety by distorting thoughts or perceptions of reality through processes Freud called ego defense mechanisms By resorting to these largely unconscious self-deceptions, the ego can maintain an integrated sense of self While searching for a more acceptable and realistic solution to a conflict between the id and superego The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Ego defenses The most fundamental ego defense mechanism is repression – unconscious forgetting Unbeknownst to the person, anxiety-producing thoughts, feelings, or impulses are pushed out of conscious awareness into the unconscious Displacement – impulses are redirected to a substitute object or person Usually one less threatening or dangerous than the original source of conflict The use of defense mechanisms is very common Many psychologically healthy people temporarily use ego defense mechanisms to deal with stressful events When they delay or interfere with our use of more constructive coping strategies, they can be counterproductive Freudian Theory: Defense Defense Mechanisms Methods for dealing with anxiety Freud thought some more mature than others Denial Sublimation Projection Reaction Formation Denial Refusing to accept that the feeling is present or that the event occurred A very primitive mechanism Example: preschoolers will convince themselves they didn't do something they wish they hadn't Projection Attributing one's undesirable traits or actions to others, so they become the problem instead of you Example from a failing student: "I'm not worried about me, but I'd hate to see Ellen flunk--she's so fragile" Reaction Formation Taking actions opposite to one's feelings in order to deny the reality of the feelings Example: A woman says she can’t stand her boss, when in reality she is in love with him Sublimation The most mature mechanism Redirecting anxiety-causing impulses into socially acceptable actions Example: Dealing with anxiety over a final by engaging in vigorous physical activity The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Personality development: The psychosexual stages Freud believed that people progress through five psychosexual stages of development The foundations of the adult personality are established during the first six years of life, as the child progresses through the oral, anal, and phallic stages The latency stage occurs during later childhood and the fifth and final stage, the genital stage, begins in adolescence The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality In Freud’s theory, the psychosexual stages are age-related developmental periods in which sexual impulses are focused on different bodily zones And are expressed through activities associated with those areas Freudian Theory: Stages Psychosexual Stages (source of libido satisfaction) Oral (0-1 year) Anal (1-3 years) Phallic (3-6 years) Latency (6-puberty) Genital (from puberty) Freudian Theory: Stages Oral Stage: Libido gratification comes from oral exploration of the world Infant learns to trust in others, esp. for food Oral Personality: Problems in the oral stage supposedly lead to pessimism about the world, hostility or passivity Freudian Theory: Stages Anal Stage: Kids learn about delay of gratification Kids gain pleasure and libido satisfaction from being in control Anal Personality: Problems in the anal stage supposedly lead to either excessive orderliness or excessive messiness Freudian Theory: Stages Phallic Stage: Freud believed sex-role identification occurred Mechanisms included castration anxiety (boys) & penis envy (girls) Phallic Personality: Problems in the phallic stage supposedly lead to sex-role identification problems, promiscuity, vanity, or excessive chastity Freudian Theory: Stages Latency Stage: A time of focus on achievement and mastery of skills Libido is channeled into mastery activities Freud thought little of interest happened here Others have argued the sense of self-esteem is established here Freudian Theory: Stages Genital Stage: The time of mature personality, intimacy with others Libido satisfied by adult-type sexual activity The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Fixation – unresolved developmental conflicts At each psychosexual stage, according to Freud, the infant or young child is faced with a developmental conflict that must be successfully resolved in order to move on to the next stage If frustrated, the child will be left with feelings of unmet needs characteristic of that stage; If overindulged, the child may be reluctant to move on to the next stage In either case, the result of an unresolved developmental conflict is fixation at a particular stage The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The Oedipus complex: A psychosexual drama The most critical conflict occurs during the phallic stage Freud believed that the child develops a sexual attraction to the opposite-sex parent and hostility toward the same-sex parent Freud called this the Oedipus complex – named after the hero of a Greek myth The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The Oedipus complex: A psychosexual drama The little boy feels hostility and jealously toward his father, but he realizes that his father is more physically powerful The boy experiences castration anxiety To resolve the Oedipus complex, the little boy ultimately joins forces with his former enemy resorting to the defense mechanism of identification He imitates and internalizes his father’s values, attitudes, and mannerisms The little girl discovers that little boys have a penis and that she does not She feels a sense of deprivation and loss that Freud termed penis envy The little girl blames her mother and develops contempt for her However, in her attempt to take her mother’s place with her father, she also identifies with her mother The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality The Neo-Freudians: Freud’s descendents and dissenters In general, the neo-Freudians disagreed with Freud on three key points Freud’s belief that behavior was primarily motivated by sexual urges Freud’s contention that personality is fundamentally determined by early childhood experiences Freud’s generally pessimistic view of human nature and society The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Carl Jung: Archetypes and the collective unconscious Swiss psychiatrist Carl G. Jung broke with Freud to develop his own psychoanalytic theory of personality He believed that people are motivated by a more general psychological energy that pushes them to achieve psychological growth, self-realization, and psychic wholeness and harmony He also believed that personality continues to develop in significant ways throughout the lifespan The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Carl Jung, continued Jung believed that the deepest part of the individual psyche is the collective unconscious Shared by all people and reflects humanity’s collective evolutionary history Contained in the collective unconscious are the archetypes The mental images of universal human instincts, themes and preoccupations Jung was the first to describe two basic personality types: Introverts – who focus their attention inward Extroverts – who turn their attention and energy toward the outside world Karen Horney Stressed need for safety & satisfaction Childhood frustration may lead to development of basic anxiety & neurosis Tyranny of the Should: Horney's term for focusing on an unrealistic, perfect self-image that leads to dissatisfaction The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Karen Horney: basic anxiety and “womb envy” German-born American psychoanalyst Karen Horney came to stress the importance of cultural and social factors in personality development, matters that Freud had largely ignored She also stressed the importance of social relationships, especially the parent-child relationship, and culture in personality Horney believed that disturbances in human relationships, not sexual conflicts, were the cause of psychological problems Such problems arise from the attempt to deal with basic anxiety The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Horney described three patterns of behavior that individuals use to defend against basic anxiety Those who move toward other people have an excessive need for approval and affection Those who move against others have an excessive need for power Those who move away from other people have an excessive need for independence and self-sufficiency Horney contended that people with a healthy personality are flexible in balancing these different needs The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Horney also sharply disagreed with Freud’s interpretation of female development, especially the notion that women suffer from penis envy She believed that what women envy in men is not their penis, but their superior status in society She contended that men often suffer from womb envy Envying women’s capacity to bear children She argued that men compensated for their minor role in reproduction by creating artifacts and other external accomplishments through their work Alfred Adler Humans motivated by the need to overcome inferiority and strive for significance Inferiority Complex: Adler's term for feelings of inferiority that interfere with development The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Alfred Adler: Feelings of inferiority and striving for superiority Austrian physician Adler broke away from Freud to establish his own theory of personality Adler believed that the most fundamental human motive was striving for superiority The desire to improve oneself, master challenges, and move toward self-perfection and self-realization This striving arises from universal feelings of inferiority These feelings motivate people to compensate for their real or imagined weaknesses The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Alfred Adler, continued When people are unable to compensate for specific weaknesses or when their feelings of inferiority are excessive they can develop an inferiority complex A sense of inadequacy, weakness, and helplessness At the other extreme, people can overcompensate for their feelings of inferiority and develop a superiority complex The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Evaluating Freud and the psychoanalytic perspective on personality Although Freudian theory has had a profound impact on Western culture and on psychology, it has been criticized on three major counts 1. 2. 3. Inadequacy of evidence Lack of testability Sexism The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Inadequacy of evidence 1. 2. Freud’s theory relies wholly on data derived from his relatively small number of patients and from self-analysis It seems impossible to objectively assess Freud’s “data” The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Lack of testability Many psychoanalytic concepts are so vague and ambiguous that they are impossible to measure or confirm objectively Yet they are often impossible to disprove, because even seemingly contradictory information can be used to support Freud’s theory Psychoanalysis is better at explaining past behavior than at predicting future behavior Nonetheless, several key psychoanalytic ideas have been substantiated by empirical research. Among them: 1. 2. 3. Much of mental life is unconscious Early childhood experiences have a critical influence on interpersonal relationships and psychological adjustment in adulthood People differ significantly in the degree to which they are able to regulate their impulses, emotions, and thoughts toward adaptive and socially acceptable ends The Psychoanalytic Perspective on Personality Sexism Horney and other female psychoanalysts have pointed out that Freud’s theory uses male psychology as a prototype However, to Freud’s credit, women were quite active in the early psychoanalytic movement The Humanistic Perspective on Personality Emergence of the “Third Force” In opposition to both psychoanalysis and behaviorism, humanistic psychology was a “third force” in psychology This view of personality emphasizes human potential and such uniquely human characteristics as self-awareness and free will It sees people as being innately good and focuses on the healthy personality The Humanistic Perspective on Personality Humanistic psychologists contended that the most important factor in personality is the individual’s conscious, subjective perception of his or her self Abraham Maslow was one of the founders of humanistic psychology: key ideas included the hierarch of needs and self-actualization The Humanistic Perspective on Personality Carl Rogers: On becoming a person Was one of the founders of humanistic psychology, developed his personality theory from his clinical experiences with his patients, Whom he referred to as “clients” to emphasize their active and voluntary participation in therapy According to Rogers, the most basic human motive is the actualizing tendency The innate drive to maintain and enhance the human organism The Humanistic Perspective on Personality The cornerstone of Roger’s personality theory is the idea of the self-concept The set of perceptions and beliefs that you hold about yourself As children develop a greater sense of selfawareness, there is an increasing need for positive regard The sense of being valued and loved by other people The Humanistic Perspective on Personality Rogers maintained that most parents provide their children with conditional positive regard The sense that the child is valued and loved only when the child behaves in a way that is acceptable to others Incongruence – a state in which a child’s self-concept conflicts with his or her actual experience Unconditional positive regard – the child’s sense of being unconditionally loved and valued, Even if she doesn’t conform to the standards and expectations of others Rogers did not advocate permissive parenting He maintained that parents can disapprove of a child’s specific behavior without completely rejecting the child herself The Humanistic Perspective on Personality Through consistent experiences of unconditional positive regard, one becomes a fully functioning person A person who has a flexible, constantly evolving self-concept Rather than defending against or distorting her own thoughts or feelings, the person experiences congruence Her sense of self is consistent with her emotions and experiences The Humanistic Perspective on Personality Evaluating the Humanistic Perspective on Personality The humanistic perspective has been criticized on two counts 1. Humanistic theories are hard to validate or test scientifically Because they tend to be based on philosophical assumptions or clinical observations, rather than on empirical research 2. Many psychologists believe that humanistic psychology’s view of human nature is too optimistic Although the influence of humanistic psychology has waned since the 60’s and early 70’s, it has made lasting contributions to psychotherapy, counseling, education, and parenting The Social Cognitive Perspective on Personality The idea that a person’s conscious thought processes in different situations strongly influence his or her actions is one important characteristic of the social cognitive perspective on personality This perspective differs from the psychoanalytic and humanistic perspectives in several ways: It relies heavily on experimental findings It emphasizes conscious, self-regulated behavior It emphasizes that our sense of self can vary The Social Cognitive Perspective on Personality Albert Bandura & social cognitive theory Several contemporary personality theorists have embraced the social cognitive approach to explaining personality; Albert Bandura is well-known for observational learning and self-efficacy Both of these topics are central to social cognitive theory Emphasizes the social origins of thoughts and actions and also stresses active cognitive processes and the capacity for self-regulation The Social Cognitive Perspective on Personality Bandura’s research has shown that we observe: The consequences that follow people’s actions The rules and standards that apply to behavior in specific situations, and The ways in which people regulate their own behavior Reciprocal determinism – a model that explains human functioning and personality as caused by the interaction of behavioral, cognitive, and environmental factors The Social Cognitive Perspective on Personality Beliefs of self-efficacy Collectively, a person’s cognitive skills, abilities, and attitudes represent the person’s self-system The most critical elements influencing the selfsystem are our beliefs in self-efficacy The degree to which we are subjectively convinced of our own capabilities and effectiveness in meeting the demands of a particular situation Developing self-efficacy begins in childhood, but it continues as a lifelong process, with each stage of the lifespan presenting new challenges Self-Efficacy Belief you will do well Greater effort & persistence Success Self-Efficacy Belief you will do poorly Less effort & persistence Failure The Social Cognitive Perspective on Personality Evaluating the social cognitive perspective on personality A key strength of the social cognitive perspective on personality is its grounding in empirical, laboratory research It is built on research in learning, cognitive psychology, and social psychology Rather than on clinical impressions Some psychologists feel the approach applies best to laboratory research The social cognitive perspective has been criticized for its limited view of personality Clinical data, rather than laboratory data, may be more reflective of human personality It ignores unconscious influences, emotions, or conflicts The Social Cognitive Perspective on Personality Evaluating the social cognitive perspective on personality By emphasizing the self-regulation of behavior, the social cognitive perspective places most of the responsibility for our behavior on ourselves And for the consequences we experience due to our behavior The Trait Perspective on Personality In contrast to the psychoanalytic, humanistic, and social cognitive theories, which emphasize the similarities among people, the trait approach to personality focuses primarily on describing individual differences Trait theorists view the person as a unique combination of personality characteristics or attributes, called traits A relatively stable, enduring predisposition to behave in a certain way Trait theory is a theory of personality that focuses on identifying, describing, and measuring individual differences The Trait Perspective on Personality Surface traits and source traits Surface traits – traits that lie on the surface and can be easily inferred from observable behavior Source traits – thought to be the most basic dimension of personality; A source trait can potentially give rise to a vast number of surface traits There are relatively few source traits, and these few represent a universal way of describing individual personality differences The Trait Perspective on Personality Two Trait Theories: Cattell and Eysenck Cattell used a statistical technique called factor analysis to identify traits that were most closely related to one another Eventually reducing his list to 16 key personality factors He developed the widely used self-report personality test, the Sixteen Personality Factor Questionnaire (16 PF) The Trait Perspective on Personality Two Trait Theories: Cattell and Eysenck British psychologist Eysenck developed a trait theory of personality that identifies three basic dimensions of personality The first dimension in introversion-extroversion, which is the degree to which a person directs his or her energies outward toward the environment and other people versus inward toward his or her inner and self-focused experiences Introversion – quiet, solitary, reserved; avoiding new experiences Extroversion – outgoing and sociable, enjoying new experiences and stimulating environments The Trait Perspective on Personality Eysenck’s trait theory of personality: three basic dimensions of personality The second major dimension is neuroticism-emotional stability Neuroticism – a person’s predisposition to become emotionally upset Stability – a person’s predisposition to be emotionally even The Trait Perspective on Personality Eysenck’s trait theory of personality: three basic dimensions of personality The third major personality dimension, which Eysenck identified in later research, is called psychoticism A person high in this trait is antisocial, cold, hostile, and unconcerned about others A person low in this trait is warm and caring about others The Trait Perspective on Personality The five-factor model The consensus among many trait researchers is that the essential building blocks of personality can be described in terms of five basic personality dimensions, sometimes called the “Big Five” The five-factor model of personality represents the structural organization of personality traits The most commonly accepted five factors are: extraversion, neuroticism, agreeableness, conscientiousness, and openness to experience The 5 Factor Theory Extraversion Outgoing Withdrawn Neuroticism Stable Unstable The 5 Factor Theory Agreeableness Low High Conscientiousness Undependable Dependable The 5 Factor Theory Openness to Experience Closed Open The Trait Perspective on Personality The five-factor model, continued Research has shown that traits are remarkably stable across time Traits are also generally consistent across different situations However, situational influences may affect the expression of personality traits However, remember that human behavior is the result of a complex interaction between traits and situations The Trait Perspective on Personality Personality traits and genetics Behavioral genetics – studies the effects of genes and heredity on behavior Using twins-reared-apart and adoption studies, behavioral geneticists have found that certain personality traits are substantially influenced by genetics Especially extraversion and neuroticism Openness to experience and conscientiousness are also substantially influenced by genetics, although to a lesser degree than extraversion and neuroticism It seems that the influence of environmental factors is at least equal to the influence of genetic factors The Trait Perspective on Personality Evaluating the trait perspective on personality Psychologists generally agree that people can be described and compared in terms of basic personality traits Like the other personality theories, the trait approach has its weaknesses. Trait theories fail to: 1. 2. 3. Truly explain human personality Explain how or why individual differences developed Address other important personality issues, like: The basic motives that drive human personality The role of unconscious mental processes How beliefs about the self influence personality, or How psychological change and growth occur Assessing Personality: Psychological Tests Psychological test – a test that assesses a person’s abilities, aptitudes, interests, or personality, Based on a systematically obtained sample of behavior A psychological test is useful insofar as it achieves two basic goals: 1. It accurately and consistently reflects a person’s characteristics on some dimension, and 2. It predicts a person’s future psychological functioning or behavior Two basic types of personality tests are projective tests and self-report inventories Assessing Personality: Psychological Tests Projective Tests A type of personality test that involves a person’s interpreting an ambiguous image Used to assess unconscious motives, conflicts, psychological defenses, and personality traits The Rorschach Inkblot Test – a projective test using inkblots, developed by Swiss psychiatrist Hermann Rorschach in 1921 The Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) – a projective personality test that involves creating stories about each of a series of ambiguous scenes The Rorschach Subject tells what each blot looks like and what aspect of the blot triggered that response The Rorschach Responses scored on use of parts vs. wholes, movement, content, use of color Criticized for lack of reliability, low validity (inability to predict behavior) The TAT Consists of 19 vague or ambiguous drawings Person describes what is happening in each The TAT A TAT-like picture: Criticized for low reliability & for reflecting temporary states rather than long-term traits Assessing Personality: Psychological Tests Strengths and weaknesses of projective tests The primary strength of projective tests is that they provide a wealth of qualitative information about an individual’s psychological functioning Projective tests have several drawbacks: The testing situation or the examiner’s behavior can influence a person’s responses The scoring of projective tests is highly subjective, requiring the examiner to make numerous judgments about the person’s responses Projective tests often fail to produce consistent results Projective tests are poor at predicting future behavior Despite their widespread use, hundreds of studies of projective tests seriously question their validity and reliability Assessing Personality: Psychological Tests Self-report inventories A type of psychological test in which a person’s responses to standardized questions are compared to established norms The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) – a self-report inventory that assesses personality characteristics and psychological disorders; Used to assess both normal and disturbed populations The California Personality Inventory (CPI) – a self-report inventory that assesses personality characteristics in “normal” populations The Sixteen Personality Factor Questionnaire (16 PF) – a selfreport inventory developed by Raymond Cattell that generates a personality profile with ratings on 16 trait dimensions The MMPI-2 The most widely-used inventory Consists of 567 true-false questions MMPI-2: Clinical Scales Hypochondriasis(Hs): Exaggerated concern about physical health Depression (D): Distress, depression Hysteria (Hy): Physical symptoms w/ no cause Psychopathic Deviate (Pd): Disregard for moral & social standards Masculinity-Femininity (Mf): Having traditional male or female traits MMPI-2: Clinical Scales Paranoia (Pa): Fear of others & suspiciousness Psychasthenia (Pt): Rigidity, tension, worry Schizophrenia (Sc): bizarre & unusual thinking Hypomania (Ma): Excitability, impulsiveness Social Introversion (S): Modesty, Shyness MMPI-2: Validity Scales Cannot Say (?): Evasiveness Lying (L): Lying in order to look good Infrequency (F): Lying in order to look bad Correction (K): Defensiveness in filling out the scale Assessing Personality: Psychological Tests Strengths & Weaknesses of self-report inventories The strengths include: Standardization and the use of established norms Reliability and validity, which, as a general rule, are greater than those of projective tests The weaknesses include: Considerable evidence that despite inclusion of items designed to detect deliberate deception, People can still successfully fake responses and answer in socially desirable ways Some people are prone to responding in a set way, whether the item accurately reflects them or not People are not always accurate judges of their own behavior, attitudes, or attributes Assessing Personality: Psychological Tests Despite their weaknesses, personality tests are generally useful strategies that can provide insights about the psychological makeup of people