* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
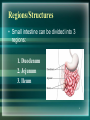
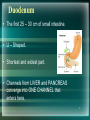
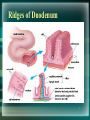
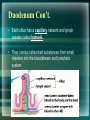
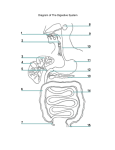
Digestion Chapter 8 Section 8.4 - 1 1 Small Intestine • Small Diameter – 2.5cm • 4X longer than Large Intestine • Physical Digestion = Segmentation • Segments = bands of circular muscle that briefly contract, chopping food into segments. • Peristalsis helps food move along. 2 Main Function of Small Intestine • Fully digest macromolecules and absorb its subunits for use in the body. • Macromolecules are digested by hydrolysis (adding water). 3 Regions/Structures • Small intestine can be divided into 3 regions: 1. Duodenum 2. Jejunum 3. Ileum 4 Duodenum • The first 25 – 30 cm of small intestine. • U – Shaped. • Shortest and widest part. • Channels from LIVER and PANCREAS converge into ONE CHANNEL that enters here. 5 Duodenum Con’t • Its Function: To increase surface area for digestion. • To increase surface area it has many hills and ridges. • ON TOP OF RIDGES are VILLI (s. villus) – Finger-like projections that extend into small intestine to further increase surface area. • MICROVILLI on top of villi – Microscopic villi (looks fuzzy) that also help to increase surface area. Ridges of Duodenum 7 Duodenum Con’t. • Each villus has a capillary network and lymph vessels called lacteals. • They conduct absorbed substances from small intestine into the bloodstream and lymphatic system. 8 Jejunum • 2.5m long • More folds and secretory glands than duodenum. • Continues to break down food. 9 Ileum • 3m long • Contains fewer and smaller villi. • Absorbs nutrients. • Pushes undigested food into large intestine. 10 Accessory Organs • There are 3 accessory organs to the small intestine: PANCREAS, LIVER and GALL BLADDER. • Their purpose is to secrete (produce) substances that aid in the digestion of food. 11 Pancreas • Secretes ~1L of fluid to duodenum everyday. • Pancreatic fluid contains many enzymes: – Proteases – Carbohydrases – Lipase 12 Pancreatic Enzymes • Proteases – – – – Digests proteins 2 proteases: Trypsin and Erepsin Trypsin is activated by the enzyme Enterokinase Enterokinase changes Trypsinogen Trypsin • Carbohydrases – Digests carbohydrates – 1 carbohydrase: Pancreatic Amylase • Lipase – Digests lipids or fat 13 Pancreatic Enzymes • They are secreted in their inactive form. • They are activated by other enzymes secreted by the duodenal lining. • Pancreas also secretes a bicarbonate (HCO3-) – Neutralizes the HCl and chyme from the stomach that enters the small intestine. 14 Liver • Largest organ in body. • Main secretion: BILE – Bile is the liver’s waste product that will be excreted in feces eventually. – It assists lipases in small intestine by breaking down fats. 15 How does bile help lipase? • Bile disperses large fat droplets into smaller droplets. • This creates a greater surface area for lipase to act on. 16 Gall Bladder • Stores bile sent from liver in between meals. • Fat-containing chyme (thick liquid from stomach) in duodenum stimulates gall bladder to CONTRACT. • This causes bile to be injected into the duodenum. 17