* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final EXAM NOTES Ancient Greece • Effects of Physical Geography
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
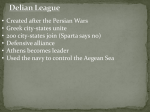
Final EXAM NOTES Ancient Greece • Effects of Physical Geography • Located on the Balkan Peninsula...it is surrounded by several seas • No rivers • Greece traded with other regions • Mountains cover 70-80% • Became skilled sailors and shipbuilders • Used seas as transportation corridors • Brought in important goods (grain, timber, animal hides & slaves) • Made transportation difficult AND it was hard to unite Greece under a single government!!! • Greek City-States • Due to phys. features, Greece was divided into small regions – Because of this, the basic form of government was the City-State City-State • Made up of city & surrounding area • Small b/c physical features limited their size • Fewer than 20,000 residents….close community • A city with its own laws, rulers and money • Cities that acted like countries • Athens & Sparta were the largest Greek city-states! • Greek City State • Athens vs. Sparta Let’s compare! Athens • Philosophical society • Government—direct democracy – Athens became the world’s first democracy around 508 B.C – All “citizens” met to vote & had a direct say in things (citizens served in the army when needed and they were also required to serve on juries) – Only free men were “citizens” – Council of Four Hundred took care of day-to-day problems – Assembly voted on policies proposed by council • Athens vs. Sparta Let’s compare! Athens • 4 social groups/classes based on income • Foreigners, women, children and slaves were not “citizens” • Slaves – 1/3 of population – Worked in homes, agriculture, industry, mines, and even alongside masters – Some earned wages & were able to buy their freedom • Athens vs. Sparta Let’s compare! Athens • Education – Boys of wealthy families started school at age 6 or 7 – Prepared them to be good citizens – Studied logic & public speaking (for preparation to be part of the assembly) – Also studied reading, writing, poetry, arithmetic & music • Athens vs. Sparta Let’s compare! Athens • Women – Expected to be good wives & mothers – Expected to keep family * society strong – Much less freedom than Spartan women – Did not attend school – Could only own land if she inherited it from her father (that is if he didn’t have a son to pass it on to) – Few learned to read or write • Athens • Athens vs. Sparta Let’s compare! Sparta • • • Sparta • • Sparta • • War/Military Society Government—combination of monarchy, democracy, oligarchy – 2 kings ruled Sparta – 5 elected citizens ran the gov’t – Council of Elders (30 older citizens & wealthy land owners) proposed laws – All citizens were part of the Assembly—they elected officials & voted on laws proposed by the council Athens vs. Sparta Let’s compare! 3 social groups – Citizens—lived in the city & spent ALL their time training – Free Non-Citizens—lived in nearby villages – Helots—slaves who worked land and provided for the citizens, thus allowing Spartan citizens to be full-time soldiers Athens vs. Sparta Let’s compare! Education – Goal=have a strong army! – At age 7 boys were taken to military houses to start training to be Spartan soldiers – Education included discipline, duty, strength, military skill and wittiness/quick thinking Athens vs. Sparta Let’s compare! Sparta • Women – Expected to be tough both emotionally & physically • “Bring back your shield, or come back on it” – Education focused on making them strong • Athletic training • Learned to defend themselves – Had a lot of freedom since the emphasis of the society was on the military, NOT on the family – Husbands spent a lot of time away – Were able to own property • Persians Invade Greece • 480 B.C Persia invaded Greece • City-states united to fight off the Persians and their massive military • Battle of Thermopylae: The Spartan army held off the Persian army of 250,000 for three days with only 300 soldiers. – This gave Athenians time to prepare for battle themselves • City-states of Greece eventually defeated invasion • NO WARM UP: TAKE OUT GREEK PKT • After Persian Wars • Greek city-states formed the Delian League for the mutual protection of all – Most city-states contributed money to fund the League • Athens began to dip into the fund to build up its navy and to beautify its city • Pericles—Athenian general & statesman largely responsible for the full development of Athenian democracy and the Athenian empire – He emerged after the Persian Wars and by 460 B.C., he was the strongest leader in Athens Peloponnesian War 27 year-long war between Athens and Sparta Causes: • • • • • Some city-states feared Athens b/c of its grab for power & prestige Under Pericles, Athens grew from a city-state to a naval empire Some Athenian settlers began to move into lands of other city-states Athens used money pooled together in the Delian League for its own devices! Peloponnesian War Sparta Had better land-based military force & its location couldn’t be attacked by sea • Cut off the Athenian food supply by destroying crops • Took control of countryside around Athens Athens Had better navy & could strike Sparta’s allies by sea. • Avoid battles on land • Rely on sea power • • • • Pericles persuaded Athenians to allow Spartans to destroy countryside He brought people from the areas surrounding Athens inside city walls for safety Peloponnesian War Pericles’ plan to bring people into Athens backfired! – The city became badly overcrowded and a plague spread quickly and easily causing Athens to loose 1/3 of its people and armed forces…even Pericles himself died from the plague! • Athens finally surrendered to Sparta in 404 B.C. • Since it lasted over 27 years, cities & crops were destroyed and thousands of Greeks died • All Greek city-states suffered losses of economic and military power • City-states were weakened, allowing King Phillip II of Macedonia to take power of all Greek city-states King Phillip II • • • His dictatorial rule ended Greek democratic practices After conquering the weak and disorganized Greek city-states, he prepared his army to attack Persia 336 B.C.—Phillip was assassinated at his daughter’s wedding – Left his 20 year-old son, Alexander, in charge Alexander the Great nd 1. 2. 3. 4. • Son of Philip the 2 and was educated by the Greek Philosopher Aristotle. Alexander continued his father’s plan for creating an empire and attacking Persia From there, he spent the next 12 years he spent creating an empire from Greece all the way to the Himalayas. (One of the largest empires in history.) During this time he was able to defeat and conquer the Persians Alexander the Great 5. He introduced Greek Culture to all the areas he conquered. Wanted people to act Greek. 6. Alexander died of Malaria at the age of 32 in 323 B.C. 7. His empire would be divided 3 kingdoms each by one of his generals, and would be independent until they were conquered by the Romans. • Alexander the Great • Important People Socrates • The first great Greek philosopher • A philosopher is someone who tries to explain the nature of life. • Socrates taught by asking questions. This method of questioning is still called the Socratic method. • Socrates • Important People ROMULUS N REMUS According to legend baby twins Romulus and Remus were cast into the wilderness to die They were found by a wolf who took care of them (made them wild) In 753 BC, they would lead a group of people to Rome Fought over who should be king Romulus killed Remus Julius Caesar Most famous Roman. (100-44B.C.) Extremely ambitious Only through victory on the battle field can someone be considered leader Julius Caesar Great General, waged war against Gaul in (58-51 B.C.) Had 1 million Gaul’s killed Became Governor of Gaul Julius Caesar 49 B.C. -Was ordered by the senate back to Rome, told not to bring army Worried he would be killed by Senators (Pompey) Would rely on loyalty of his troops Julius Caesar Crossed the Rubicon with his army, Point of no Return. Engaged in a Civil War Became victorious and would become dictator of Rome Julius Caesar As a dictator he devoted himself to the poor of Rome. This made his popular. 1) Gave food to the poor 2) Land for the soldiers 3) Changed the calendar 4) Outlawed Extortion 5) Created a newspaper that discussed the events of the government 6) Asked the people to make him dictator for life Julius Caesar th People of the Senate didn’t like this so on March 15 44 B.C. he was assassinated by the senate (Stabbed 35 times) AUGUSTUS Octavian changes his name to Augustus. (The Revered One) st Octavian becomes the 1 emperor of Rome. Augustus Caesar’s Accomplishments Reorganized the Roman Empire (1 man leads!!) Ruled with restraint Gave more grain to Rome’s poor. Build more aqueducts (increased water supply) Created a fire and police service in Rome 27 B.C. was given constitutional power for life. Ushered in a period in time called the Pax Romana PAX ROMANA Roman Peace. Lasted from 27 B.C. to 180 AD. (Height of the Roman Empire) Augustus Roman Coliseum Originally the Flavian Amphitheatre is an arena in the center of the city of Rome. Admittance was free (Romans loved going to the coliseum) Showed gladiatorial combat (Fight to the death) Executions, criminals eaten by wild animals. Reenactments of famous battles. At one point there were 170 days of games MIDDLE AGES/RENAISSANCE Chivalry: An attitude of honor, generosity, and courtesy. Crusades: Journey of 100,000 European Knights to take control of Jerusalem (Holy Land). Feudalism: A system of government in which a lord or noble man owned the land and protected the people who worked on it. Jousting: A tournament where knights pretended to fight so they could practice their skills. Middle Ages : aka Dark Ages aka Medieval Times Roman Empire Falls — 476 Renaissance — 1400s Characterized by: – Bubonic Plague (“Black Death”) – Uneducated Society – Feudalism – Catholic Church – “Barbarian” Invasions Feudalism: A kind of society where people worked and fought for a local lord in return for protection and the use of the land – For safety and defense, people in the Middle Ages formed small communities around a central lord or master – These lords would allow peasants to live on their land if they farmed it – The peasants would then give part of their harvest to the lords Catholic Church • Only church in Europe during the Middle Ages • Church leaders sat on the king's council and played leading roles in govt. • Life was so miserable for most people (serfs) that the church was the only thing that gave them hope – the promise of a better life after death Crusades • Journey of 100,000 European Knights to take control of Jerusalem (Holy Land). • Crusade means “marked with the cross” • Holy wars (religious wars) • Roman Catholic Church fighting a war to free the Holy Land (Israel) from the Muslims • Continued for about 200 years • Failed and the Holy Land was again controlled by the Muslims Impact of Crusades 1. Improved trade 2. Strengthened power of kings 3. Weakened the feudal system 4. Encouraged learning, enriched culture, and knowledge 5. The church became the most important part of Western European civilization 6. Showed Europeans support of Christianity Bubonic Plague (Black Death) • A disease that struck western Eurasia in the Middle Ages – Its victims experienced severe chills, fever, convulsions, and vomiting & would die within 3-5 days • • • • Developed dark spots on their skin and swollen glands. • Bubonic Plague spread from Asia by rats carrying infected fleas • Impact of Bubonic Plague • Massive loss of life in Africa, Asia, and Europe • 20-30 million people were killed by the Plague • Wars stopped and trade declined for a short period • Paving the way for the Renaissance Beginnings of the Renaissance • The Age of Exploration made European monarchs VERY RICH!! • Traders & merchants of all the new goods got rich too. • Became new group of people in the society=middle class. • New middle class paid taxes to monarchs • The middle class now had enough time and money to become educated, as well as enjoy art. • This rebirth of interest in learning and art is called the Renaissance Renaissance 1. Humanism 2. Scientific Revolution • The Renaissance • French for the word “Rebirth” • Started in Italy • 1300’s -1500’s • Rebirth in interest in art and education such as: – Write poetry, plays, books – Built buildings – Art (paintings, sculptures, etc) • Europeans would rediscover many of the ideas of the past, especially from the Romans and the Greeks – Art in the Renaissance Art in the Renaissance • More realistic • New techniques: perspective & shadows—made paintings more life like • Art in the Renaissance • Famous People from the Renaissance • Leonardo da Vinci • William Shakespeare • Michelangelo • Machiavelli • Galileo Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) An Italian scientist, engineer, inventor, and painter. • • Started many projects but finished very few Leonardo Da Vinci most famous works are the LAST SUPPER and the MONA LISA Very observant, wrote down 5,000 pages in his notebook of his observations. Michelangelo Italian Renaissance painter, sculptor, architect, and poet. • Michelangelo’s passion was sculpture. He would spend a lot of time chiseling his statues out of marble. • Michelangelo Best known works Of Michealangelo • Painting the ceiling ofthe Sistine Chapel • The dome on St.Peter’s Basilica • Sculpture of David Niccolo Machiavelli • (1469-1527) was an Italian political philosopher, best known for writing the book Il Principe, (The Prince) • The Prince is a how to book of how to lead a country. (Basically the ends justify the means) • Best known for the quote, “Is it better to be feared or loved.” • When it comes to being a leader is it better to be feared or loved or both? Tell me why you think that way and include examples from your life that back up your thoughts. William Shakespeare • (1564-1616) Considered the greatest writer of the English language. • During his life he wrote 38 plays. His plays were divided into 3 types: – Histories – Comedies – Tragedies • William Shakespeare • Shakespeare’s most famous plays include – Midsummer's Night’s Dream (Comedy) – Romeo and Juliet (Tragedy) – Julius Caesar (History) Galileo Galilei • Physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher • Improved the telescope • Believed in idea that the earth went around the sun. • • – Spend last years of his life under house arrest for his belief that that earth went around the sun. Galileo Galilei Galileo Galilei IMPERIALISM ALSO CALLED…COLONIALISM AND/OR COLONIZATION “WHEN A MORE POWERFUL NATION TAKES OVER A WEAKER NATION FOR ECONOMIC, STRATEGIC, OR POLITICAL REASONS..” • European Objectives • 1500s—looking for slaves for colonies in N./S. America • 1700s/1800s—industrial revolution causes an increased demand of two things: – Resources needed to run factories (coal, iron) – Crops/raw materials needed for factories to make products • Main Cause of African Imperialism The Berlin Conference 1884 • Representatives from 14 European countries made decisions about dividing Africa • No African representatives were invited or consulted • Berlin Conference Results • Superimposed boundaries! (made boundaries with out Africans say so) – African people divided – Unified regions ripped apart – Hostile societies were thrown together – Migration routes closed off • Divide and Conquer. The hatred various tribes had toward each other prevent the Africans from cooperating with each other to resist Apartheid in South Africa APARTHEID- A rigid separation of races in south Africa. The Republic of South Africa • South Africans were classified as black, white, and “coloured” (mixed) • Laws were created to legalize separation of races – White only busses, beaches, bathrooms, restaurants, and schools…BY LAW • Opposition groups were banned from speaking out (ANC) Nelson Mandela is imprisoned for 27 years for opposing racial segregation Struggle Against Apartheid • Archbishop Desmond Tutu strongly opposed apartheid, but not through violence (won Nobel Peace Prize) • Freedom marches and boycotts spread across South Africa • During the 1980’s the U.S put an economic sanction on South Africa – import taxes, export taxes, & trade barriers Apartheid Ends • Ban on opposition groups lifted • 1990 – Nelson Mandela is released from prison – His release symbolized hope for the people of South Africa • 1991 – South Africans were no longer classified by race • 1992 – citizenship is given to blacks • 1994 – Mandela is elected President • • • • • • • • • • China China is the most populous country in the world, with a population of 1.3 billion people China is one of the world's oldest continuous civilizations. How geography effects history. Geography has played a very important role in the history of China. The Chinese civilization developed along the fertile Huang He River in the north and the Yangzi River in central China. Natural barriers such as mountains, deserts, and plateaus prevented invasions on all sides of China. China China is one of the world's oldest continuous civilizations The Chinese created some of following inventions – Paper – The Compass – Gunpowder – Printing Great Wall of China • Is 35,000 miles of fortified walls with a roadway along the top, constructed for defense. • Emperor Qin, China’s first emperor created the Great Wall to keep people out. • Qin would use millions of people to create the great wall. • Great Wall of China Mao Ze Dong • Mao Ze Dong (1893-1976) was the communist leader who drastically changed China. • Mao ZeDong • Mao Ze Dong (1893-1976) was the communist leader who brought about changes in China. • In 1949 he would win the Chinese Civil War and make China a communist government. • The people he was fighting against would flee to Taiwan. Great Leap Forward- 1958-1961 The Chinese plan to radically modernize their society. – Lack of incentives caused there to be shortages in food. – People were uneducated and could not industrialize effectively. – Food shortages killed 20 million Cultural Revolution – 1966-1976. a reform movement in China to eliminate anyone who is anti communist. – Intellectuals were imprisoned and executed. – Some were sent to re-education camps. • Improvement through Entrepreneurship. • During the 1970’sThe communists realized that the policies of Mao hurt China. • After Mao’s death the leaders of China gradually introduced a Free Enterprise system. – Ok to make money • Today China is the fastest growing economy on earth. • Why is China Growing? • Cheaper to make goods in China – Low salary – Work really hard – Americans will purchase the cheapest items. – US companies will try to make items as cheap as possible. – Loss of American manufacturing Jobs to China (Outsourcing) Japan • 日本(国) • Ancient Japan • For most of Japan’s history clans, fought each other for land and power. – CLAN: Group of people who can claim a common ancestor. – Yamato Clan would control Japan – They claimed to be descended from the Sun god. (Amatarasu) – The Yamato Rulers would become emperors of Japan. • Ancient Japanese social structure (FEUDALISM) • Japan was once a feudal society ruled by Emperors with military generals called shoguns. – Emperors-spiritual leader, Little power – Shoguns-Actual ruler of Japan – Daimyo-wealthy land owners – Samurais-soldiers of the wealthy land owners, (daimyo) th – Peasants- 3/4 the population. Code of the Samurai “Bushido • Bushido (meaning the way of the warrior). Is the strict code of conduct of the samurai. • Influenced how the samurai dressed, spoke, talked, ate, married, and died. • It stresses bravery, self-discipline, and loyalty. • If a samurai was dishonored or defeated, he was expected to commit seppuku or ritual suicide. • Europeans and the Japanese Commodore Perry and the Meiji Era • Opening up Japan • 1854 Commodore Matthew Perry landed in Japan with a fleet of warships. – He carried a letter from the president of the United States wishing to open relations with Japan. Japan is forced to Open The size and strength of Perry’s warships forced Japan to open it’s borders. – Japan realized that they were behind the world in technology. • Opening of Japan The Meiji Era • 1868 to 1912, the time when the Japanese rapidly modernized and became a world power. – The Japanese rapidly started to industrialize and become modern. – By the 1920’s they were in industrial power. – . • Japanese Empire 1912-1945 • They copied the European powers at the time and started to colonize other countries. • World War 2 and its aftermath • 1941-1945 The Japanese fought the U.S. in World War 2. •