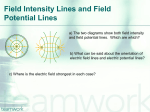
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kinetics and Equilibrium
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Reaction progress kinetic analysis wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics Kinetics deals with rates of reactions (how quickly a reaction occurs). Kinetics: The Collision Theory Frequency of collisions: more collisions = faster rate Effective collisions: must have 1) proper orientation and 2) enough energy Factors Affecting Rate 1. Type of substance: Ionic substances react faster: bonds require less energy to break AgNO3 (aq)+NaCl(aq)AgCl(s)+NaNO3 (aq) In solution ionic solids dissociate into ions: Ag+ NO3Na+ Cl- Factors Affecting Rate Covalent react more slowly: bonds require more energy to break H2 (g)+I2 (g)2 HI (g) Bonds must be broken then be reformed. (takes more time) Factors Affecting Rate 2. Temperature increase Average kinetic energy increases and the number of collisions increases. Reactants have more energy when colliding. This increases rate. Factors Affecting Rate 3. Concentration increase Increases rate due to the fact that more particles are in a given volume, which creates more collisions. Factors Affecting Rate 4. Surface Area Increase Increases rate due to increased reactant interaction or collisions (powder vs. lump) Factors Affecting Rate 5. Pressure Increases Increases the rate of reactions involving gases only As pressure , volume so: spaces between molecules frequency of effective collisions Factors Affecting Rate 6. Catalyst: substance that increases rate of reaction, provides a shorter or alternate pathway by lowering the activation energy of the reaction. Catalysts remain unchanged during the reaction and can be reused. Activation energy: amount of energy required to “start” a reaction Quick Review – Factors that affect reactions Ionic solutions have faster reactions than molecule compounds. (bonding) Temp. Rate conc. rate surface area rate Pressure rate, P rate Catalysts speed up reactions. Potential Energy Diagrams A potential energy diagrams graphs heat during the course of a reaction. Potential Energy Diagrams In an endothermic process, the potential energy (PE) of products is more because energy is gained. Potential Energy Diagrams In an exothermic process, the potential energy (PE) of products is less because energy is lost. Potential Energy Diagrams Activation energy (Ea) is the energy level that the reactant molecules must overcome before a reaction can occur. Potential Energy Diagrams Activation energy (Ea) can be lowered by adding a catalyst. Potential Energy Diagrams The activated complex is the structure at the maximum energy point along the reaction path. It is very unstable. Potential Energy Diagrams The change in enthalpy (ΔH) is the heat lost or gained in a chemical reaction. ΔH = Hproducts – Hreactants ΔH = Hproducts – Hreactants ΔH is positive when the reaction is endothermic. Heat of products are greater than reactants. ΔH is negative when the reaction is exothermic. Heat of reactants were greater than the products. Stability of Products and H Products tend toward lower energy (-ΔH) Products tend toward more randomness (entropy) Products of exothermic reactions are usually more stable. Result in lower amounts of heat. The more negative the H, the more stable the product is.