* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Murrin-CH02 - Arbortown Properties
Indentured servitude in the Americas wikipedia , lookup
Colonial American bastardy laws wikipedia , lookup
Shipbuilding in the American colonies wikipedia , lookup
Plymouth Colony wikipedia , lookup
Indentured servitude in Pennsylvania wikipedia , lookup
New Netherland wikipedia , lookup
Colony of Virginia wikipedia , lookup
History of Jamestown, Virginia (1607–99) wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
Roanoke Colony wikipedia , lookup
Province of Maryland wikipedia , lookup
Massachusetts Bay Colony wikipedia , lookup
Colonial American military history wikipedia , lookup
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in the colonial United States wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
Jamestown supply missions wikipedia , lookup
Pilgrims (Plymouth Colony) wikipedia , lookup
Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
London Company wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church in the Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
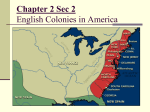
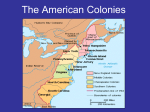
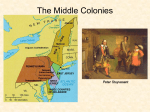
Chapter 2 2 Chapter The Challenge to Spain and the Settlement of North America The Protestant Reformation and the Challenge to Spain • Martin Luther – 95 Theses • John Calvin – Institutes of the Christian Religion (1536) • France, Netherlands, England all experienced powerful Protestant movements – challenged Spanish Power New France: Early French Explorers • Giovanni da Verrazano • Jacques Cartier • Henry IV – Huguenots – Edict of Nantes (1598) • Samuel de Champlain Missions and Furs • • • • • coureur de bois Society of Jesus (Jesuits) Algonquian Iroquoian Hurons New France Under Louis XIV • • • • Jean-Baptiste Colbert in Canada Quebec, Three Rivers, Montreal habitants seigneurs The Dutch and Swedish Settlements • 17th Century Dutch: more active overseas than French • Profit – main motivation in Dutch expansion overseas The East and West India Companies • Henry Hudson • Dutch West India Company – New Amsterdam – Fort Orange • patroonships New Netherland as a Pluralistic Society • William Kieft: Pavonia Massacre (1643) • War ensued with nearby Algonquians Swedish and English Encroachments • Fort Christina (Wilmington) • English settled around Chesapeake Bay and New England The Challenge from Elizabethan England • Giovanni Cabato (John Cabot), 1497 – Newfoundland The English Reformation • Elizabeth I • Church of England (Anglicanism) – Book of Common Prayer • Puritans • Separatists (colony of Plymouth) Hawkins and Drake • John Hawkins • Francis Drake Gilbert, Ireland, and America • History of English attempts at control in Ireland • Sir Humphrey Gilbert • Colonization of Ireland by the English (1560-1640) • English turn to America for colonization Raleigh, Roanoke, and War with Spain • Sir Walter Raleigh – Roanoke Island • Spanish Armada & War 1588-1604 • Richard Hakluyt (elder and younger) The Swarming of the English • Over 700,000 immigrated from Europe or (forcibly) Africa to English colonies in North America and the Caribbean – Many arrived with hope for a better lot in life – Many arrived as servants – Most immigrants were to plantation areas The Pattern of Settlement in the English Colonies up to 1700 The Chesapeake and West Indian Colonies • King James I of England, 1606 – Chartered the Virginia Company to colonize North America between 34th and 45th parallels – 2 headquarters: • Plymouth Company, Sagadahoc, bankruptcy • London Company and Jamestown The Jamestown Disaster • Jamestown (1607) – – – – – – Over 65% death rate 1st years John Smith’s leadership Powhatan and the 1st Indian War (1609-1614) Near abandonment in 1610 Pocahantas: war ending hostage John Rolfe and tobacco Reorganization, Reform, and Crisis • • • • • House of Burgesses “head-right” system Opechancanough and the Massacre of 1622 2nd Indian War Royal Intervention 1624 Tobacco, Servants, and Survival • Natives driven between James & York rivers • Tobacco exports financed importation of indentured servants • Limited upward mobility • Virginia heads toward oligarchy Maryland • Sir George Calvert (Lord Baltimore) – Catholic, prominent officeholder • Maryland Charter 1632: the Proprietary model • Economic and class structure similar to Virginia • Toleration Act of 1649 Chesapeake Family Life • • • • • • • Men greatly outnumbered women in 17th century Population becomes self-sustaining 1680 Men outlived women Pre-marital 1st pregnancies over 50% Groom in his 30’s, bride in her early 20’s Frequent remarriage Family loyalty and kinship The West Indies and the Transition to Slavery • Leeward Islands – – – – St. Christopher Nevis Montserrat Antigua The Rise of Slavery in North America • Africans appeared in Virginia before 1619 • Uncertain status of Africans – Some treated as servants – England had no history of slavery at home • By 1680: rigid caste system set in Chesapeake colonies – Fewer indentured servants – Expanding English navy and army competed for young men – Slaves cost more, but served for life The New England Colonies • New England settlers reproduced mixed economy of old England with some variations • Radical communitarian vision • Early settlers questioned the English ways • Over time, these settlers became more conservative than earliest settlers The Pilgrims and Plymouth • Mayflower – Mayflower Compact • William Bradford • Wampanoag – Massasoit Covenant Theology • Charles I • Puritans – large exodus settled Massachusetts Bay, 1630-1641 • Idea of the covenant becomes powerful social metaphor – “City upon a Hill” – John Winthrop Massachusetts Bay • Massachusetts Bay Company • Settlers: broad middle range of English society (few rich, few poor) • Organized original settlements around congregation • Puritan orthodoxy and economics of survival Puritan Family Life • • • • New Englanders robust vs. sickly Virginians Puritan families grew rapidly New England families: intensely patriarchal New England towns settled into a tight community – fearful of letting “strangers” in Conversion, Dissent, and Expansion • New Haven Colony – Thomas Hooker • Roger Williams • Anne Hutchinson – Antinomian heresy • Colony of Rhode Island Congregations, Towns, and Colony Governments • Congregationalism – Cambridge Platform (1648) • Town becomes distinct from the congregation • Town Meetings • Bicameral legislature, 1640’s Massachusetts Infant Baptism and New Dissent • 1640s, Baptists – only converted adults receive right to baptism – Harvard College • Quakers – came from England in the 1650s to New England • Half-Way Covenant (1662) The English Civil Wars • Oliver Cromwell • The “Restoration” – Charles II The First Restoration Colonies • 6 colonies founded under Restoration era (1660-1688) • These new colonies founded by men with big ideas, but small purses – Tried to persuade existing settlers to move to new colonies – Promised religious toleration or religious liberty Carolina, Harrington, and the Aristocratic Ideal • Fundamental Constitutions of Carolina (1669) – Anthony Ashley-Cooper – James Harrington New York: An Experiment in Absolutism • Dutch ceded New Amsterdam – becomes New York • English absolutism makes it difficult to attract English colonists to New York • New York goes to Dutch hands again (New Orange), then back to English • Edmund Andros Brotherly Love: The Quakers America • Society of Friends (Quakers) – “Inner Light” – Weekly meetings – No established clergy • Quakers infuriated other Christians – Pacifists – Denounced oath-taking – Others saw them as “dangerous radicals” Quaker Families • • • • Mary Dyer Affectionate families Large houses To marry outside Quaker religion = expulsion from the Society • Strong need to provide for their children and protect from worldly corruption (c) 2003 Wadsworth Group All rights reserved West New Jersey • Sir George Carteret • John, baron Berkeley • West Jersey Concessions and Agreements (1676) Pennsylvania • William Penn, gentleman and a Quaker • Granted a charter for a proprietary colony: Pennsylvania • Led a group of Quaker colonists to America • Pennsylvania: – economic success – Policy of of religious freedom Conclusion • France, Netherlands, England all founded colonies in North American and Caribbean in 1600s • New France: missionaries and traders, cooperation with Indians • New Netherland: fur trading • New England: desired land – establishment of colonies