* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 - HCC Learning Web
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Halogen bond wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular biology wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Hartree–Fock method wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Molecular graphics wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Pseudo Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
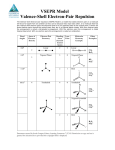
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Student: ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. The shape of the SF4 molecule is A. B. C. D. E. 4. According to VSEPR theory, the shape of the PH3 molecule is best described as A. B. C. D. E. 6. linear. trigonal planar. tetrahedral. bent. trigonal pyramidal. The shape of the ClF3 molecule is best described as A. B. C. D. E. 8. tetrahedral. trigonal pyramidal. trigonal planar. square planar. distorted tetrahedron (seesaw). distorted tetrahedron. trigonal planar. tetrahedral. T-shaped. trigonal pyramidal. According to the VSEPR theory, the molecular shape of beryllium chloride is A. B. C. D. E. linear. trigonal planar. bent. tetrahedral. trigonal pyramidal. 10. According to the VSEPR theory, the molecular shape of boron trichloride is A. B. C. D. E. linear. trigonal planar. bent. tetrahedral. trigonal pyramidal. 12. According to the VSEPR theory, which one of the following species should be linear? A. B. C. D. E. H2S HCN BF3 H2CO SO2 14. According to VSEPR theory, which one of the following molecules should be nonlinear? A. B. C. D. E. CO2 C2H2 SO2 BeCl2 KrF2 16. Which one of the following molecules has tetrahedral geometry? A. B. C. D. E. XeF4 BF3 AsF5 CF4 NH3 18. Predict the geometry around the central atom in PO43-. A. B. C. D. E. trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal tetrahedral trigonal bipyramidal octahedral 20. Predict the geometry around the central atom in XeO4. A. B. C. D. E. trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal tetrahedral trigonal bipyramidal octahedral 22. Which of the following substance is/are planar? (i) SO3 A. B. C. D. E. (ii) SO32- (iii) NO3- (iv) PF3 (v) BF3 only (i) and (ii) only (i), (iii), and (v) only (iv) all are planar except (iv) all are planar except (ii) 24. The F-S-F bond angles in SF6 are A. B. C. D. E. 90 and 180. 109.5. 120. 180. 90 and 120. 26. According to the VSEPR theory, the actual F-As-F bond angles in the AsF4- ion are predicted to be A. B. C. D. E. 109.5. 90 and 120. 180. < 109.5. < 90 and < 120. 28. Which one of the following molecules is nonpolar? A. B. C. D. E. NH3 OF2 CH3Cl H2O BeCl2 30. Which one of the following molecules has a non-zero dipole moment? A. B. C. D. E. BeCl2 Br2 BF3 IBr CO2 32. Which one of the following molecules is polar? A. B. C. D. E. PBr5 CCl4 BrF5 XeF2 XeF4 34. Predict the geometry and polarity of the CS2 molecule. A. B. C. D. E. linear, polar linear, nonpolar tetrahedral, nonpolar bent, nonpolar bent, polar 36. Indicate the type of hybrid orbitals used by the central atom in PCl3. A. B. C. D. E. sp sp2 sp3 sp3d sp3d2 38. Indicate the type of hybrid orbitals used by the central atom in SF6. A. B. C. D. E. sp sp2 sp3 sp3d sp3d2 40. What is the hybridization on the central atom in NO3- ? A. B. C. D. E. sp sp2 sp3 sp3d sp3d2 42. What is the hybridization of As in the AsF4- ion? A. sp B. sp2 C. sp3 D. sp3d E. sp3d2 44. The hybridization of the central nitrogen atom in the molecule N2O is A. B. C. D. E. sp. sp2. sp3. sp3d. sp3d2. 46. In which of these molecules do the two nitrogen atoms have different hybridizations? A. B. C. D. E. NH4NO3 N2H4 N2O4 N2O5 none of these 48. Which of the following molecules have the same geometries? A. B. C. D. SF4 and CH4 CO2 and H2O CO2 and BeH2 N2O and NO2 50. The number of pi bonds in the molecule below is A. B. C. D. E. 2. 4. 6. 10. 15. 52. Consider the species Cl2+, Cl2, and Cl2-. Which of these species will be paramagnetic? A. B. C. D. E. Only Cl2 Cl2+ and Cl2 Cl2 and Cl2Cl2+ and Cl2All three are paramagnetic. 54. In which of the following would the bonding be strengthened with the addition of an electron to form the negative molecular ion? A. B. C. D. E. N2 O2 F2 all of these none of these 56. In which of the following would the bonding be weakened with the addition of an electron to form the negative molecular ion? A. B. C. D. E. B2 C2 N2 all of these none of these 58. Which of the following is not true of molecular orbitals? A. B. C. D. E. The number of molecular orbitals formed is always equal to the number of atomic orbitals combined. A molecular orbital can accommodate up to two electrons. When electrons are added to orbitals of the same energy, the most stable arrangement is predicted by Hund's rule. Low-energy molecular orbitals fill before high-energy molecular orbitals fill. For any substance, the number of electrons in molecular orbitals is equal to the sum of all the valence electrons on the bonding atoms. 60. Which of the following correctly lists species in order of increasing bond length? A. B. C. D. E. O2 < O2+ < O2O2- < O2 < O2+ O2+ < O2 < O2O2- < O2+ < O2 O2+ < O2- < O2 62. Which of the following correctly lists species in order of increasing bond order? A. B. C. D. E. C2 < Li2 < Be2 < N2 Be2 < Li2 < C2 < N2 N2 < Be2 < Li2 < C2 N2 < C2 < Li2 < Be2 Be2 < C2 < N2 < Li2 Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Key 2.E 4.E 6.D 8.A 10.B 12.B 14.C 16.D 18.C 20.C 22.B 24.A 26.E 28.E 30.D 32.C 34.B 36.C 38.E 40.B 42.D 44.A 46.A 48.C 50.B 52.D 54.E 56.C 58.E 60.C 62.B