* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Measuring Voltage Drop and Current
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
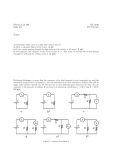
Measuring Voltage Drop and Current Electricians often measure the voltage and current in a circuit to make sure the circuit is working properly. HOW DOES A VOLTMETER WORK? A voltmeter is used to measure the “voltage drop” in a circuit. Voltage drop refers to the amount of energy lost or gained between two points in a circuit. Voltmeters are connected to circuits in parallel. The positive portion of the voltmeter (known as the positive terminal) is attached to the positive side of the circuit. The negative terminal of the voltmeter is attached to the negative side of the circuit. Example of a circuit with a voltmeter: In this example, the voltmeter is connected in parallel to the cell (battery). The voltmeter would read that the battery produces 1.5V. HOW DOES AN AMMETER WORK? An ammeter measures how much current passes through the circuit. An ammeter is connected in series in a circuit. Example of a circuit with an ammeter: Connecting Both a Voltmeter and an Ammeter When building circuits, it is also possible to wire them with parts that are wired in series and parts that are wired in parallel. Let’s take a look at some examples: Example 1: Create a circuit with 3 cells, a closed switch, two light bulbs wired in series, and 2 light bulbs wired in parallel. Connect a voltmeter across the cell and connect an ammeter between the second and third light bulbs. Example 2 Create a circuit with four cells, an open switch, a TV, clock, and a light bulb wired in parallel. Connect an ammeter between the TV and clock and connect a voltmeter across the light bulb. Classwork/Homework Complete the practice questions on the handout provided to you Circuit Continuity Worksheets