* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LESSON 5 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION The
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
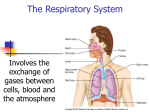
LESSON 5 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION The respiratory system is the most important system to the continuation of life. A person can only sustain life for 4-6 minutes without breathing. Brain damage may happen when life sustaining air is cut off for 3 ½ to 4 minutes. Respiration is an automatic mechanical process from the time of birth until death. Most of the time respiration is an unconscious act of exchanging oxygen between the environment around us and the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. Our environmental air contains about 21 percent oxygen, 78 percent nitrogen, 0.4 percent carbon dioxide and the rest is made up of microgases. As air enters the alveoli of the lungs, the oxygen, which has a greater affinity attachment to the red blood cells than carbon dioxide, replaces the carbon dioxide on the surface of the red blood cells in the small capillaries of the lung. The exhaled air now has about 16 percent oxygen and 5 percent carbon dioxide. External respiration is the exchange of oxygen between the outside air and the red blood cells of the lungs. Internal respiration occurs a short time later. Internal respiration is the exchange of oxygen in the blood stream’s tiny capillaries and the cell. In internal respiration, the exchange is the release of carbon dioxide from the cell and the uptake of oxygen by the cell from the blood stream. Cellular respiration takes place inside the mitochondria of the cell. Oxygen is needed in cellular respiration, and carbon dioxide is the waste gas of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a part of the energy cycle, sometimes referred to as the Kreb cycle, of the body and is used in the manufacture of the chemical of cellular energy, adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ANATOMY Air enters the body through a passageway called the nose or external nares. It passes through a cavity called the nasal cavity or internal nares. The nose and nasal cavity are lined with mucous membranes and fine hairlike structures called cilia. Mucous and cilia trap and help remove or filter dust and pathogens from the environment. The air is warmed and moistened in the nasal cavity. Surrounding the nasal cavity are hollow chambers called paranasal sinuses. The sinuses produce a lubricating mucous and help in the formation of different sounds. Located directly posterior to the nasal cavity is the pharynx. The pharynx has three areas: the nasopharynx located directly behind the nose; the oropharynx located directly behind the mouth; and the laryngopharynx, sometimes called the hypopharynx, located between the lower jaw and the larynx or voice box and the esophagus. The pharynx contains lymphatic tissue called adenoids or pharyngeal tonsils, located in the nasopharynx, and the palatine tonsils, located in the oropharynx. The pharynx is a common area for both air and food or drink. To prevent the passage of food or drink into the larynx and then into the lungs, a cartilage flap covers the opening (or glottis) into the larynx. This flap of cartilage is called the epiglottis. When swallowing food or drink, the epiglottis unconsciously closes over the glottis to prevent entrance of solids or liquids into the larynx. Air passes through the larynx and enters a 4½ inch tube called the trachea or windpipe. The trachea is strengthened and kept opened by rings of cartilage and fibrous connective tissue covering its full length. The trachea branches into the two tubes called bronchi. The singular bronchus each divide into several smaller tubes called bronchioles. At the end of these separate bronchioles are millions of small air sacs or alveoli. Each one of these singular alveolus is made up of one layer of epithelial cells. Surrounding the alveolus are very small one-celled, thick blood vessels called capillaries. The external respiration process occurs between the alveoli and the very small capillaries of the lungs. Oxygen is bound to the red blood cells of the lung’s capillaries by an iron (Fe) molecule. The whole structure of oxygen, iron, and red blood cells is called the hemoglobin molecule. Hemoglobin then carries the oxygen to the cells where internal respiration removes the oxygen into the cell and allows the waste carbon dioxide to attach to the hemoglobin and then be removed from the body. Inside the cell membrane, oxygen is used in a process called cellular respiration and carbon dioxide is formed as a product of the cellular respiration. Cellular respiration produces the energy chemicals needed in the biochemical processes of life. Surrounding each lung is the double-layered membrane called pleura. The outer layer is called parietal pleura and the inner layer is called visceral pleura. The pleura is lubricated by a watery fluid, surfactant, that allows the member to move freely without friction. The right side of the lung is large and contains three lobes, while the left side is smaller and contains two lobes. The top or uppermost area of the lung is called the apex. The lower part of the lung is called the base. The middle area of the lung is called the hilum or hilus. Blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic fluid enter and exit the lungs in the hilus area. The muscle at the bottom of the thoracic cavity is called the diaphragm. The diaphragm's contractions and relaxation cause the lungs to expand or contract. When the lungs fill full of air it is called inhalation; as the air escapes from the lungs it is called exhalation. The movement of the diaphragm is under the control of the involuntary or autonomic nervous system. However, we can override this, causing our diaphragm to contract or relax at will. The Action Suffixes Many suffixes in medical terminology show actions, surgical procedures, or processes where medical tools and instruments are used. Some of these are now included so the student may get to know their action or use when introduced in this and future lessons: -ectomy = the action of surgically removing body tissue, organs, or structures. -otomy = the action of surgically cutting into body tissue. -otome = the tool used to surgically cut into body tissue or to remove body tissues or structures. -ostomy = the action of surgically making a temporary or artificial opening into a cavity or tube. -opsy = the action to view or see body tissue. -oscopy = the action of surgically viewing tissues, organs, structures, tubes, vessels, or structures. -oscope = the instrument to view body structures, organs, or tissue. -graphy = the action of medically obtaining pictures, visualizations of a body structures, or other indirect viewing methods of body functions, structures, organs, or tissues. -grapy = the instrument used to get the picture or other viewing method of body function, structures, organs, or tissue. -gram = the actual record or picture (x_ray, EKG, EEG) to be viewed. -plasty = the action of surgically repairing structures, tissues, or organs. -orraphy = the action of surgically suturing (sewing_up) tissues. -orrhea = the action of discharging body fluids, generally refers to normal body fluids flowing, except where it is not normal to have fluids coming from that body area. -orrhage = the action of bursting forth of body fluids, usually blood is in the -metry size, or = discharge and it is usually abnormal or life threatening. the action or process of measuring of body structures, tissue -meter structures, = the counting of cells in a defined area. the instrument used in the measuring or counting of body -centesis = (withdrawing) cells, or tissues the action of surgically puncturing and aspirating -desis = -orrhexis -pexy = = -tripsy or other = fluid from body cavities. the action to surgically fuse (fixation) of body structures or tissues. the action to wreck, break, destroy, or rupture tissue the action to surgically fixate, put back into place structures, organs, tissue the action of surgically crushing tissue, structures, calcified, = stones the action to surgically control the flow of blood or other -ostasis fluids. -ostat = the tool used to surgically control the flow of blood or other body fluids. LESSON 5 - GRAPHICS TERMS FOR LESSON 5: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Organs to Know Nose Nasal septum Paranasal sinuses Pharynx - throat Tonsils Adenoids Larynx Epiglottis Trachea Brochus Bronchioles Alveolus Lungs Superior lobes Middle lobe Inferior lobes Pleura Diaphragm Mediastinum Word Parts to Know - Respiratory adenoid/o alveoli/o bronch/i bronch/o bronchiol/o dialat/o diaphragmat/o epiglott/o glott/o laryg/o lob/ lobar/o nas/o rhin/o pharyng/o pleur/o pneum/o pneumat/o pneumon/o pulmon/o sinus/o thorac/o tonsill/o trache/o atel/o muc/o orth/o ox/o ox/i ox/y py/o spir/o uvul/o Prefixes to Know - Respiratory andysendointraeupan- Suffixes to Know - Respiratory -algia -ar -ary -capnia -cele -centesis -desis -eal -ectasis -emia -gram -graphy -graph -meter -metry -orrhexis -orrhagia -ostasis -ostat -ostomy -otomy -oxia -pexy -phonia -pnea -scope -scopy -spasm -stenosis -thorax -tripsy Diagnostic Terms to Know - Respiratory adenoiditis atelectasis bronchiectasis bronchitis bronchopneumonia diaphragmatocele epiglottitis laryngitis laryngotracheobronchitis lower respiratory infection (LRI) nasopharyngitis pansinusitis pharyngitis pleuritis pneumatocele pneumonitis pneumoconiosis pneumothorax pulmonary neoplasm pyothorax rhinomycosis rhinorrhagia thoracalgia tonsillitis tracheitis tracheostenosis asthma chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) coccidioidomycosis cor pulmonale croup cystic fibrosis emphysema influenza pertussis pleural effusion pulmonary edema pulmonary embolism upper respiratory infection (URI) Surgical Terms to Know - Respiratory adenoidectomy bronchoplasty laryngectomy laryngocentesis laryngoplasty laryngostomy laryngotrachelotomy lobectomy lobarectomy pleurocentesis pleuropexy pneumobronchotomy pneumonectomy rhinoplasty sinusotomy thoracocentesis thoracotomy tonsillectomy tracheloplasty trachelostomy trachelotomy Diagnostic Procedural Terms to Know - Respiratory bronchogram bronchography bronchoscope bronchoscopy laryngoscope laryngoscopy lobar pneumonia oximeter spirometer spirometry Additional Terms to Know - Respiratory acapnia adenotome anoxia aphonia apnea bronchoalveolar bronchodilator bronchogenic bronchospasm diaphragmatic dysphonia dyspnea endotracheal eupnea hypercapnia hyperpnea hypoxemia hypoxia laryngeal laryngospasm mucoid mucous orthopnea nasopharyngeal rhinorrhea airway asphyxia aspirate bronchoconstrictor cough hiccup hyperventilation hypoventilation mucopurulent mucus nebulizer paroxysm patent sputum ventilator PRACTICE EXERCISES FOR LESSON 5 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM MATCHING: ---- alveoli ---- bronchi ---- larynx ---- lungs ---- pharynx ---- pleura ---- tonsils ---- trachea a b c d e f g h i tube carrying air to lungs windpipe located in thoracic cavity membrane around lungs behind nasal cavity food and air passageway voice box air sacs keeps food out of windpipe MATCHING: ---- algia ----- ar, -ary, -eal ---- capnia ---- cele ---- centesis ---- ectasis ---- emia ---- gram ---- graph ---- graphy ---- meter ---- metry ---- rrhage a b c d e f g h i j k l m record stretching - out surgical puncture to aspirate process to measurement carbon dioxide pertaining to hernia instrument to measure process of getting the record rapid flow of blood blood condition pain instrument to process the recording a b c d e f g h i j k l m incision instrument for visual exam rapid flow construction, narrow sound make artificial opening involuntary muscle contraction chest pertaining to oxygen breathing surgical fixation carbon dioxide visual exam MATCHING: ---------------------------------- orrhagia ostomy otomy pexy phonia pnea scope scopy spasm stenosis thorax DEFINE: laryng/o: bronch/o, bronch/i: pleur/o: pneum/o: tonsill/o: bronchiol/o: pulmon/o: diaphragmat/o: trache/o: alveol/o: pneumon/o: thorac/o: adenoid/o: pharyng/o: rhin/o: sinus/o: lob/o: epiglott/o: pneumat/o: nas/o: WRITE THE MEDICAL ROOT FOR: nose larynx lung, air lung tonsils trachea adenoids bronchiole pleura diaphragm sinus thorax alveoli pharynx bronchi lobe epiglottis DEFINE: ox/o ox/i ox/y spir/o muc/o atel/o orth/o py/o WRITE THE MEDICAL ROOT: breathe, breathing oxygen imperfect straight pus mucus DEFINE: endo dys a an pan eu WRITE PREFIX FOR: difficult, bad within normal good without all DEFINE: -thorax -ar, -ary, -eal -stenosis -cele -ostomy -pexy -meter -spasm -algia -scopy -centesis -otomy -scope -orrhagia -ectasis -gram -pnea -metry -graphy -emia -oxia -capnia -phonia -tripsy -stasis DEFINE: pleuritis nasopharyngitis pneumothorax hemopneumothorax hemostasis pansinusitis atelectasis rhinomycosis tracheostenosis epiglottitis thoracalgia pulmonary neoplasm pulmonary embolism bronchiectasis tonsillitis pneumoconiosis bronchopneumonia pneumonitis laryngitis lobar pneumonitis pneumatocele pyothorax rhinorrhagia bronchitis pharyngitis tracheitis laryngotracheobronchitis adenoiditis DEFINE: tracheotomy laryngostomy adenoidectomy rhinoplasty pleurocentesis tracheostomy sinusotomy laryngoplasty pneumobronchotomy bronchoplasty pneumobronchotomy bronchoplasty thoracotomy laryngectomy thoracocentesis tonsillectomy laryngocentesis pleuropexy DEFINE: spirometer laryngoscope bronchogram spirometry oximeter bronchography laryngoscopy bronchoscope laryngeal eupnea bronchogenic mucoid apnea hypoxia laryngospasm endotracheal anoxia dysphonia bronchoalveolar dyspnea hypocapnia bronchospasm orthopnea acapnia hemostat hypopnea hypoxemia aphonia rhinorrhea rhinorrhage rhinotripsy adenotome mucus nasopharyngeal diaphragmatic REVIEW AND DEFINE: dematogenic erythrocytometer melanonychia mycology myomalacia myonecrosis tonsillomycosis viscerosomatic rhinolaryngologist otorhinolaryngologist otolaryngologist laryngologist pneumologist respiratory therapist inhalation therapist thoracic surgeon ASSIGNMENT FOR LESSON 5 Medical Terminology, HS 280 Respiratory System MATCHING ---- 1 alveoli ---- 2 bronchi ---- 3 larynx ---- 4 lungs ---- 5 pharynx ---- 6 pleura ---- 7 tonsils ---- 8 trachea b c d e f g h i windpipe keeps food out of windpipe food and air pathway membrane covering lungs voice box lymphoid tissue behind nasal cavity between trachea and lungs located in thoracic cavity air sacs MATCH THESE WORD ROOTS - May Be Used More Than Once ---- 9 adenoid/o a epiglottis ---- 10 pulmon/o b lung ---- 11 pneum/o c thorax (chest) ---- 12 pneumat/o d nose ---- 13 thorac/o e adenoids ---- 14 rhin/o ---- 15 nas/o ---- 16 epiglott/o DEFINE THESE WORD ROOTS: 17 oxy/oxi/o: 18 spir/o: 19 muc/o: 20 atel/o: 21 orth/o: 22 py/o: DEFINE THESE PREFIXES AND SUFFIXES: 23 a-, an24 dys25 endo26 eu- 27 panAssignment for Lesson 5, Respiratory, pg. 2 28 29 -algia -ar, -ary 30 31 32 -capnia -cele -centesis MATCHING ----------------------------------- 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 -algia -stenosis -scopy -cele -centesis -ectasis -emia -gram -graphy -meter -metry a b c d e f g h i j k l hernia stretching out pain blood condition record measurement narrow condition instrument used to measure recording process visual examination to aspirate fluid surgically instrument for drawing fluid DEFINE: 44 pneumoconiosis 45 rhinorrhagia 46 cystic fibrosis 47 emphysema 48 pertussis 49 pleuropexy 50 thoracotomy 51 hemostasis 52 rhinotripsy 53 rhinorrhexis 54 rhinoplasty 55 chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder 56 asthma Assignment for Lesson 5, Respiratory, pg. 3 57 pneumothorax 58 hemopneumothorax 59 rhinorrhea 60 acapnia 61 hypocapnia 62 hypercapnia 63 hypoxia 64 dyspnea 65 apnea