* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UP8.LP2.OtherCelestialBodies
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
Near-Earth object wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Juno (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
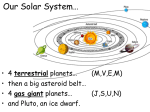
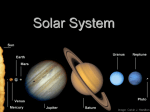
April 6th and 7th Unit 8: Space Science Objective(s): 1. Open-Minded 2. MATERIALS NEEDED: 1. Guided Notes 2. Pencil SWBAT identify the four Galilean moons of Jupiter by their physical properties. SWBAT compare and contrast meteoroids, asteroids, and comets Relevance: While we know much about the solar system, there is still a lot of unknown aspects for scientists and we must keep an open-mind when researching and learning about those unknowns. Do Now: Four-Square Do Now Other Celestial Bodies • Other than the planets, there are many other types of celestial bodies that are orbiting in our solar system. • What other celestial bodies can you think of? • Six of the eight planets have moons that orbit them including Jupiter which has four of the largest moons in the entire solar system orbiting it. Moons • • • Moons are smaller celestial objects that orbit planets. All of the planets, except Mercury and Venus, have moons. Scientists collect data about their physical properties using satellites and telescopes. What do planets orbit? What do moons orbit? Galileo Galilei • • • During the 1600s, Galileo Galilei discovered four large moons orbiting Jupiter using a telescope he made. At the time, these were the first moons ever found orbiting a planet other than the Earth. These four moons are now known as the Galilean moons. Stop and Jot Why are the four largest moons of Jupiter known as the Galilean moons? Galilean Moons • • The Galilean moons are four of the six largest moons in our solar system. In order of their distance from Jupiter they are called – Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. What are the four Galilean moons called? Io • • • It orbits Jupiter. Io is the closest Galilean moon to Jupiter. It is the most volcanically active body in the entire solar system. Europa • • • Europa is the second Galilean moon from Jupiter. It has an icy surface that likely floats on top of a liquid ocean. The ocean underneath these blocks of ice is an environment that could support life forms. Ganymede • • Ganymede is the third Galilean moon from Jupiter. It is the largest moon in the entire solar system – even larger than Mercury! Callisto • • • Callisto is the fourth Galilean moon from Jupiter. It is the third largest moon in the solar system. It is also the most heavily cratered body in the entire solar system. Turn and Talk What are the four largest moons of Jupiter called? Other Moons • • • Titan is the second largest moon in the entire solar system – it orbits Saturn. Composed primarily of ice and rocky material. The only moon known to have a dense atmosphere. Other Moons • • • Our moon is the fifth largest moon in our solar system. The surface is thick with dust and rocks. There is no water and no atmosphere. Word Scramble Challenge! GANYMEDE EYNAGMDE Definition: A Galilean moon – the largest in the entire Solar System. 30 sec! Asteroids, Meteoroids, Comets • • The solar system contains other objects than moons and planets. Some of these objects include asteroids, meteoroids, and comets. Asteroids • • • • Asteroids are the next largest objects in the solar system after moons. Asteroids are rocky bodies that revolve around the Sun. Asteroids vary in shapes and sizes but are mostly made of iron, nickel, and stone. Most asteroids in the solar system can be found between Mars and Jupiter – this is called the asteroid belt. Meteoroids, Meteors, and Meteorites • Meteoroids are stone-like or metal-like material that travel through space. • They may have been formed from collisions between other bodies in the solar system or parts of planets. Meteoroids, Meteors, and Meteorites • When a meteoroid strikes the Earth’s atmosphere, they burn up in bright streaks and become meteors. • If a meteor survives and hits the ground, it is called a meteorite. What is the difference between a meteoroid, meteor, and a meteorite? Comets • • • • Comets are icy bodies that release gas or dust when heated. Comets’ orbits are long, narrow ellipses – more elliptical than any other orbit. They spend a very short amount of time near the Sun before swinging out beyond Pluto. They are usually very hard to see, but as they approach the Sun, they begin to release gas and dust and are lit up by the sunlight to form huge tails. Match ‘em Up! 30 sec! A. Meteoroid B. Meteor C. Meteorite 1. When an object from space survives Earth’s atmosphere and hits the ground. 2. Stone-like object that travels through space. 3. An object burning up in Earth’s atmosphere. Word Scramble Challenge! ASTEROID RDIAOTSE Definition: Second largest objects in the Solar System after moons, most of them are found between Mars and Jupiter. 30 sec! Turn and Talk What is the difference between asteroids, meteoroids, and comets? Think-Pair-Share Is there a possibility that there could be life elsewhere in the solar system? 20 min • • • • Solar System BINGO Each scholar has a different BINGO card. I will read the clues for different types of celestial bodies in the solar system or various vocabulary words. Silently use your notes to identify the word and mark it on your BINGO card. We will talk about the word before moving on. 25 min Independent Practice RAFT Activity Role: Travel Agent Audience: People who want to travel to outer space. Format: Travel Poster or brochure Topic: There are people interested in moving to outer space to live. Create a poster to present to them. Exit Ticket Complete the exit ticket silently. Turn in as you leave!!!!! You may pack up your things. STOP Cards S T O P Summarize: Summarize the day’s lesson and what we learned. Trait: What IB trait relates to the lesson? Objective: Re-state in your own words and say whether or not we met that objective for the day. Purpose: What was the purpose of this lesson?