* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab #2 Question Sheet
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
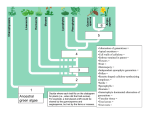
Name: ________________ September 2013 Biology 102 Laboratory 2: Seedless Plants Pre-Lab Directions: The answers to these questions can be found in the lab manual (p. 348 to 361) and text book (Chapter 32 – The Evolution of Plants: p. 661 to 669). 1) Plants are complex, eukaryotic, and multicellular organisms and their closest living ancestor are unicellular aquatic green algae charophytes in the phylum Chlorophyta. a. Recall last week’s lab, what protist species is in the phylum Chlorophyta? Draw and identify the food habits of this organism. 2) Plants have to overcome many challenges to living in a terrestrial environment (on the land). a. What is an adaptation that plants have to reduce water loss? b. Because terrestrial plants do not living in water, they need a way to get minerals, nutrients, and water to and from their cells. i. Identify the key evolution innovations that allows vascular plants to transport water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and nutrients (produced by photosynthesis) from the leaves to the roots. ii. Identify which plant from lab (Mosses or Ferns) have this adaptation. 3) A major evolutionary innovation that allowed plants to thrive in a terrestrial environment is called the alternation of generations. a. Define the life cycle called “alternation of generations”? Define gametophyte and sporophyte. Which type of plant tissue has haploid tissue and which type of tissue has diploid tissue? b. Describe the life cycle of mosses and their two generations. 4) Why do mosses and ferns have to live close to water and in moist environments?