* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Example: The Input Offset Voltage
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
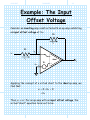
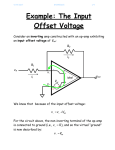
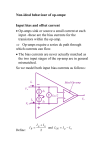
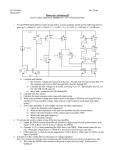
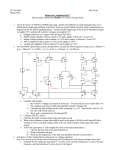
4/30/2017 769818055 1/3 Example: The Input Offset Voltage Consider an inverting amp constructed with an op-amp exhibiting an input offset voltage of Vos: R2 i2 R1 vi v1 - i1 v2 + Vos ideal + vo - + Applying the concept of a virtual short to the ideal op-amp, we find that: v1 0 Vos 0 Vos Thus, v1 v2 ! For an op-amp with an input offset voltage, the virtual “short” equation turns out to be: 4/30/2017 769818055 2/3 v1 Vos v2 Recall, however, that the input offset voltage is typically very small (i.e., Vos 5 mV ), so that v1 v2 . The current into each terminal of the op-amp is still zero, so that: i1 i2 where: i1 vi v1 R1 i2 v1 vo R2 and: Combining, we find: vi Vos Vos vo R1 R2 Performing a little algebra, we can solve this equation for output voltage vo : vo and rearranging: Vos R1 Vos R2 vi R2 R1 4/30/2017 769818055 vo v i 3/3 Vos Hey! We could have easily found this result by applying superposition! Note that if the input offset voltage is zero (its ideal value), this expression simply reduces to the normal inverting amplifier expression: R vo 2 vi R1 Thus, the term: R2 1 Vos R 1 represents an output offset voltage. Note this offset voltage is a constant with respect to vi --its value does not change, even if the input voltage is zero!.