* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Example: The Input Offset Voltage
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
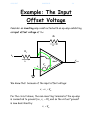
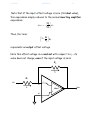
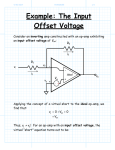
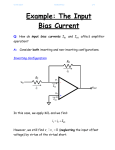
4/29/2017 840950635 1/4 Example: The Input Offset Voltage Consider an inverting amp constructed with an op-amp exhibiting an input offset voltage of Vos: R2 i2 R1 vin v- - i1 Vos v+ + ideal vout + - + We know that because of the input offset voltage: v v Vos For the circuit above, the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp is connected to ground (i.e., v 0 ), and so the virtual “ground” is now described by: v Vos 4/29/2017 840950635 2/4 The current into each terminal of the op-amp is still zero, so that from KCL: i1 i2 where form KCL and Ohm’s Law: i1 and: i2 vin v vin Vos R1 R1 v vout Vos vout R2 R2 Combining, we find: vin Vos Vos vout R1 R2 Performing a little algebra, we can solve this equation for output voltage vout : V R V R v R vout os 1 os 2 in 2 R1 and rearranging: R R vout 2 vin 1 2 Vos R1 R1 Q: Hey! Couldn’t we have easily found this result by applying superposition? A: Absolutely! 4/29/2017 840950635 3/4 Note that if the input offset voltage is zero (its ideal value), this expression simply reduces to the normal inverting amplifier expression: R vout 2 vin R1 Thus, the term: R2 1 V R1 os represents an output offset voltage. Note this offset voltage is a constant with respect to vi --its value does not change, even if the input voltage is zero!. R2 i2 R1 vin v- - i1 ideal + v+ + vout 4/29/2017 840950635 4/4