* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Take Home 11 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
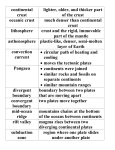
Take Home 11 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not write the questions… just the answers. 1) What kind of evidence do scientists use to locate boundaries of plates and interpret what type of boundary is present? A. matching fossil records D. the way the continental coastlines fit together like a B. similar rock layers puzzle C. distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes 2) What kind of movement on a plate boundary causes mountain building? A. Divergent movement C. Transform movement B. Convergent movement D. Biome movement 3) Which of the following discoveries caused science to re-evaluate its opinion of Wegener's hypothesis about continental drift? A. Sea floor spreading in the Atlantic Ocean B. Valley and delta land forms on Mars C. The coastlines of Africa and South America have similar fossils D. The global rate of volcanic activity has changed over time 4) If science accepts the conclusion that continents have drifted, what are they assuming is true? A. Gravity works the same on Earth as it does on other planets and stars in the universe B. Convection currents worked in the past the same way they work now C. The world's climate hasn’t changed a lot over time D. Carbon dating is an accurate way to measure age 5) Where are earthquakes most likely to occur on Earth? A. They are spread evenly around the globe B. On plate boundaries C. On continents D. On the sea floor E. In mountains Use the map to answer questions #6-9 6) Which symbols on the map show evidence of plate movement? A. hot spot B. active volcano C. plate boundary D. lines 7) Why are there more volcanoes where ocean and land meet? A. Wave action on land plate B. Ocean plate pulling away from land plate C. Land plate moving past ocean plane D. Ocean plate colliding with land plate 8) What type of plate boundary is located on the west side of Africa? A. Convergent C. Transform B. Divergent D. Strike/Slip 9) Where are the most volcanoes located? A. Atlantic Ocean B. Pacific Ocean C. African Continent D. Asian Continent 10) The earth’s crust is broken into pieces called plates. These plates interact with each other at boundaries. Which of the following is the best data to use when classifying plate boundaries? A. The length of the boundary between the two plates. B. The size of the two plates that meet at a boundary. C. The motion of the two plates relative to each other at the boundary. D. The speed at which the two plates are moving as they meet at a boundary. 11) Alfred Wegener proposed that 200 million years ago, continents broke apart from the supercontinent Pangaea and have drifted apart over time. This idea is known as continental drift. Which of the following is the best fossil evidence for continental drift? A. Fossils of the same land dwelling animals were found on widely separated continents. B. Fossils of the same ocean dwelling organisms were found in different oceans. C. Fossils of the same warm climate organisms were found on continents with warm climates. D. Fossils of the same freshwater organisms were found on areas with abundant freshwater. 12) How has technology changed scientists’ understanding of sea floor spreading and how it is evidence of plate tectonics? A. Earthquakes are evidence of changes in the ocean floor. B. The measurement of the weight of the ocean gave evidence of sea floor spreading. C. The ocean floor was mapped and studied using sonar and magnetometers. D. Scientists used computer measurements of volcanic activity to give details of the ocean floor. 13) Wegener’s theory of continental drift was not accepted until the mid-1900’s. Which of the following are technological advances that led to the acceptance of this theory and laid the ground work for plate tectonics? A. Sonar and magnetometers mapped the ocean floor and detected magnetic striping. B. Satellites created communication networks for scientists on other continents. C. Computer systems were used to simulate tectonic patterns on other planets. D. Seismometers were developed to accurately measure volcanic activity. 14) Which of the following explains the role of Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift and the development of the theory of plate tectonics? A. Wegener’s is the only scientist who worked on the continental drift hypothesis. B. A hypothesis usually has more evidence than a theory does. C. Wegener’s hypothesis was contradicted by recent scientific information. D. Evidence over the years has filled in the gaps in the continental drift hypothesis. 15) Consider the following three pieces of data. I. The continents on Earth fit together like a puzzle. II. The same plant fossils are found on many different continents. III. Climate data indicates that some continents in the Arctic once were tropical and warm. Which of the following best describes the relationship between the above statements? A. They are evidence for continental drift. D. There is no relationship. They are separate areas of B. They describe major areas of geologic studies. science. C. They help to explain why the plates on Earth move. Match the following words with the correct definition: 16) Inner Core _____ 17) Pangaea _____ 18) Divergent _____ 19) Strike Slip _____ 20) Continental Drift _____ 21) Sonar _____ 22) Basalt _____ 23) Granite _____ 24) Tectonics _____ 25) Asthenosphere _____ 26) Subduction _____ 27) Normal _____ 28) Outer core _____ 29) Crust _____ 30) Magma _____ 31) Mid-Ocean Ridge _____ 32) Lithosphere _____ 33) Rift _____ 34) 35) 36) 37) 38) Mantle _____ Reverse _____ Convergent _____ Transform _____ Plate _____ A. Fault that occurs on a divergent boundary. B. Hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s surface. C. Molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle. D. Dark, dense, igneous rock found in the ocean crust. E. Fault where the plates are converging. F. Theory that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. G. Deep valley that forms where two continental plates move apart. H. Usually light-colored rock that is found in continental crust. I. Layer of molten iron and nickel that surrounds the inner core of Earth. J. Rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and crust. K. System that uses sound waves to calculate the distance to an object. L. Name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and drifted apart into continents. M. Plate boundary where two plates move away from each other. N. Undersea mountain chain; divergent plate boundary. O. Plate boundary where two plates move toward each other. P. Layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer surface. Q. Process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle. R. Dense sphere of solid iron and nickel in the center of Earth. S. Type of fault where rocks on either side move past each other sideways. T. Type of boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions. U. Layer of hot, solid material between the crust and core. V. Section of the lithosphere that slowly moves over the asthenosphere. W. Soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats. 39) Essay (100+ words) 4 pts.--Wegener died on a research expedition in Greenland years before the theory of continental drift, one of the most ridiculed of scientific hypothesis in history, was accepted. Today is no different from the past. Often, scientific theories that are accepted today will be discounted or modified to fit newfound truths in the future. Theories that are rejected now may, in the future, be validated with newly-found evidence. What lesson can we learn from Alfred Wegner and how the scientific community treated him? Check the boxes of all the resources you used to answer the questions on this take home: Parents Siblings Internet Friends Blog, Assignments Other _________________ (describe) Email/Asking Teacher Notebook