* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review session for exam-I
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
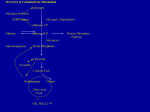
Review session for exam-III Q1. Which of these is able to cross the inner mitochondrial membrane? A. B. C. D. E. fatty acyl-CoA malonyl-CoA acetyl-CoA fatty acyl-carnitine none of the above can cross Q2. The normal sequence of action of these components of the hormonal hierarchy is: adrenal cortex hypothalamus anterior pituitary anterior pituitary adrenal cortex hypothalamus anterior pituitary hypothalamus adrenal cortex hypothalamus adrenal cortex anterior pituitary hypothalamus anterior pituitary adrenal cortex Q3. Describe five possible fates for glucose 6-phosphate in the liver. Q3 answer (1) conversion to liver glycogen; (2) dephosphorylation and release of glucose into bloodstream; (3) oxidation via the pentose phosphate pathway; (4) oxidation via glycolysis and the citric acid cycle; (5) oxidation to acetylCoA, which then serves as precursor for synthesis of triacylglycerols, phospholipids, and cholesterol. Q4. What is leptin? How does it function in the long-term maintenance of body mass? Q4 Answer Leptin is a small polypeptide that is produced in adipocytes and is carried by the blood to the brain. It is produced when there are adequate stores of lipid in the adipocytes and interacts with a receptor in the hypothalamus. This interaction produces a cascade of effects that tend to suppress appetite and increase energy expenditure. Q5. Which of the following cannot be used as an energy source by the brain? a. b. c. d. glucose ketone bodies fatty acids acetoacetate Q6. . Which of the following is a major effect of insulin binding to its receptor? a. autophosphorylation of tyrosine b. dephosphorylation of substrates such as IRS-1 c. binding of phosphatidylinositol-3kinase to the receptor Q7. What hormone(s) is (are) a signal of the "fed state"? a. b. c. d. Insulin Glucagon both insulin and glucagon aldosteron Q8. Which of the following is NOT true of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate? A. B. C. D. They can provide energy for brain cells. They allosterically modify other enzymes. They are produced from the acetyl CoA of fats. They cannot be used in liver. Q9. During prolonged starvation, what is the last cellular material to be utilized? a. b. c. d. Glycogen Fats Proteins Cholesterol Q10. Which of these can be synthesized by plants but not by humans? A. B. C. D. E. palmitate (18:0) stearate (20:0) linolenate [18:3(D9,12,15)] Arachidonic acid phosphatidylcholine Q11. Type 2 Diabetes is a disease characterized by overproduction of glucose by the liver and its underutilization by other organs. Which of the following is NOT a cause of diabetes? a.inability to produce insulin b.loss of ability to respond to insulin when it is produced c.the generation of enzymes in the blood that rapidly degrade insulin after release from the pancreas Q12. What are plasma lipoproteins? What is their general role in mammalian metabolism? Q13. The synthetic compound mevinolinic acid, also called lovastatin, is a potent competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reducdase (hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase). Predict and explain the effect of this drug on serum cholesterol levels in humans. Q14. The glycerol produced during the lipolysis of triglycerides A. is a waste product that is excreted from cells. B. is stored within the cell for future synthesis of tryglycerides. C. can be used as either a source of energy or for gluconeogenesis. Q15. Write additional enzymes to oxidize fatty acids that have double bonds. Q16. The degradation of an 18-carbon saturated fatty acid would be expected to yield how many NADH and FADH2 per fatty acid molecule? A. 6 B. 10 C. 7 D. 8 E. 9 Q17. The NADPH used in the reductive steps of fatty acid biosynthesis comes from a. b. c. one NADPH being generated per citrate leaving the mitochondria. the degradation of glucose via the pentose phosphate pathway exclusively both a and b. Q18. Cholesterol is synthesized from: A. B. C. D. E. acetyl-CoA. choline. lipoic acid. malate. oxalate. Q 19. Which of these statements about the regulation of cholesterol synthesis is not true? A. B. C. D. E. Cholesterol acquired in the diet has essentially no effect on the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver. Failure to regulate cholesterol synthesis predisposes humans to atherosclerosis. High intracellular cholesterol stimulates formation of cholesterol esters. Insulin stimulates HMG-CoA reductase. Some metabolite or derivative of cholesterol inhibits HMG-CoA reductase. Q20. The synthesis of fatty acids and their breakdown by b oxidation occur by separate pathways. Compare the two paths by filling in the blanks below. (Some blanks may require more than one answer.) Activating group Electron carrier coenzyme(s) Basic units added or removed Cellular location of process Synthesis b oxidation ————————————————— _______________ ___________ _______________ ___________ _______________ ____________ _______________ ____________ Q20. Answer Activating group Electron carrier coenzyme(s) Basic units added or removed Cellular location of process Synthesis b oxidation ————————————————— acyl carrier protein CoA—SH NADPH NAD+ malonyl- and acetyl acetylcytosol in animals mitochondrial matrix Q21. Which of the following metabolic pathways and intracellular localization of the pathway are correctly paired a. b oxidation of fatty acids; mt. matrix b. Citric acid cycle; cytoplasm c. Fatty acid synthesis; cytoplasm d. Glycolysis; mitochondrial matrix e. Pentose phosphate pathway; peroxisomes Q22. Which of the following statements about metabolism in the mammalian liver is false? A. B. C. D. E. Most plasma lipoproteins are synthesized in the liver. The enzymatic complement of liver tissue changes in response to changes in the diet. The liver synthesizes most of the urea produced in the body. The presence of glucose 6-phosphatase makes liver uniquely able to release glucose into the bloodstream. Under certain conditions, most of the functions of the liver can be performed by other organs. Q23. The Cori cycle is: A. B. C. D. E. the conversion of lactate to pyruvate in skeletal muscle to drive glycogen synthesis. the interconversion between glycogen and glucose lphosphate. the production of lactate from glucose in peripheral tissues with the resynthesis of glucose from lactate in liver. the synthesis of alanine from pyruvate in skeletal muscle and the synthesis of pyruvate from alanine in liver. the synthesis of urea in liver and degradation of urea to carbon dioxide and ammonia by bacteria in the gut. Q24. The largest energy store in a wellnourished human is: A. B. C. D. E. ATP in all tissues. blood glucose. liver glycogen. muscle glycogen. triacylglycerols in adipose tissue. Q25. What distinguishes eicosanoids from other potent biological signaling molecules such as epinephrine? Answer for Q25 Eicosanoids are paracrine hormones: they generally do not move long distances between their points of release and their points of action. Remember the terms: endocrine, paracrine, autocrine Q26. In animals, the carbon backbone of glucose _____ be metabolically converted and stoichiometrically utilized for synthesis of fatty acids; in animals, the carbon backbone of fatty acids _____ be metabolically converted and stoichiometrically utilized for synthesis of glucose. a. b. c. d. e. Can; can Can; cannot Can only; can only Cannot; can Cannot; cannot Q27. Which of the following intermediate in cholesterol biosynthesis is the substrate for the enzyme at the key regulatory step of the pathway a. b. c. d. e. Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA 3-isopentyl pyrophosphate Malonyl-CoA Mevalonate Q28. Which of the following best describes, in order, the complete series of catalyzed reactions that occurs as a molecule of acyl-CoA is shortened by one two-carbon unit during fatty acid degradation a. b. c. d. e. Hydration; oxidation; thiolysis Oxidation; hydration; oxidation; thiolysis Oxidation; hydration; reduction; thiolysis Oxidation; hydration; thiolysis Reduction; hydration; oxidation; thiolysis Q28 Answer a. b. c. d. e. Hydration; oxidation; thiolysis Oxidation; hydration; oxidation; thiolysis Oxidation; hydration; reduction; thiolysis Oxidation; hydration; thiolysis Reduction; hydration; oxidation; thiolysis Q29. During b oxidation, the carbon backbone of fatty acids is converted into which of the following a. b. c. d. e. Carbon dioxide Pyruvate Acetyl groups Malonyl groups Succinyl groups Q29 answer a. b. c. d. e. Carbon dioxide Pyruvate Acetyl groups Malonyl groups Succinyl groups Q30 The following figures were selected to review them. You need to study each figure in detail and understand what is being emphasized there, GOOD LUCK!