* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Algebra 1 Syllabus
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Series (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Limit of a function wikipedia , lookup
Sobolev space wikipedia , lookup
Matrix calculus wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
History of calculus wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Lebesgue integration wikipedia , lookup
Multiple integral wikipedia , lookup
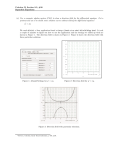
1 AP Calculus Syllabus Teacher: Anthony Melton Course Description: AP Calculus is a college-level course for students who have the ability and desire to pursue college level study in high school. The content covered will include a semester of differential calculus and a semester of integral calculus. College credit can be obtained by passing the AP Exam. Due to deadlines, after-school and Saturday classes may be required. Prerequisites: Algebra 1, Algebra 2, Geometry, and Pre-Calculus (honors level courses preferred). Admittance to the class will be based on previous mathematics course grades, teacher recommendations, and a student application. Textbook: Calculus of a Single Variable Ninth Edition Brooks/Cole Copyright 2010 Belmont, CA ISBN 0-547-21290-9 Students will cover units on the following topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Preparation for Calculus Limits and Their Properties Differentiation Applications of Differentiation Integration Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Differential Equations Applications of Integration AP Calculus Examination Review Grading Scale: 90-100 80-89 70-79 60-69 0-59 A B C D F 2 Grades are determined as follows: Tests and quizzes 60% Daily assignments, homework, open responses, notebooks, etc. 40% Notebooks will include the title of each section, all notes and examples from the board kept in order according to date, a section for AP Exam Questions, and an assignment page. Materials needed for class: Three ring binder—two-inch Loose leaf paper Tabs for notebook Pencils Graph paper Graphing calculator TI-84 Preferred Classroom rules: Be on time Be prepared Respect others Follow student handbook No food or drink in class Late Work Policy: All work must be turned in on time to receive full credit. Any late work, if accepted, will lose 20 points per day. Class Attendance: It is very important to attend class every day. When class is missed for any reason, it is your responsibility to get all notes and assignments for the day(s) missed and complete the assignments as soon as possible. 3 Basic Understanding: We are here to do a job. Mine is to teach, yours is to learn. It will take teamwork for us to be successful in accomplishing this task. Therefore, behaviors that prohibit me from doing my job or you from doing yours will not be tolerated. Maximum Time Usage: It is very important for us to maximize our time usage in this class. When time is wasted, the result is that you will spend more time at home doing homework. Extra Class Time: Homework discussions will be scheduled after school as needed. AP Calculus AB study sessions will be held on 3 Saturdays prior to the AP Exam. Every student is expected to attend these Saturday sessions. Also, when we miss school due to a snow day, you will be expected to complete a snow packet assignment for each day missed. These will be collected on the next day that school is in attendance. If the number of snow days is excessive, more Saturday meetings may be required. Unit 1 Preparation for Calculus (1-2 weeks) Sketch the graph of an equation Find the intercepts of a graph Test a graph for symmetry with respect to an axis and the origin Find the points of intersection of two graphs Interpret mathematical models for real-life data Find the slope of the line passing through two points Write the equation of the line with a given point and slope Interpret slope as a ratio or as a rate in a real-life application Sketch the graph of a linear equation in slope-intercept form Write equations of lines that are parallel or perpendicular to a given line Use function notation to represent and evaluate a function Find the domain and range of a function Sketch the graph of a function Identify different types of transformations of functions Classify functions and recognize combinations of functions Fit a linear model to a real-life data set Fit a quadratic model to a real-life data set Fit a trigonometric model to a real-life data set 4 Unit 2 Limits and Their Properties (2-2.5 weeks) Understand what Calculus is and how it compares to Pre Calculus Understand that the tangent line problem is basic to Calculus Understand that the area problem is basic to Calculus Estimate a limit using a numerical and graphical approach Learn different ways that a limit can fail to exist Evaluate a limit using properties of limits Develop and use a strategy for finding limits Evaluate a limit using dividing out and rationalizing techniques Evaluate a limit using the Squeeze Theorem Determine continuity at a point and continuity on a open interval Determine one-sided limits and continuity on a closed interval Use properties of continuity Understand and use the Intermediate Value Theorem Determine infinite limits from the left and from the right Find and sketch the vertical asymptotes of the graph of a function Unit 3 Differentiation (5-5.5 weeks) Find the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a point Use the limit definition to find the derivative of a function Understand the relationship between differentiability and continuity Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Multiple Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Sum and Difference Rules Find the derivatives of the sine and cosine functions Use derivatives to find rates of change Find the derivative of a function using the Product Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Quotient Rule Find the derivative of a trigonometric function Find a higher-order derivative of a function Find the derivative of a composite function using the Chain Rule Find the derivative of a function using the General Power Rule Simplify the derivative of a function using algebra Find the derivative of a trigonometric function using the Chain Rule Distinguish between functions written in implicit form and explicit form Use implicit differentiation to find the derivative of a function Find a related rate Use related rates to solve real-life problems 5 Unit 4 Applications of Differentiation (5-5.5 weeks) Understand the definition of extrema of a function on an interval Understand the definition of relative extrema of a function on an open interval Find the extrema on a closed interval Understand and apply Rolle’s Theorem Understand and apply the Mean Value Theorem Determine intervals on which a function is increasing or decreasing Apply the First Derivative Test to find relative extrema of a function Apply the First Derivative Test to find relative extrema of a function Determine intervals on which a function is concave upward or concave downward Find any points of inflection of the graph of a function Apply the Second Derivative Test to find relative extrema of a function Determine (finite) limits at infinity Determine the horizontal asymptotes, if any, of the graph of a function Determine infinite limits at infinity Analyze and sketch the graph of a function Solve applied minimum and maximum problems Approximate a zero of a function using Newton’s Method Understand the concept of a tangent line approximation Compare the value of the differential, dy, with the actual change in y, ∆y Estimate a propagated error using a differential Find the differential of a function using differentiation formulas Unit 5 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration (4-4.5 weeks) Write the general solution of a differential equation Use indefinite integral notation for antiderivatives Use basic integration rules to find antiderivatives Find a particular solution of a differential equation Use sigma notation to write and evaluate a sum Understand the concept of area Approximate the area of a plane region Find the area of a plane region using limits Understand the definition of a Riemann sum Evaluate a definite integral using limits Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals Evaluate a definite integral using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Understand and use the Mean Value Theorem for Integrals Find the average value of a function over a closed interval Understand and use the Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Understand and use the Net Change Theorem 6 Use pattern recognition to evaluate an indefinite integral Use a change of variables to evaluate an indefinite integral Use the General Power Rule for Integration to evaluate an indefinite integral Use a change of variables to evaluate an definite integral Evaluate a definite integral involving an even or odd function Approximate a definite integral using the Trapezoidal Rule Unit 6 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions (4-4.5 weeks) Develop and use the properties of the natural logarithmic function Understand the definition of the number e Find derivatives of functions involving the natural logarithmic function Use the Log Rule for Integration to integrate a rational function Integrate trigonometric functions Verify that one function is the inverse of another function Determine whether a function has an inverse function Find the derivative of an inverse function Develop properties of the natural exponential function Differentiate natural exponential functions Integrate natural exponential functions Define exponential functions that have bases other than e Differentiate and integrate exponential functions that have bases other than e Use exponential functions to model compound interest and exponential growth Develop properties of the six inverse trigonometric functions Differentiate an inverse trigonometric function Use the basic differentiation formulas for elementary functions Integrate functions whose antiderivatives involve inverse trigonometric functions Use the method of completing the square to integrate a function Review the basic integration rules involving elementary functions Unit 7 Differential Equations (2-2.5 weeks) Use initial conditions to find particular solutions of differential equations Use slope fields to approximate solutions of differential equations Use separation of variables to solve a simple differential equation Use exponential functions to model growth and decay in applied problems Recognize and solve differential equations that can be solved by separation of variables Use differential equations to model and solve applied problems 7 Unit 8 Applications of Integration (2-2.5 weeks) Find the area of a region between two curves using integration Find the area of a region between intersecting curves using integration Describe integration as an accumulation process Find the volume of a solid of revolution using the disk method Find the volume of a solid of revolution using the washer method Fid the volume of a solid with known cross sections Unit 9—AP Calculus Examination Review (5-6 weeks) Review the major topics on the AP Calculus AB Examination Take two AP Calculus AB practice exams (On two separate Saturdays in the month prior to the AP Calculus Exam—if needed)