* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction Comes to Georgia
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
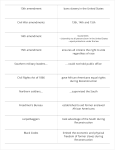
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction Comes to Georgia 1. What was the Freedman’s Bureau, and what role did it play during Reconstruction? A government agency established in 1865 to help both freed slaves and poor whites cope with their everyday problems by offering them clothing, food, and other necessities. They later focused on providing education and job training to freed slaves. 2. Define Reconstruction: A plan to rebuild the South and restore the southern states to the Union as quickly and easily as possible. 3. What was Lincoln’s two-step plan for Reconstruction? a. All southerners had to take an oath of allegiance to the U.S. b. Once 10% of the voters in each state had taken the oath, the state could form a government and ask for readmission to the Union 4. Why did Congress and Lincoln disagree over Reconstruction? Congress felt southern states should be punished for the war 5. What was Johnson’s original plan for Reconstruction? Same as Lincoln’s except the group who qualified to take the oath was smaller (any civilian or Confederate government official was not allowed a general pardon) 6. Define disfranchised: taking away the right to vote from a particular group of people 7. What three additions were made to Johnson’s plan for Reconstruction after radicals complained? a. Had to approve 13th amendment b. Had to nullify ordinances of secession c. Had to promise not to repay institutions and individuals who had funded the Confederacy 8. What was the purpose of the 13th amendment? Abolished slavery 9. What were the Black Codes? Laws passed in south to restrict the rights of freedmen. These laws determined the types of jobs they could hold, established labor hours (sunup to sundown), etc. 10. How did Congress respond to the Black Codes? Passed the Civil Rights Act of 1866 which gave citizenship to African Americans and gave the federal government the right to intervene in issues of discrimination. The 14th amendment was also passed at this time 11. What was the purpose of the 14th amendment? Gave citizenship to freed men, and guaranteed equal protection under the law 12. What did the Congressional reconstruction plan require of southern states? Had to ratify 14th amendment 13. What happened as a result of the southern states refusing to ratify the 14th amendment? Invalidated the new governments and placed the states under military control 14. What were carpetbaggers? Northerners who moved south after the war 15. What were scalawags? Southerners who supported the Radical Republican congress’ reconstruction plan 16. What three things were approved during the Constitutional Convention of 1867? a. Civil rights for all Georgia citizens b. Free public education for all children c. Married women were allowed to control their own property 17. What type of governor was elected in Georgia in 1868 for the first time as a result of the African American vote? Republican 18. Who was Henry McNeal Turner? One of 29 black legislators elected to the Georgia General Assembly after the Election of 1868 19. What happened to the 32 African Americans elected to the Georgia General Assembly in 1868? They were expelled after it was determined they had been given the right to vote, but not the right to hold office 20. What was the Ku Klux Klan? A secret organization (formed in Pulaski, TN in 1865) that tried to keep freed men from exercising their new civil rights 21. What methods of terrorism did the Ku Klux Klan use to intimidate African Americans? Beatings, whippings, and murder 22. What right did the 15th amendment give to all Americans? It gave all male citizens the right to vote 23. What four things did Georgia do to finally get full readmission to the Union? a. Ruled that blacks were allowed to hold office b. Reseat the expelled African American representatives in the General Assembly c. Approve the 14th amendment d. Ratify the 15th amendment 24. What political party regained control of Georgia after the 1870 elections? Democratic 25. Define sharecropping: Landowner provided land, a house, farming tools & animals, seed and fertilizer to the worker. Workers agreed to give the owner a share of the harvest. 26. Define tenant farming: Similar to sharecropping except the tenant provided tools, seed & fertilizer. At the end of the year the tenant paid the landowner or shared the harvest. 27. What happened to the soil as a result of all of the demands put on it by continual farming? Soil was ruined from the high demands put on it by farmers 28. What did this mean for farmers? Farmers became poorer and poorer 29. Which crop was still the most important in Georgia? cotton 29. Which businesses in Georgia expanded during the period of Reconstruction? Industry (textile mills), banking, railroads & shipping businesses