* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP World History
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
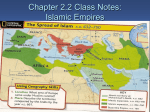
AP World History The First Global Civilization: The Rise and Spread of Islam Mr. Soff I. Desert and Town: The Pre-Islamic Arabian World Islam appeared first on the Arabian Peninsula, an area occupied by nomadic pastoralists and on the periphery of the “civilized” zones Much of the peninsula is desert, which supported both goat and camel nomadism among peoples called Bedouin. Sedentary agricultural communities were limited to the far south of the peninsula, and trading towns like Mecca developed along or near the coasts. The Bedouin tribal culture of clan loyalty and rivalry provided a critical backdrop for the emergence of Islam. Women enjoyed somewhat greater freedom, art was largely nonexistent, and religion was a blend of animism and polytheism. II. The Life of Muhammad and the Genesis of Islam In the 7th century CE, a new religion arose on the Arabian peninsula. Built on the revelations received by the prophet Muhammad, a merchant and trader from Mecca, the new faith won over many camel-herding tribes on the peninsula within decades. Islam united Arabs and provided an important ethical system. Though initially an Arab religion, Islam’s beliefs and practices (including the five pillars) eventually made it one of the great world religions. III. The Arab Empire of the Umayyads Although some Bedouin tribes renounced their allegiance to Islam after Muhammad’s death in 632 CE, the Prophet’s followers were able to conduct military campaigns restoring the unity of the Islamic community. Abu Bakr assumed leadership of the umma (community of the faithful). Ali, Muhammad’s son-in-law and cousin, was passed over, which would later cause an important rift in the Islamic community. Once the rebellious tribesmen were brought back into the umma, Muslim armies began to launch attacks on neighboring civilizations outside of Arabia. Within a short period of time, Arab armies exploited weaknesses in their enemies’ forces and captured Mesopotamia, northern Africa, and Persia. A new dynasty, the Umayyads, ruled this Arabic empire. The question of succession soon led to the Sunni-Shi’a split. Umayyad extravagance ultimately led to the empire’s overthrow. IV. From Arab to Islamic Empire: The Early Abassid Empire The Abbasid rulers moved the empire’s capital to Baghdad, and lived a life of luxury which alienated many followers. The Abbasids fully integrated the mawali, or non-Arab Muslims, into the Islamic community. Merchants and landlords grew in wealth and status. Cities grew, the dhow improved sailing, and slave labor became increasingly important. Arab scholarship and learning flowered, as scholars sought to preserve to great works of the classical Greek and Roman civilization. Key Terminology: 1. shaykhs: 2. Quraysh: 3. Ka’ba or Ka’aba: 4. hijira: 5. jihad: 6. Copts and Nestorians: 7. Mu’awiya: 8. jizya: 9. dhimmi: 10. hadiths: 11. wazir: 12. mosque: 13. minbar: 14. ayan: Focus Questions: 1. What was the general name of the nomadic Arabic tribes? 2. Describe the status of women in Bedouin society (before Islam) and during the Abbasid Empire. 3. What was the nature of the material culture of Bedouin society? 4. What was Muhammad’s teaching with respect to the revelations of other monotheistic religions? 5. What was the initial response of the Umayyads to Muhammad’s new faith? 6. What was the principle advantage of the Islamic concept of the umma? 7. What was the issue that confronted Muslims following Muhammad’s death, and the issue which eventually split Muslims into Shi’ite and Sunni sects? 8. What was the largest weakness of the early Muslim empires? 9. Why didn’t Arab warriors want to convert large numbers of people to Islam? 10. These were the wars to defeat rival prophets and restore the unity of Islam. 11. The office of the political and religious successor of Muhammad was called? 12. What was the result of the civil war between Ali and the Umayyads after the assassination of Uthman? 13. This famous battle in southern Iraq (680 C.E.) permanently set the split between the Sunni and Shi’a sects. 14. What was the Umayyad attitude towards other religions? 15. What was the nature of citizenship within the Umayyad Empire? 16. What was the most significant of the transformations brought about by the Abbasids’ rise to power? 17. What was the nature of slavery within the Abbasid social system? 18. What was the nature of the economy of the Abbasid period? 19. What was the primary cultural contribution of the Muslims during the Abbasid period? 20. What were some of the differences between the Abbasid Empire and Umayyad Empire?