* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is a city-state?
Survey
Document related concepts
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
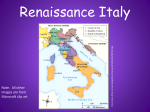
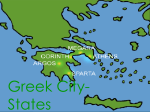
What is a city-state? A city-state is a region that is independently ruled by a major city. Italy wasn't one unified country, but a number of small independent city-states. Who were the aristocrats or “Urban Noble”? In Medieval Europe, Nobles got their wealth from land, not trade. In fact, they looked down on trade and believed themselves to be above the town merchants. In the Italian city-states, old noble families moved to the cities mixing with wealthy merchants and decided that money from trade was just as good as money from land. These new “Urban Nobles” became known as aristocrats. Aristocrats copied the manners and lifestyle of noble families. Soon, the sons and daughters of the “old nobles” and aristocrats married and eventually they blended together to become the upper class (special people) of the city-states. How Were Italian City-States Run?At first, many of the city-states were republics, or representative democracies, controlled by its citizens. Not everyone was a citizen, however, only the artisans and merchants who had membership in the city’s guilds were citizens. Some of these cities were run by elected leaders. In Venice, the head of government was the duke, or doge (DOHj). Others, such as Florence, were controlled by the powerful families, like the Medici family. Were there “issues” in the City-States? Politics on the Italian Peninsula was “complicated”. Within each city, the rulers had to keep the poor from rebelling and prevent wealthy people from seizing power. They had to make deals with merchants, bankers, landlords, church leaders, and mercenaries (people hired for military purposes). Fighting often broke out between city-states. Italians used diplomacy, or the art of negotiating, or making deals, with other countries. Each city-state sent ambassadors to live in other city-states and act as representatives for their city. Why were City-States important? The wealth of the Italian citystate played an important role in the Renaissance. They all had access to trade routes connecting Europe with Asian markets. Also, they serve as trading centers for distribution of goods to northern Europe. This wealth allowed prominent families to become Patrons, people who support artists, scientists, and philosophers spurring on new ideas and artistic movements. Florence: Florence, the “city of flowers,” is where the Renaissance first began. Located in the hill country of north-central Italy, Florence prospered because of the wool industry. Sheep were raised in the rock hill country of central Italy, and Florence was a center of wool processing. A university was built by 1349 AD. During most of the Renaissance, wealthy merchants dominated Florence. It was the first city-state to gain great wealth It was ruled by the powerful Medici Family who used their money to support artists such as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo. One of the early architectural achievements of the Renaissance was the massive dome on the Florence Cathedral. Florence was known for its textile production as well as a banking center. Milan: In the early 1400s, the duchy (ruled by a duke) of Milan was still a Middle Ages city focused on war and conquering Florence. However, the Sforza family took over in 1450. They brought peace to the region and with peace came the new ideas and art of the Renaissance. It was one of the richest cities controlling trade through the Alps on the northern Italian Peninsula. Milan was famous for its metalwork which included suits of armor. Venice: Venice was founded in the 400s AD, by people fleeing from Barbarians. They settled on a group of islands on the northeastern edge of the Italian peninsula. Shipbuilding was the primary industry in Venice. During the Crusades, Venetian ships provided transportation to the Holy Land. By the 13th century, Venice was the most prosperous city in Europe. The city became rich by collecting taxes on all merchandise brought into its harbor, especially spices and silk. Venice built huge warships that protected the valuable cargo of its merchant ships from pirate raids. With the vast wealth from trade, many of the leading families of Venice vied with one another to build the finest palaces or support the work of the greatest artists. However, when the Ottoman Empire conquered Constantinople, Venice's trade empire began to shrink. Venice controlled the seas around the east coast of Italy and was famous for its artistic glassware. Rome: The pope ruled both the Catholic Church and the city-state of Rome, known as the Papal States. A university was built by 1303 AD. Much of the city of Rome was re-built under the leadership of Nicholas V beginning in 1447. Popes became patrons of the arts and supported the Renaissance through commissions to artists such as Raphael and Michelangelo. Michelangelo worked as architect on St. Peter's Basilica and painted the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel. Naples: The city-state of Naples ruled much of southern Italy at the time of the Renaissance, in the city-state known as the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. It was one of the last city-states to embrace the movement, but in 1443 King Alfonso I conquered the city. He supported Renaissance artists, writers, and philosophers. Naples also became known for its music and is where the mandolin was invented. Also, it had a university by 1224 AD. Naples was captured by Spain in 1504. Genoa: Genoa, located on the western coast of Italy, controlled trade routes in the western Mediterranean Sea. Trade, shipbuilding and banking helped support one of the largest and most powerful navies in the Mediterranean. After the Black Death hit Genoa, the government became like Venice, adopting a Doge. The Bank of Saint George, founded in 1407, is among the oldest in the world and has played an important role in the city’s prosperity since the middle of the 15th century.[ Ferrara: Located between Venice and the Papal States, Ferrara was ruled by the powerful d'Este family. They achieved wealth and influence through alliances, or partnerships with France and Spain and going against the Pope. Alfonsod’Este, Duke of Ferrara, created a truly magnificent place, attracting famous writers (Ariosto), poets (Petrarch) and painters (Bellini & Titian). The Duke's art collection was to become famous. The city-state of Ferrara was also known for its music and theater. Urbino: Before coming under control of the Papal States, the duchy (ruled by a duke) of Urbino prospered under the rule of,Federico da Montefeltro, Duke of Urbino from 1444 to 1482. It hosts the University of Urbino, founded in 1506, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Urbino. The City-State of Urbino was known for its library as well as its beautiful ceramics. 1. Compare and Contrast Ancient Greece/Rome with the Renaissance….focus paragraphs 1-5 for assistance. 2. Compare and Contrast the Middle Ages with the Renaissance…..focus on paragraphs 2-4 for assistance. 3. How did the city-states and the people living in them impact the Renaissance? 4. Which city-state(s) seem to be the most powerful? Why? Which city-state(s) would you most like to be a part of? Why?