* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What was the Renaissance?
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance painting wikipedia , lookup
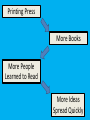
RENAISSANCE 800 A.D. 1095 A.D. 1233 A.D. Feudalism begins in Europe 1346 A.D. First Crusade Inquisition 1350 A.D. Black Death arrives in Europe RENAISSANCE BEGINS During the middle ages much of the great advancements made by the Greeks and the Romans had been forgotten due to the decline of living conditions in Western Europe. People went from living comfortable lives with good jobs and educations, to living in very poor conditions, where there was constant turmoil, war, poverty, and hunger. This time period is known as the dark ages. The dark ages lasted for hundreds of years, as many generations of individuals lived and died in these terrible conditions. Then in the middle A.D. 1300s things slowly began to improve. People began again to discover the arts, and technologies of the Romans and Greeks, making life a little easier. We call this period of time the Renaissance. The Renaissance began around A.D. 1350 in Italy, and continued until about A.D. 1600. What was the Renaissance? • Period following the middle ages (1350-1550) • Means “Rebirth” of classical Greek and Roman art and learning. • Began in Italy What was the Renaissance? After years of death and destruction, Europeans began looking to the past when times seemed better. What is Humanism? During the Renaissance, Europeans began to focus on the individual. Many thought that people could help make the world better. What is Secularism? • Religion was still very important. • But human success was also important. • People became more secular. • Secular means they were more interested in this world than religion and getting to heaven. PAGE 2 (CITY-STATES) ITALIAN CITY-STATES Why Italy? 1) Center of the old Roman Empire 2) Italy’s city-states became very wealthy Ruins and art surrounded the Italians and reminded them of their past They could pay painters, sculptors, architects, and artists to produce new works 3) City-states competed with each other Florence, Venice, Genoa, Milan, and Rome Italian City-States • During the Middle Ages, no ruler was able to unite Italy into a single kingdom. • Roman Catholic Church did not want a powerful kingdom in Italy • City-states fought each other • City-states became very wealthy : which helped keep them independent • Made money through trade (geography) Florence FLORENCE • • • • • No city was more famous At first grew wealthy from trade Trade brings in different types of coins Different types of coins : banks Later Florence became wealthy through BANKING Venice • the wealthiest city-state of all was Venice • built on swampy islands in northern Italy • today many streets are just canals • grew wealthy through ship building PAGE 3 •Polo (POH-loh) •Medici (MEH-duh-chee) •Machiavelli (Ma-kee-uh-VEH-lee) MARCO POLO He was a merchant from Venice who journeyed to China. He was sent on business all over China and learned more about Asia than any other European. He published a book about his travels. His stories got Europeans interested in China. MEDICI FAMILY •Goods from all around the world were pouring into Italy • Merchants needed to know the value of foreign coins • Bankers began exchanging and lending money • The Medici family became Florence’s richest family and were bankers NICCOLO MACHIAVELLI He was a diplomat in Florence who wrote a book called The Prince. He wrote that rulers should not worry about being good, but should do anything to keep their power. Machiavellian: being tricky and not thinking about being good. Everyone realizes how praiseworthy it is for a prince to honor his word and to be straightforward rather than crafty in his dealings; “ nonetheless experience shows that princes who have achieved great things have been those who have given their word lightly, who have known how to trick men with their cunning, and who, in the end, have overcome those abiding by honest principles . . . . A prince, therefore, need not necessarily have all the good qualities I mentioned above, but he should certainly appear to have them . . . . He should not deviate from what is good, if that is possible, but he should know how to do evil, if that is necessary.” --The Prince, Niccolò Machiavelli, George Bull, trans., 1981 PAGE 4 HUMANISM •Was a new way of understanding the world •Humanist believed that humans and the individual were important, they wanted to balance religion and reason •Italians began to study ancient Greek and Roman works •Francesco Petrarch: famous humanist poet and scholar who studied ancient Roman writings He told Europeans to look for Latin writings in monasteries New libraries were built to hold these writings Known as the Father of the Italian Renaissance HOW DID HUMANISM AFFECT SOCIETY? •Humanist scholars began to study many different topics. • Increases knowledge for society PAGE 5 Da Vinci (duh VIHN chee) Alighieri (a luh GYEHR ee) Michelangelo (My kuh LAN juh loh LEONARDO da VINCI Leonardo da Vinci was a famous Italian scientist, artist and inventor. He sketched inventions for early helicopters, gliders, and tanks. He also painted The Last Supper. He is best known for his painting, The Mona Lisa. WHEN I SAY DA VINCI, YOU SAY MONA LISA! Dante Alighieri Dante Alighieri was a poet who wrote The Divine Comedy. This long poem, 14,000 lines, tells of a journey from hell to heaven. It was so widely read because it was written in the vernacular. Dante’s Inferno DANTE = DIVINE COMEDY Johannes Gutenberg Johannes Gutenberg invented the printing press which helped spread humanist ideas faster. The Gutenberg Bible was the first European book made on the new press. Printing Press More Books More People Learned to Read More Ideas Spread Quickly MICHELANGELO BUONARROTI He painted what the Sistine Chapel in Rome. He sculpted the statue David as well as Moses. PAGE 6 Shakespeare (SHAYK spihr) Cervantes (suhr VAN teez) Gutenberg (GOO tuhn BUHRG) WILLIAM SHAKESPEARE William Shakespeare was a great English writer who wrote such tragedies as Romeo and Juliet and Hamlet. MIGUEL DE CERVANTES Miguel Cervantes was a Spanish author who is widely known for his novel, Don Quixote de la Mancha. PAGE 7 Art and Frescos How did medieval and Renaissance artists differ? MEDIEVAL • Not meant to look realistic (birth of Jesus) • More symbolic RENAISSANCE • Followed Greek and Roman models • Tried to show people as they really were, realistic • Tried to show emotion • Three dimensional