* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rolling resistance wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Frictional contact mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
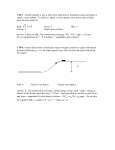
565324871 Name______________________ Page 1 of 4 AP Physics Date__________________ Notes: Friction Forces 4.6 Forces of Friction When an object is in motion on a surface or through a viscous medium, there will be a resistance to the motion o This is due to the interactions between the object and its environment This is resistance is called friction Friction is proportional to the normal force The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic friction The coefficient of friction (µ) depends on the surfaces in contact The direction of the frictional force is opposite the direction of motion The coefficients of friction are nearly independent of the area of contact Static friction acts to keep the object from moving If F increases, so does ƒs If F decreases, so does ƒs ƒs µ n The force of kinetic friction acts when the object is in motion ƒk = µ n Variations of the coefficient with speed will be ignored 565324871 Page 2 of 4 Block on a Ramp, Example Axes are rotated as usual on an incline The direction of impending motion would be down the plane Friction acts up the plane Opposes the motion Apply Newton’s Laws and solve equations Example 4.11: Suppose a block with a mass of 2.50 kg is resting on a ramp. If the coefficient of static friction between the block and ramp is 0.350, what maximum angle can the ramp make with the horizontal before the block starts to slip down? 565324871 Page 3 of 4 Example 4.12: The hockey puck in the diagram struck by a hockey stick, is given an initial speed of 20.0 m/s on a frozen pone. The puck remains on the ice and slides 1.20 x 102 m, slowing down steadily until it comes to rest. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction between the puck and the ice. 565324871 Page 4 of 4 Connected Objects Apply Newton’s Laws separately to each object The magnitude of the acceleration of both objects will be the same The tension is the same in each diagram Solve the simultaneous equations Example 4.13: A block with mass m1 = 4.00 kg and a ball with mass m2 = 7.00 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley, as shown in the diagram. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.300. a. Find the acceleration of the two objects and the tension in the string. b. Check the answer for the acceleration by using the system approach. Example 4.14: A block of mass 5.00 kg rides on top of a second block of mass 10.0 kg. A person attaches a string to the bottom block and pulls the system horizontally across a frictionless surface, as in the diagram. Friction between the two blocks keeps the 5.00 kg block from slipping off. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.350, what maximum force can be exerted by the string on the 10.0 kg block without causing the 5.00 kg block to slip?