* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 53 - Angelfire
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Mechanics of planar particle motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Proper acceleration wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
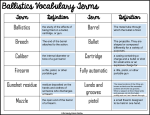
6E/S&J 2.42. A ball is thrown directly downward, with an initial speed of 8.00 m/s, from a height of 30.0 m. After what time interval does the ball strike the ground? 6E/S&J 2.43. A student throws a set of keys vertically upward to her sorority sister, who is in a window 4.00 m above. The keys are caught 1.50 s later by the sister’s outstretched hand. (a) With what initial velocity were the keys thrown? (b) What was the velocity of the keys just before they were caught? 6E/S&J 2.47. A baseball is hit so that it travels straight upward after being struck by the bat. A fan observes that it takes 3.00 sec for the ball to reach its maximum height. Find (a) its initial velocity and (b) the height it reaches. 6E/S&J 2.50. A woman is reported to have fallen 144 ft from the 17th floor of a building, landing on a metal ventilator box, which she crushed to a depth of 18.0 in. She suffered only minor injuries. Calculate (a) the speed of the woman just before she collided with the ventilator box, (b) her average acceleration while in contact with the box, and (c) the time it took to crush the box. 6E/S&J 2.51. The height of a helicopter above the ground is given by h = 3.00t3, where h is in meters and t is in seconds. After 2.00 s, the helicopter releases a small mailbag. How long after its release does the mailbag reach the ground? 6E/S&J 2.53. Automotive engineers refer to the time rate of change of acceleration as the “jerk.” If an object moves in one dimension such that its jerk J is constant, (a) determine expressions for its acceleration ax, velocity vx, and position x, given that its initial acceleration, speed, and position are axi, vxi, and xi, respectively. (b) Show that ax2 = axi2 + 2J(vx – vxi). 6E/S&J 2.55. The speed of a bullet as it travels down the barrel of a rifle toward the opening is given by the expression v = (-5.0 x 107)t2 + (3.0 x 105)t, where v is in meters per second and t is in seconds. The acceleration of the bullet just as it leaves the barrel is zero. (a) Determine the acceleration and position of the bullet as a function of time when the bullet is in the barrel. (b) Determine the length of time the bullet is accelerated. (c) Find the speed at which the bullet leaves the barrel. (d) What is the length of the barrel? 6E/S&J 3.6. If the polar coordinates of the point (x, y) are (r, ), determine the polar coordinates of the points (a) (-x, y), (b) (-2x, -2y), and (c) (3x, -3y). 6E/S&J 3.9. A plane flies from base camp to lake A, a distance of 280 km at a direction 20.0 north of east. After dropping off supplies, it flies to lake B, which is 190 km and 30.0 west of north from lake A. Graphically determine the distance and direction from lake B to the base camp. 6E/S&J 3.15. Each of the displacement vectors A and B shown in Figure P3.15 has a magnitude of 3.00 m. Find graphically (a) A + B, (b) A – B, (c) B – A, (d) A – 2B. Report all angles counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. 6E/S&J 3.27. Given the vectors A = 2.00i + 6.00j and B = 3.00i – 2.00j, (a) draw the vector sum C = A + B and the vector difference D = A – B. (b) Find solutions for C and D, first in terms of unit vectors and then in terms of polar coordinates, with angles measured with respect to the + x-axis. 6E/S&J 3.35. The helicopter view in Figure P3.35 shows two people pulling on a stubborn mule. Find (a) the single force that is equivalent to the two forces shown and (b) the force that a third person would have to exert on the mule to make the resultant force equal to zero. The forces are measured in units of newtons (abbreviated N). 6E/S&J 3.38. In an assembly operation illustrated in Figure P3.38, a robot moves an object first straight upward and then also to the east, around an arc forming one quarter of a circle of radius 4.80 cm that lies in an east-west vertical plane. The robot then moves the object upward and to the north, through a quarter of circle of radius 3.70 cm that lies in a northsouth vertical plane. Find (a) the magnitude if the total displacement of the object, and (b) the angle the total displacement makes with the vertical. 6E/S&J 3.49. Three displacement vectors of a croquet ball are shown in Figure P3.49, where |A| = 20.0 units, |B| = 40.0 units, and |C| = 30.0 units. Find (a) the resultant in unit-vector notation and (b) the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement.