* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name Date Period ______ STUDY GUIDE: ECOLOGY Matching: a
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
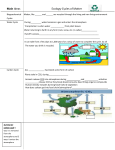
Name __________________________________________ Date ________________________________ Period _________ STUDY GUIDE: ECOLOGY Matching: a. Biosphere c. species e. biome g. population b. Community d. ecosystem f. ecology _____ 1. Scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment _____2. All life within the hydrosphere, geosphere (lithosphere), and atmosphere _____3. Arctic foxes that breed and produce offspring _____4. All the Crape Myrtle trees in the front of the school _____5. All the Crape Myrtle trees, grasshoppers, hawks, mice and ants living around the school _____6. All the Crape Myrtle trees, grasshoppers, hawks, mice and ants living around the school interacting with the soil, water, sunlight and air _____7. All the Rainforests of the world 8. On the food web below draw in the arrow heads according to the flow of energy. Then, place one of the following terms under each organism. Note: some terms may be used more than once Carnivore, Decomposer, Herbivore, Producer, Frist Order Consumer, Second Order Consumer 9. List a food CHAIN from the web above. Include the arrows of energy flow. CIRCLE the organism in your food chain with the most amount energy; put a SQUARE around the organism with the lease amount of energy 10. For each situation below, label as (A) Abiotic Factor or (B) Biotic factor _____a. Elephant drinking water from a pond _____c. A wasp stinging a human _____b. Bushes thriving in fertile soil _____d. Wind blowing the leaves off of a tree Define: 11. Biodiversity 12. Trophic Level 13. Pioneer (Keystone) species 14. Niche 15. Label a possible energy pyramid using organisms for a natural environment in Georgia. Then complete the amounts of energy for each level. Assume that the autotroph (producer) in your pyramid contains 35,000 kJ of energy. AMOUNT OF ENERGY _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ 16. The statements below have parenthesis with choices. For each, circle the correct term: a. In nature energy is (released, recycled) and matter is (released, recycled). b. In any ecosystem the 1st trophic level has the (least, most) energy and the (least, most) biomass c. A lion lives in a den; this is his (habitat, niche). This particular lion is in charge of hunting for the pride; this is his (habitat, niche) 17. Choose the correct term for each of the following scenarios: (a) mutualism (b) commensalism (c) parasitism _____i. Lichen is the name for an organism that is the result of a fungus and algae living closely with one another. The algae provides oxygen and food for the fungus. The fungus provides nutrients and CO2 for the algae. _____ii. Cattle Egrets are birds that forage in fields among cattle or other livestock. As cattle, horses, and other livestock graze on the field, they cause movements that stir up various insects. As the insects are stirred up, the Cattle egrets following the livestock catch and feed upon them. The egrets benefit from this relationship because the livestock have helped them find their meals, while the livestock are typically unaffected by it. _____iii. A fungus that grows on the skin uses the nutrients of the skin cells which eventually destroys the skin tissue. _____iv. A bacterium named Rhizobium lives on the roots of bean plants and provided them with a constant source of usable nitrogen. The plants cannot use the nitrogen gas in the air, but the bacteria convert it into nitrate, which the plant readily uses. The plants, in turn, provide the underground bacteria with a constant supply of energy from the products of photosynthesis. 18. Compare and contrast the following: CHEMOTROPH vs. PHOTOTROPH Biogeochemical (Nutrient) Cycles 19. Match the diagram to its title. Then use the diagrams to answer the questions that follow: _____H2O Cycle _____ Carbon Cycle _____ Nitrogen Cycle _____ Phosphorus Cycle _____ i. This process performed by bacteria returns nitrogen to the atmosphere. a. evaporation b. denitrification c. nitrogen fixation d. lightning _____ii. Water vapor moving into the atmosphere from plants. a. transpiration b. precipitation c. condensation d. photolysis _____ iii. Burning fossil fuels give off ____ gas into the atmosphere a. NH4 b. Oxygen c. Vapor d. CO2 _____iv. When this element is cycling through nature there is no gaseous phase where it is released into the atmosphere a. C b. H c. P d. O _____v. The niche of nitrifying bacteria in nature is to: a. move N deep into the soil b. photosynthesize c. fix un-usable N2 gas into a usable form d. eat away at sediment deposits from water runoff 20. Succession: Follow the ordered pictures in the diagram below (1 – 8) to answer the questions that follow: i. Which type of succession is shown in the diagram above? _______________________ ii. Circle the correct answer for each: Pictures 1 & 8 represent a (climax, pioneer) community while picture 5 shows a (climax, pioneer) community. iii. What term is used to describe the organisms moving back into the community in picture 5? ______________________ 21. Biomes: Fill in the chart below…be detailed & thorough! Biome Climate Plant (list some and describe how they have adapted to the environment) Animals (list some and describe how they have adapted to the environment) Desert Grassland Tiaga (coniferous) Temperate Forest Tropical Rain Forest Tundra Grassland (Chaparral, Savanna and/or Steppe) 22. Name the biome in which Georgia belongs? ____________________________________________ 23. Population Changes: Use the following graphs to answer the questions that follow: A. B. i. This graph shows exponential growth. __________ ii. This population has no limiting factors. _________ iii. What does the dashed line in Graph A represent?______________________________________ Explain: 24. List several density-dependent factors that effect and ecosystem and describe how they effect a population. Do the same for several density-independent factors. DENSITY-DEPENDENT vs. DENSITY-INDEPENDENT 25. Select one ecological problem caused by man (acid rain, pollution, habitat disruption, species endangerment, global warming, etc.). Analyze its impact and identify a possible solution. BE SPECIFIC and THOROUGH! 26. Choose 3 plant adaptations and describe how each allows the plant to withstand stressful environmental conditions. ● ● ● 27. Choose 3 animal adaptations and describe how each allows the animal to withstand stressful environmental conditions. 27. Human Impact Terms: Fill in the blanks with the letter of the appropriate terms. Use each term only once a. greenhouse effect b. sustainable use f. acid rain g. biodiversity k. nonrenewable resource l. p. pollutant ecosystem diversity endangered species u. smog q. v. aquaculture c. conservation h. habitat fragmentation m. global warming r. soil erosion d. ozone layer e. desertification i. extinction j. genetic diversity n. species diversity renewable resource o. deforestation t. invasive species s. w. biological magnification _____________ 1. resource that can regenerate quickly and that is replaceable _____________ 2. resource that cannot be replenished by natural processes _____________ 3. using natural resources at a rate that does not deplete them _____________ 4. wearing away of surface soil by water and wind _____________ 5. in areas with dry climates, a process caused by a combination of poor farming practices, overgrazing, and drought that turns productive land into desert _____________ 6. destruction of forests _____________ 7. farming of aquatic organisms _____________ 8. gray-brown mixture of chemicals that occurs as a haze in the atmosphere _____________ 9. harmful material that can enter the biosphere through the land, air, or water _____________ 10. rain containing nitric and sulfuric acids _____________ 11. biological diversity; the sum total of the variety of organisms in the biosphere _____________ 12. variety of habitats, living communities, and ecological processes in the living world _____________ 13. number of different species in the biosphere _____________ 14. Sum total of all the different forms of genetic information carried by all organisms living on Earth today _____________ 15. disappearance of a species from all parts of its geographical range _____________ 16. natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth’s atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and other gases _____________ 17. species whose population size is rapidly declining and will become extinct if the trend continues _____________ 18. splitting of ecosystems into small fragments _____________ 19. increasing concentration of a harmful substance in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain or food web _____________ 20. plants and animals that have migrated to places where they are not native _____________ 21. wise management of natural resources, including the preservation of habitats and wildlife _____________ 22. band of ozone, a gas made up of three oxygen atoms _____________ 23. increase in the average temperatures on Earth