* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2017_midterm_exam
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
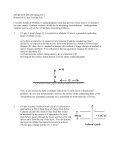
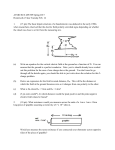
ATMO/ECE 489/589 Midterm Exam March 7, 2017 Everyone should answer Question #1. Then answer any 3 of the remaining 4 questions (please start each problem on a new sheet of paper) Allow about 15 minutes per question 1. (15 pts) Answer any three of the following short answer questions allowing about 5 minutes per question. 1a. We generally assume that the current density, Jz, is constant with altitude. When or why is that a reasonable assumption? 1b. What is meant by the term electrical mobility? Do positively-charged small ions have a larger, smaller, or the same electrical mobility than(as) negatively-charged small ions? Why? 1c. Would the small uncharged metal ball (hanging from the insulating string) be attracted to, repelled, or unaffected by the negatively charged bell in the figure at right? What if the left bell were positively charged? 1d. In 10 balloon flights between 1911 and 1913 Victor Hess observed that the rate of the of ionization of air initially decreased with increasing altitude. By 5000 ft. altitude, however, the rate of ionization was higher than at sea level. What explanation was given for these observations? Incidentally, Hess and Carl D. Anderson were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1936. 1e. What does q in the three expressions below stand for or represent? (underlined variables in bold font are vectors) J=2Nqv dn/dt = q - αn2 E = q Q r /( 4πεo r3 ) What does λ in the two expressions below stand for or represent? Er (r) = λ/(2πεo r) J = λE What does α in the two expression below stand for or represent? radon α decay 1f. dn/dt = q - αn2 Does the E field sounding shown at right indicate a cloud layer that is positively or negatively charged? How can you tell? 2. (15 pts) What is the capacitance of two 1 m x 1 m metal plates a distance d apart? You can assume that there is no bending of the electric field lines at the edges of the plates (i.e. for the purposes of determining the electric field it's as if the plates are of infinite horizontal extent). 3. (15 pts) A simplified small ion balance is given below dn/dt = q - αn2 - βnZ Derive an expression for n(t) for the case where ion-particle attachment is the dominant loss process and ion-ion recombination can be neglected. Note you are being asked to find n(t), not n at steady state. Assume that n(t) = 0 at t = 0. 4. (15 pts) Given the thunderstorm cloud charge distribution shown at right, determine the charge, q, that would be needed in order for the E field to be zero at D = 0 on the ground directly underneath the charge centers. Assume that the ground is a flat conducting surface. 5. (15 pts) On the first day of class we made a rough estimate of the time it would take the fair weather current in the global electric circuit to discharge (neutralize) all of the charge residing on the earth's surface: As charge on the earth is neutralized the electric field and also J (J = λ E) will also decrease. That is something we didn't include in the estimate above. Derive an expression, Q(t), for how the charge Q on an area A of the earth's surface will change with time taking into account the fact that E and J both depend on Q. Assume that Q = Qo at time = 0.