* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Week 10: Cardiovascular system
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
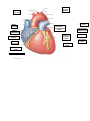
2016 NURS1004: Laboratory report Week 10: Cardiovascular system Laboratory activities 100 minutes Learning objectives Describe the structure if the heart and how blood travels through the chambers. Describe the differences between the pulmonary and systemic circulation. Describe what is occurring in the heart during systole and diastole. Explain the relationship between the electrical conductivity of the heart and the cardiac cycle Explain the relationship between blood pressure and the cardiac cycle Describe the events in the heart during various stage of the ECG. Preliminary work (complete before attending the laboratory session) Read and note Martini et al. 2015. pp. 711- 744 (anatomy of the heart and related blood vessels). Martini et al. 2012, pp. 670–694 Watch the video of the sheep heart dissection for Activity 3 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k7BxV9IdeMs accessed 27/1/15 Activity (10 mins) 1. Please complete these diagrams before the session as we have a lot to cover including the dissection of the heart. Identify the following structures then label the following diagrams (Martini et al. 2015, p. 714). Superior vena cava RIGHT ATRIUM RIGHT VENTRICLE Left pulmonary artery Auricle of left atrium Brachiocephalic trunk Left subclavian artery Auricle of right atrium Fat and vessels in anterior interventricular sulcus Fat and vessels in coronary sulcus Pulmonary trunk Left common carotid artery Arch of aorta Ascending aorta Descending aorta Moderator band Superior vena cava RIGHT ATRIUM Trabeculae carneae Left pulmonary arteries Aortic arch Left subclavian artery Right pulmonary arteries Pulmonary trunk Ascending aorta RIGHT VENTRICLE Inferior vena cava LEFT VENTRICLE Brachiocephalic trunk Papillary muscles Left common carotid artery Fossa ovalis Pulmonary valve Chordae tendineae LEFT ATRIUM Opening of Aortic valve coronary sinus Conus arteriosus Interatrial septum Pectinate muscles Interventricular septum Cusp of left AV (mitral) valve Left pulmonary veins Cusp of right AV (tricuspid) valve (Martini et al. 2015, p. 717) Laboratory activities Activity 1—Cardiovascular system models Working in your groups, use the models to help you answer the following questions. (40minutes) 1. Begin the tutorial by defining and understanding the meanings of: Anatomy ................................................................................................... Physiology ................................................................................................ Discussion point—Ensure that you know and understand the structure AND functioning of the heart. 2. Name the three layers of the heart. Which layer contracts and relaxes with each heart beat? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 3. Name the double-layered sac that surrounds the heart. What is contained within this sac, and why? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 4. Why is the myocardial layer of the heart different on the right and left sides? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................ 5. List the major difference between the right and left ventricles. Why is this difference necessary? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 6. Describe the flow of blood from when it enters the heart to the point of exiting (i.e. blood flow OF the heart AND blood flow THROUGH the heart—two pathways). ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 7. Which structures control the flow of blood through the heart? What governs the functioning of these structures? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................... 8. What are the differences between the systemic and pulmonary circulatory systems? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 9. Describe the coronary circulation and list the major coronary blood vessels. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 10. What are the factors that assist venous return (i.e. the return of blood from the venous system to the heart)? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 11. Identify health issues around coronary artery disease and angina. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Relevance to nursing practice Myocardial infarction and assessing chest pain 12. How might the nurse assess the person with chest pain to rule out respiratory, gastrointestinal or musculoskeletal pain? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 13. Make a list of the types of questions the nurse could ask to assist in the assessment of chest pain. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Activity 2—Tutorial session (40 minutes) Discuss what is meant by the cardiac cycle. What is blood pressure and what do measurements such as 120 / 80 mean in terms of physiology? Discuss the logic underlying blood pressure assessment. 14. Why does the blood flow through an artery have to be momentarily occluded, and what does this reading represent? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................... 15. What do the terms systolic and diastolic represent for each heart chamber? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 16. What does the term cardiac cycle mean? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... 17. Label the ECG tracing representing a usual cardiac cycle. Be sure to identify each stage and resultant blood flow (Martini et al. 2012, p. 687). P wave (atria depolarize) P–R interval T wave (ventricles repolarize) S–T interval S–T Q–T interval segment QRS interval (ventricles depolarize) Millivolts P wave (atria depolarize) P–R segment T wave (ventricles repolarize) Activity 3—Dissection of the heart and demonstration in lunginflation (20 minutes) The animal’s heart is similar in structure to the human heart. Use one heart between four (4) students. DURING THE DISSECTION USE SCISSORS AND A PROBE. PLEASE FOLLOW THE STEPS OUTLINED BELOW TO ENSURE THAT YOU SEE EVERYTHING. a) Note the accumulation of fatty (adipose) tissue around the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle itself. The walls of the heart consist of MYOCARDIUM (cardiac muscle) reinforced with a dense network of connective tissue. 1) There are four (4) chambers in the heart: two atria and two ventricles. The chambers are separated by a SEPTUM (INTERATRIAL or INTERVENTRICULAR, depending on which chamber it divides). 2) Can you hold the heart as it would be orientated in your body? The thin-walled atria, which are located superiorly, receive venous blood under low pressure. The thick-walled ventricles are located inferiorly and pump blood out of the heart under relatively high pressure. b) Identify the base and apex of the heart, and the two (2) wrinkled AURICLES, extensions of the atria. The auricles serve to increase the atrial volume. The longitudinal fissures that carry the coronary blood vessels mark the separation of left and right ventricles. You may have to remove some adipose tissue from around the coronary blood vessels in order to see these fissures. c) Compress the walls of the ventricles and note the differences in the thickness. d) Hold the heart in the correct anatomical position—the anterior aspect facing you—and identify the major vessels emerging from the base of the heart. e) These blood vessels are the PULMONARY TRUNK (which branches into the pulmonary arteries) and the AORTA. Which of these blood vessels has the thickest walls? Which of these blood vessels is most anterior? f) Use scissors to cut down through the anterior wall of the PULMONARY TRUNK until you can see the valve clearly. Pour a little water into the pulmonary trunk to observe the action of the cusps of the PULMONARY SEMILUNAR VALVE. g) Carefully cut down the wall of the aorta with scissors until you see the AORTIC SEMILUNAR VALVE. You can see how this valve works by dropping a little water down the aorta. h) Find the two openings to the left and right CORONARY ARTERIES, which lie just superior to the aortic semilunar valve (i.e. away from the ventricle). i) Now turn the heart so that the POSTERIOR aspect is facing you. If the atria are present, identify and examine the four PULMONARY VEINS entering the left atrium, and the SUPERIOR and INFERIOR VENA CAVAE entering the right atrium. j) Use scissors to cut down through the wall of the SUPERIOR VENA CAVA to see the inside of the right atrium and the RIGHT ATRIOVENTRICULAR VALVE. Make a note of the number of cusps present. How many cusps does the RIGHT atrioventricular valve have? What is the other name for this valve? k) Ensure you see the following structures: 1) Each heart chamber 2) Major blood vessels entering and leaving the heart 3) Papillary muscle 4) Interventricular septum 5) Chordae tendinae 6) All four heart valves. l) Now turn the heart to view the ANTERIOR aspect. Extend the cut you started in the aorta down into the left ventricle. Compare the myocardium of the left ventricle with that of the right once more. m) Continue this cut up into the left atrium. Observe the LEFT ATRIOVENTRICULAR VALVE and note the number of cusps present. Activity 4—ECG traces (10 minutes) Students will be given an ECG tracing of a usual cardiac cycle. Label the points (i.e. PQRST) indicating the diastolic and systolic movements in the heart chambers. Also indicate the closure and opening of the four heart valves. Relevance to nursing practice 2. When does a nurse take an ECG reading? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... You have now completed the week 10 A&P Laboratory report. Save and submit it via FLO.