* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
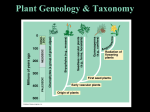
Kingdom Plantae Plants are ___________, __________ organisms. Plants are ________, meaning that they produce their own food through the process of ___________________. Plants have a life cycle in which they alternate between two forms (called ______________________________): i) Haploid form Called a ____________________ (produces gametes) ii) Diploid form Called a ____________ (result of the union of two gametes) Major Divisions Plant Kingdom Non-Vascular Plants (bryophytes) e.g. mosses Vascular Plants (tracheophytes) Seedless Plants (pteridophytes) e.g. ferns Plants with Seeds (spermatophytes) "Naked Seeds" (gymnosperms) e.g. conifers "Enclosed Seeds" (angiosperms) e.g. trees, shrubs, flowers Monocots e.g. corn Dicots e.g. beans Vascular and Non-vascular Plants Most plants consist of ______________________________: - Roots penetrate the soil to ________ the plant and to reach sources of ______ - Leaves provide a greater _____________ to carry out ___________________ - Stems supply rigid tissues that _______ and __________ the ___________ In order for roots, leaves and stems to grow they need a regular supply of ______, and _____________ These tasks are carried out by vascular tissue - vascular tissue are made up of cells that conduct solutions throughout the plant (similar to a circulatory system) There are two main types of vascular tissue: Xylem Phloem - Evolution of vascular tissue has allowed plants to increase in ________ Non-vascular Plants (Mosses and their Relatives) There are three divisions of Mosses: 1. Mosses (__________________) - Lack vascular tissue and do not have well-developed roots - Thrive in diverse habitats such as bogs, tundra, exposed rocks and deep shade 2. Liverworts (_____________________) - Grow flat and close to the ground - Rarely more than 30 cells thick 3. Hornworts (______________________) - Gametophytes are broad flat and usually less than 2 cm in diameter - Have a blue-green colour Seedless Vascular Plants (Ferns and their Relatives) Developed vascular tissue that allowed them to grow tall Sporophyte generation is the dominant stage Gametophyte generation are tiny, short-lived and depended on moisture to carry out sexual reproduction Vascular Plants (disperse by seeds) Seeds allow a plant to reproduce sexually without needing water Seeds also provide protection against harsh environmental conditions There are two groups of seeds: 1. Gymnosperms "naked seeds" These are ___________ plants with most possessing ________. There are both male and female cones. Generalized life cycle of a gymnosperm: In male cones, microspore mother cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid pollen grains, the male gametophytes. Female cones have ovules in which a megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produces only one megaspore, or female gametophyte. Pollen gets trapped on sticky sap secreted by the female cone. After fertilization, the diploid zygote develops into an embryo, which remains in the ripened ovule, now called a seed. Mature "naked" seeds fall out of the female cones. It may be several years before the seedling grows into a mature plant to produce its own cones. 2. Angiosperms _________ plants that protect their seeds within a _____. Monocots have one _______ (seed leaf) and dicots have two cotyledons. Generalized life cycle of an angiosperm: Within the anther chambers, microspore mother cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid pollen grains, or male gametophyte. Within the ovule, a megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce only one megaspore, or female gametophyte. Pollination is aided by wind, insects, birds, and bats. Pollen gets trapped by the sticky substance on the stigma. Self-pollination involves one plant only; cross-pollination involves two separate plants. After fertilization, the diploid zygote grows into an embryo, which remains in the ripened ovule, now called a seed. As the seeds develop, the ovary and other parts develop into the fruit enclosing the seeds. The Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant