* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 8. Energy
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
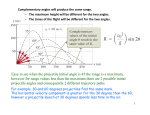
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Conceptual Physics Mid-Term Review Packet Ch.2 Linear Motion 1. What are Vectors and what are scalars. Give examples. 2. What is motion usually measured relative to? 3. Define Speed ? What are its units? 4. What is average speed? How is it measured? 5. Define Velocity. What are its units? 6. What is instantaneous speed ? Does your speedometer refer to average or instantaneous speed? 7. If an object covers the same distance of 10 m every second, what are its velocity and Acceleration? 8. What are the speed and distance of a freely falling object which is dropped from rest 9. What are the instantaneous velocity and acceleration of a ball thrown straight up, at the top of its path 10. In the absence of air resistance which will reach the ground first, a tennis ball or a bowling ball. 11. If a ball is thrown up at a speed of 40 m/s, how much time will it take to reach the maximum height ? In how much time will it hit the ground. g = 10 m/s2 12. How do you measure hang time for an athlete who jumped 1 m high? 13. What is the maximum height jumped by an athlete who has a hang time of 0.8 s. Ch.3 Projectile Motion 14. How do you find the components of a vector? How do you find resultant of two vectors? 15. What is the resultant of two vectors, each of length 100 units and at right angles to the other 16. What is the ground speed of a plane which is traveling at 80 km/h, if it encounters 17. What are the horizontal and vertical forces acting on a projectile in the absence of air resistance? Does the above projectile have horizontal or vertical acceleration during flight? 18. Are the horizontal and vertical components of a projectile dependent on each other? For a projectile launched at some angle, does the ball have horizontal or vertical velocity at the top of its path? 19. What is the launch angle for a projectile to travel the (a) farther horizontal distance and the (b) greatest vertical height ? Ch. 4 – Ch.6 Newton’s Laws 20. State Newton’s three laws of motion 21. Define mass, weight & volume. What are their units. 22. Would an object of mass 20 kg have greater weight on the Moon, Earth or Jupiter? 23. If an object weighs 400 N, what is its mass? 24. What happens when a net force acts on an object? 25. If no net force acts on an object, what is necessarily zero (a) Velocity (b) Acceleration 26. If you hang from a clothesline when is the tension in the line greater, if the line is strung 27. What is the gravitational force acting on an object of 1 kg mass. g = 10 m/s2 28. If the 1 kg object is thrown up, does the net force change during its flight? No 29. The acceleration of an object acted upon by a force is directly proportional to the applied force and inversely proportional to the mass. 30. Based on Newton’s 2nd law, if mass of an object doubles, for the same applied force, what happens to its acceleration? 31. For the same mass if the force is doubled, what happens to its acceleration? 32. What is terminal velocity? What is the acceleration of an object at terminal velocity? 33. Define Pressure. What are the units? 34. Is the force of gravity the same for 1 kg and 10 kg object? Is g the same for both? 35. A cannonball is fired. Is the force acting on the ball and the cannon the same? Are the magnitudes of their acceleration equal? 36. If the Earth’s gravitational pull on a falling apple is the Action force, what is the Reaction force? Are they equal? 37. Do Action and Reaction force act on the same object. 38. If a horse drawn cart is to move faster, should the horse push harder on the ground or pull harder on the cart ? Ch. 7 Momentum 39. Define Momentum and state its units 40. Impulse is the change in momentum and is equal to Force x time. Impact is the force. 41. One egg is dropped on a concrete floor and a second egg on a soft cushion. Why is impact force on the second egg reduced? 42. Which condition must be met for total momentum to be conserved? 43. If the velocity of an object is doubled and the mass remains constant, what happens to its momentum ? 44. What is the momentum of an object at rest? It is zero. 45. If a ball moving with a momentum of 2 kg.m/s collides with another ball at rest and they both stick together, moving as a combination of 2 balls; (a) what is the momentum of the combined mass (b) Is the velocity of the combination reduced, increased or the same? A ball of 5 kg mass and 10 kg. m/s momentum has a velocity of 2 m/s. Ch. 8. Energy 46. What are the different forms of mechanical energy? 47. Define Potential and Kinetic Energy. What are the units? 48. Can an object at rest have Potential or Kinetic Energy? 49. Define Power. What are its units? 50. What is the law of conservation of energy? Refer to handouts & textbook. 51. A simple machine multiplies or changes the direction of (a) Forces (b) Energy (c) Work 52. Define efficiency of a machine. 53. Define Mechanical Advantage. 54. How is mechanical energy converted from kinetic to potential energy in an ideal simple Pendulum? At which position does a pendulum have maximum kinetic and potential energy?