* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
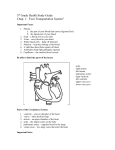
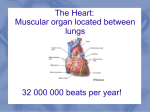
Name ____________________________________________________ Date __________ Per _______ Cardio Worksheet 1. Arteries always: a) lead toward the heart b) carry oxygenated blood c) carry deoxygenated blood d) lead away from the heart 2. The left atrium: a) Receives blood from the lungs b) Forces blood to the lungs c) Channels blood to the right atrium d) Receives blood from the left ventricle 3. The correct layers of the heart, from deep to superficial, are: a) myocardium, pericardium, endocardium b) epicardium, myocardium, pericardium c) epicardium, myocardium, endocardium d) endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 4. What is the protective membrane surrounding the heart? a) endocardium b) pericardium c) epicardium d) myocardium 5. The artery that supplies the heart with blood is the: a) Coronary artery b) Jugular Artery c) Carotid Artery d) Minstral Artery 6. The ___________________ carries deoxygenated blood from the head to the right atrium. a) Aorta b) Nervous Veins c) Deoxy receptor and transferal vessel d) Superior vena cava 7. Contraction of the right ventricle forces blood into the: a) Right atrium b) Pulmonary arteries c) Pulmonary veins d) Septum 8. Which is the correct order of blood flow through the heart? a) Right ventricle, inferior/superior vena cava, right atrium, pulmonary veins, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta b) inferior/superior vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary veins, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta c) Right atrium, inferior/superior vena cava, pulmonary veins, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta, right ventricle d) Pulmonary veins, inferior/superior vena cava, left atrium, right atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta 9. What is the difference between the Atrioventricular valves and the Semi-lunar valves? a) Semi-lunar valves release blood into the atria while AV valves permit blood flow away from the heart. b) AV valves release blood into the ventricles while Semi-lunar valves permit blood flow away from the heart. c) The vasodilative receptors in the semi-lunar valves are less sensitive than those of the atrioventricular valves. d) Atrioventricular valves are double the size of the semi-lunar valves. 10. The atrioventricular valves are also called the: a) semilunar valves b) aortic valves c) cuspid valves d) pulmonary valves 11. Semilunar valves prevent backflow of blood into the a) lungs b) atria c) ventricles d) vena cava 12. What part of the heart separates the left ventricle from the right ventricle? a) The Aorta b) The Septum c) The Pericardium d) Inferior Vena Cava 13. What function does the Chordae Tendinae serve? a) They serve to hold the heart in its place. b) They serve to hold the muscular fibers of the heart together. c) To provide support for the Atrioventricular valves d) They provide support for the Semi-lunar valves. 14. Which ventricle requires thicker, more muscular walls to function properly? a) The left ventricle b) The right ventricle c) The Atria d) The Superior/Inferior Vena Cava 15. The heart fills with deoxygenated blood: a) On the right side only b) On the left side only c) On both side at the same time d) At the septum 16. If the value at H was open and the valve at G was closed: a) The ventricle would be contracting b) The ventricle would be filling c) The atrium would be filling d) The atrium would be relaxing 1 17. When does the first heart sound occur? a) During ventricular contraction when the AV valves close b) During atrial contraction when the AV valves close c) During ventricular contraction when the SL valves close d) During atrial contraction when the SL valves close 18. What is the first node that the nerve pulse comes in contact with? a) The atrioventicular node b) The sinoatrial node c) The pacemaker node d) The initial receptor node 19. What is known as the heart’s pacemaker? a) atrioventricular node b) sinoatrial node c) sinoventricular node d) semilunar node 20. When the pulse is received at the AV node, the ______ contract(s): a) Atria b) Left atrium only c) Ventricles d) Cardiacular pulmonaric atrial receptor 21. What nervous fibers extend through the septum? a) Bundle of His b) Purkinje Fibers c) Nephron Fibers d) Cytoplast Nerve 22. What is the normal pattern of impulse conduction? a) SA node, AV bundle, purkinje fibers, AV node b) AV node, SA node, bundle of His, purkinje fibers c) SA node, AV node, bundle of His, purkinje fibers d) AV node, SA node, purkinje fibers, bundle of His 23. What is the diagram to the right a depiction of? a) pulse rate b) heart beat c) EKG d) blood pressure 24. An EKG/ECG P wave represents a) atrial depolarization b) atrial repolarization c) ventricular depolarization d) ventricular repolarization 25. A heart attack effects which vessel? a) coronary arteries b) coronary veins c) pulmonary arteries d) pulmonary veins Matching 1. _____ heart attack a. atherosclerosis 2. _____ decreased blood supply to tissue b. ischemia 3. _____ tissue death c. aneurysm 4. _____ necrosis that has progressed to decay d. necrosis 5. _____ arteriosclerosis due to lipids e. gangrene 6. _____ section of an artery that is abnormally wide f. hemorrhoids 7. _____ varicose veins in rectum g. phlebitis 8. _____ vein inflammation h. stroke 9. _____ clot formation i. myocardial infarction 10. _____ cerebral vascular accident j. thrombus 11. _____ leaky mitral valve k. stenosed valves 12. _____ valve abnormally narrow l. MVP 2