* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Tutorial: Inductance and Transformers
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
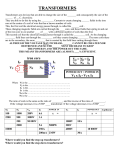
Physics Tutorial: Inductance and Transformers A transformer is an apparatus for changing a given electrical current into another current of different voltage. There are two kinds of transformers: step down and step up. Step up transformers increase the voltage where step down transformers decrease the voltage. Explanation: We call this device a transformer because it transforms electrical energy into magnetic energy, and then back to electrical energy again. A transformer consists of two coils of wire both wrapped around the same core. The primary coil is the input coil and the secondary coil is the output coil. The relationship between the number of turns in the coil, voltage, and current in is V s / Vp = Ip / Is = Ns / Np. The V represents voltage, I represents current, and N represents the number of turns of the coil. The s represents secondary and p represents primary. A transformer’s basic operating principle is that of mutual inductance. Mutual inductance occurs when two coils are so close together that the magnetic field of one coil links with the magnetic field of the other coil. Current is induced in the second coil when the magnet field produced by the first coil changes. A transformer only works with alternating current. Direct current would cause a magnetic field in the core, but not a changing one. This would cause the voltage induced in the second coil to be equal to zero. A transformer is used because they cause almost no energy loss. Application: Power is supplied to houses everywhere in the developed world. In the power grid, voltage can be as high as 765000V. This power is stepped down to 72000V at your local substation. From here, the power is stepped down to about 220V at a transformer on a utility pole. The voltage is so high in the beginning so it can travel long distances. It is stepped down so often so it can be used in the home. Certain appliances like air conditioners and stoves use about 220V where smaller appliances use less. If such a high voltage were applied to these appliances they would need step down transformers installed in them. More about transformers: AC vs DC generators Transformers only work on AC, which is one of the great advantages of AC. Transformers allow 240V to be stepped down to convenient levels for digital electronics (only a few volts) or for other low power applications (typically 12V). Transformers step the voltage up for transmission, as mentioned above, and down for safe distribution. Without transformers, the waste of electric power in distribution networks, already high, would be enormous. It is possible to convert voltages in DC, but more complicated than with AC. Further, such conversions are often inefficient and/or expensive. AC has the further advantage that it can be used on AC motors, which are usually preferable to DC motors for high power applications. Step Up Transformer This type of transformer used for increase the incident voltage. Number of turns in secondary coil is larger than the number of turns in primary coil. Step Down Transformer This type of transformer used for decrease incident voltage. Number of turns in primary coil is larger than the number of turns in secondary coil.