* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
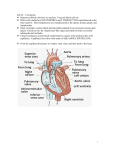
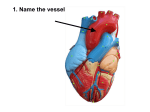
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System: • Delivery - of what? • Removal - of what? • Fighting Disease - how so? Structure of the heart: • What is the approximate size of the heart? • The heart is made of vessel cells and _____________________ cells • How are these cells of the heart “serviced?” Label the following in the diagram: (as you’re looking in the mirror - think reverse) • atria • ventricles • valves Heart Beat: • lub = • dub = • Which ventricle has the stronger push? Why? • What is blood pressure? Vessels: 1. Artery - how does blood flow in relation to the heart? Visit or Away • How many layers thick is this vessel? • Rigid or Floppy? 2. Arterioles - how do they compare to arterioles in terms of thickness? 3. Capillaries - why is this vessel only one cell layer thick? • What type of blood do capillaries carry? Oxygenated or Deoxygenated? 1. Vein - how does blood flow in relation to the heart? Visit or Away • Is this vessel rigid or floppy? Why? • Veins have valves - why? 2. Venule - why is this vessel only one cell layer thick? • What type of blood do venules carry? Oxygenated or Deoxygenated? • Where does the blood come from that flows into venules? Diagram of vessels all connected (we’ll draw this together): Blood: • Why does the blood in your veins look blue? • Red blood cells (RBCs) - what is their function in the blood? • What is the name of the protein that carries oxygen? To what atom does the oxygen bind? • How long do they survive (days)? • Where are new RBCs made? • Do they have a nucleus? Why or why not? • White blood cells (WBCs) - what is their function in the blood? • Platelets - how are they involved in clotting of the blood? • Plasma - what gas is carried in this watery liquid? What happens to the pH of the watery plasma when this gas is present in quantity?