* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
James Franck wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
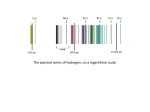
PHYSICS (P 3.5 - ATOMIC/NUCLEAR) WORKSHEET TWO: QUANTUM CONCEPTS C = 3 x 108 ms-1 , h = 6.63 x 10-34 Js, e = 1.6 x 10-19 C , R = 1.097 x 107 m-1 1. The energy of the electron in a particular orbit in the hydrogen atom is give by En = Rch/n2 where n= 1, 2, 3.... (a) Calculate the value of Rch using the constants at the top of the worksheet. (b) Where is the Zero point of this energy? (c) Is the electron's energy greater in the first or the sixth orbit? Explain why. (d) If an electron falls from the third orbit to the first, how much energy does it lose? (e) What happens to the energy lost by the electron in (d)? (f) Using ΔE = hf, calculate the frequency and wavelength of the spectral line emitted in (d). (g) Electrons will have angular momentum as they orbit the nucleus. What important discovery was made about this by Niels Bohr? 2. Explain how the Emission Spectral lines of hydrogen could be generated in the Laboratory. 3. What did scientists learn from the first Spectral line analysis of the SUN ? 4. (a) Draw an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom and show on it how the Lyman and Balmer series of spectral lines are produced. Label the two series clearly. Energy (b) The Balmer series appears in the visible part of the spectrum. Sketch the first three of its spectral lines on the display below. Label the lines as jumps from L = 3, L = 4, and L = 5. Increasing wavelength