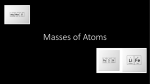* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The periodic table and the atom part 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
The periodic table and the
atom part 2
Lesson 8
Atomic Number and Atomic
mass
Element
Name
Atomic
Number
Z
Element
Symbol
Atomic
Mass
A
Atomic Number: (Z)
The number of protons in an atom defines
what element it is. For example carbon
atoms have six protons, hydrogen atoms
have one, and oxygen atoms have
eight. The number of protons in an atom
is referred to as the atomic number of that
element. The number of protons in an
atom also determines the chemical
behavior of the element.
Atomic Symbol:
The atomic symbol is one or two letters
chosen to represent an element ("H" for
"hydrogen," etc.). These symbols are
used internationally.
Atomic Mass: (A)
The atomic mass is the average mass of an
element in atomic mass units . Though
individual atoms always have an integer
number of atomic mass units, the atomic
mass on the periodic table is stated as a
decimal number because it is an average of
the various isotopes of an element. The
average number of neutrons for an element
can be found by subtracting the number of
protons (atomic number) from the atomic
mass.
How to calculate the number
of Neutrons
The number of neutrons does not always
equal the number of protons. We can find
the number of neutrons by using the
formula
A–Z=N
A= Atomic mass
Z= Atomic Number (number of protons)
N= Number of Neutrons
Example: How many Neutrons does K
have?
A = 39 , Z = 19, N= ?
N= A-Z = 39-19 = 20 Neutrons