* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 6B Practice midterm 1
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
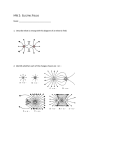
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Physics 6B Practice midterm 1. A mass on a spring oscillates with a period T. If both the mass and the force constant of the spring are doubled, what will the new period be? 2. The motion of a piston in an automobile engine is approximately simple harmonic. If the stroke (twice the amplitude) of an engine is 0.100 meters and the engine runs at 3500 rpm, A) compute the acceleration at the endpoint of its stroke. B) If the piston has mass 0.450 kg, what net force must be exerted on it at this point? C) What are the speed and kinetic energy of the piston at the midpoint of its stroke? 3. A certain simple pendulum has a period on Earth of 1.60 seconds. What is its period on the surface of Mars, where the acceleration due to gravity is 3.71 meters per second squared? 4. The equation describing a transverse wave on a string is: y( x, t ) (1.50mm) sin (157s 1 )t (41.9m 1 ) x a) Find the wavelength, frequency and amplitude of this wave. b) Find the propagation velocity of the wave. c) The transverse displacement of a point on the string when t=0.100s and x=0.360m. 5. A wind chime consists of an open tube 30cm long. Find the frequency and wavelength of the fundamental mode, and the first two overtones. 6. Green light has a wavelength of 500nm. Yellow light has a wavelength of 550nm. How fast would I have to drive toward a traffic light in order to make a yellow light appear green? (You can use c for the speed of light.) 7. An ore sample weighs 17.5N in air. When the sample is suspended by a light cord and totally immersed in water, the tension in the cord is 11.2N. Find the total volume and density of the sample. 8. You are designing a hydraulic lift for an automobile garage. It will consist of two oil filled cylindrical pipes of different diameters. A worker pushes down on a piston at one end, raising the car on a platform on the other. To handle a full range of jobs, you must be able to lift cars up to 3000kg, plus the 500kg platform on which they are parked. To avoid injury to your workers, the maximum amount of force a worker should need to exert is 100N. The diameter of the piston the worker pushes down on is 25cm. A) What should be the diameter of the pipe under the platform? B) If the worker pushes down with a stroke 50cm long, by how much will he raise the car at the other end? 9. Air streams horizontally past a small airplane’s wings such that the speed is 70.0 m/s over the top surface and 60.0 m/s over the bottom surface. If the plane has a mass of 1340 kg and a wing area of 16.2 square meters, what is the net vertical force (including gravity) on the airplane? The density of air is 1.20 kg/m^2. 10. Water is flowing in a pipe with varying cross-sectional area, and at all points the water completely fills the pipe. At point 1, the cross-sectional area of the pipe is 0.070 square meters and the magnitude of the fluid velocity is 3.50m/s. What is the fluid speed at points in the pipe where the cross-sectional area is A) 0.105 m^2, B)0.047 m^2? 11. Two positively charged masses hang from the ceiling as in the figure. The masses have equal charge and mass. Each mass is 100g, the length of each string is 40cm, and the masses are in equilibrium when they hang at a 30 degree angle from the vertical. a) Find the charge on each mass b) Find the tension in each string 12. Consider the following arrangem ent of charges. A +2 microcoul omb charge lies at the origin of the x-y plane. A -3 microcoulomb charge lies at the coordinates (3,4). a) What is the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on the positive charge by the negative charge? b) What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at point P0, located at (3,0)? c) What is the electric potential at point P0, assuming the electric potential very far away is zero? d) How much work would it take to move a charge of +1 microcoulomb from very far away to point P0? 13. An electron passes through a region with a downward oriented electric field with an initial velocity of v0 to the right. If the magnitude of the electric field is E, and the length of the region with the electric field is l, find: a) The direction the electron is deflected. b) The distance the electron is deflected. c) The energy the electron gains while passing through the electric field. d) The magnitude and direction of the electron’s final velocity. Note: use m for the mass of the electron, q for the charge on the electron, E for the strength of the electric field, l for the length of the region, and v0 for the electron’s initial velocity.